Connecting to an HBase Normal Cluster Using HBase Shell
You can use the HBase shell to access a cluster by manually installing a client or deploying a client with one click on an ECS. You are advised to deploy a client with one click. If a security channel is enabled for the cluster, connect to the cluster by referring to Connecting to an HBase Security Cluster.
Constraints
- The HBase cluster and the ECS must be in the same region, AZ, and VPC.
- The HBase cluster and the ECS must be in the same security group.
- The IP address of the local host has been added to the ECS security group.
Deploying a Client with One Click
- Prepare a Linux ECS.
To use the one-click client deployment tool, you are advised to use EulerOS, CentOS, Ubuntu, or SUSE Linux ECSs. For details, see Preparing an ECS.
- Download the one-click client deployment tool.
Use an SSH login tool (such as PuTTY) to remotely log in to the Linux ECS through the EIP and run the following command to obtain the one-click client deployment tool:
curl -O -k "https://cloudtable-publish.obs.myhuaweicloud.com/quick_start_hbase_shell.sh"
This command applies to HBase 1.x.
curl -O -k "https://cloudtable-publish.obs.myhuaweicloud.com/cloudtable-client/quick_start_hbase_shell.sh"
- This command applies to HBase 2.x.
- The one-click deployment package contains the verification file.
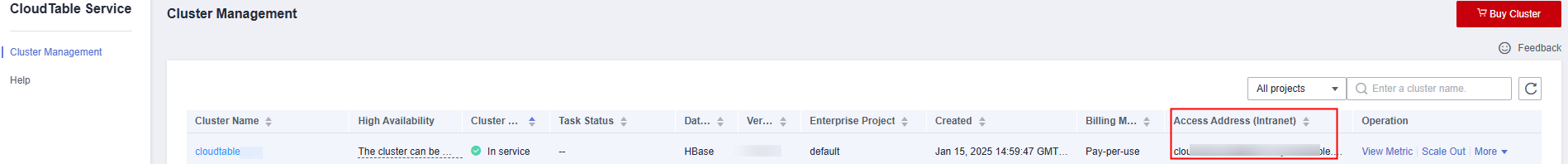
- Obtain a cluster access address.
Choose Cluster Management in the navigation pane. In the cluster list, locate the required cluster and obtain the address in the Access Address (Intranet) column. The parameter value is the cluster access address, as shown in Figure 1.
- Use the tool to deploy the client.
Replace $zookeeper_address in the following command with the address you obtained in 3. Then, run the command on the CLI of the ECS to deploy the client with one click.
- Command for one-click client deployment for normal clusters:
source quick_start_hbase_shell.sh $zookeeper_address
- Command for one-click client deployment for security clusters:
source quick_start_hbase_shell $zookeeper_address enable
- Command for one-click client deployment for normal clusters:
- Start the shell to access the cluster.
After you run the source command to automatically deploy the client, the HBase shell is automatically started. You can also run the bin/hbase shell command to start the HBase shell to access the cluster.
Manually Installing a Client
- Prepare a Linux ECS.
For details, see Preparing an ECS.
- Download the client and verification file.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Help. In the right pane, click the button for downloading client and Download the Client Verification File to download the client installation package and client verification file.
- Install the client and verify the client.
- Use a file transfer tool (such as WinSCP) to upload the client installation package to the Linux ECS.
- Use the SSH login tool (such as PuTTY) to log in to the Linux ECS through the EIP.
For details about how to log in to the Linux ECS, see Logging In to a Linux ECS > "Login Using an SSH Password" in the Elastic Cloud Server User Guide.
Run the following command to decompress the client installation package:
cd <Path of the client installation package> tar xzvf hbase-1.3.1-bin.tar.gz
cd <Path of the client installation package> tar xzvf hbase-2.4.14-bin.tar.gz
<Path of the client installation package>: Replace it with the actual path.
- Decompress the client verification file to the same directory as the client.
- Decompress the client verification file.
cd <Path for storing the client verification file > tar xzvf Client_sha256.tar.gz
- Obtain the client verification code.
sha256sum HBase_Client_2.4.14.tar.gz
- Check the verification code in the client verification file and compare it with the client verification code. If they are the same, the client is not tampered with. If they are different, the client is tampered with.
less HBase_Client_2.4.14.tar.gz.sha256
- Decompress the client verification file.
- Configure the ZooKeeper address in a configuration file.
In the decompression directory of the client installation package, open the hbase/conf/hbase-site.xml file and set the following parameters:
- hbase.zookeeper.quorum: The value of this parameter is the cluster's access address (Intranet) obtained in the cluster list.
Choose Cluster Management in the navigation pane. In the cluster list, locate the required cluster and obtain the address in the Access Address (Intranet) column. See the following figure.
Figure 2 Obtaining the access address
- mapreduce.cluster.local.dir: Check whether the configuration item exists. If it does not exist, add it.
The following is an example of configuring the client for a cluster with security channel encryption disabled:
<configuration> <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>xxx-zk1.cloudtable.com:2181,xxx-zk2.cloudtable.com:2181,xxx-zk3.cloudtable.com:2181</value> </property> <property> <name>mapreduce.cluster.local.dir</name> <value>${hadoop.tmp.dir}/mapred/local</value> </property> </configuration>For details about how to configure the client for a cluster with security channel encryption enabled, see Connecting to an HBase Security Cluster Using the HBase Shell.
- hbase.zookeeper.quorum: The value of this parameter is the cluster's access address (Intranet) obtained in the cluster list.
- Start the shell to access the cluster.
Run the bin/hbase shell command to start the shell to access the cluster.
Getting Started with HBase
This section describes common HBase shell commands. For more HBase shell commands, visit https://learnhbase.wordpress.com/2013/03/02/hbase-shell-commands/.
- Obtain online help.
After you run the help command in the HBase shell, all command information as well as common command instructions and use methods will be returned.
hbase(main):001:0> help
- Create a table.
Run the create command to create a table. When creating a table, you must specify the table name and column family name.
hbase(main):007:0> create 'cloudtable','cf' 0 row(s) in 1.5530 seconds => Hbase::Table - cloudtable
- Query a table.
hbase(main):009:0> list TABLE cloudtable 1 row(s) in 0.0060 seconds => ["cloudtable"]
- Insert a record to a table.
Run the put command to insert a data record to the table. You need to specify the table name, primary key, custom column, and the value to be inserted.
hbase(main):004:0> put 'cloudtable','row1','cf:a','value1' 0 row(s) in 0.2720 seconds
The parameters in the command are as follows:
- cloudtable: table name
- row1: primary key
- cf:a: custom column
- value1: value to be inserted
- Scan records.
Run the scan command to scan a table. You need to specify the table name to scan the entire table or specify a scan range.
hbase(main):001:0> scan 'cloudtable' ROW COLUMN+CELL row1 column=cf:a, timestamp=1504866237162, value=value1 1 row(s) in 0.2420 seconds
- If the TTL of a cell is set when data is inserted, the TTL attribute cannot be viewed. However, you can check whether the TTL takes effect.
- If the TTL of a cell is not set when data is inserted, the system automatically inserts the current time as the timestamp.
- Query a single record.
Run the get command to query a single record. You must specify the name and the primary key of the table.
hbase(main):001:0> get 'cloudtable','row1' COLUMN CELL cf:a timestamp=1504866237162, value=value1 1 row(s) in 0.2280 seconds
- Disable a table.
Before modifying or deleting a table, you need to disable the table. Run the disable command to disable the table. When you perform operations on a disabled table, ERROR is displayed, indicating that the table is disabled.
hbase(main):002:0> disable 'cloudtable' 0 row(s) in 2.3550 seconds
- Enable a table.
If you want to use a table that has been disabled, run the enable command to enable it.
hbase(main):004:0> enable 'cloudtable' 0 row(s) in 1.2500 seconds
- Delete a table.
Run the drop command to delete a table that is no longer needed. Before deleting a table, disable it first. Otherwise, ERROR will be displayed, indicating that the table is enabled. Deleting a table will cause data loss. Exercise caution when deleting a table.
hbase(main):007:0> disable 'cloudtable' 0 row(s) in 2.2380 seconds hbase(main):008:0> drop 'cloudtable' 0 row(s) in 1.2600 seconds
- Exit the HBase shell.
Run the quit command to exit the HBase shell.
hbase(main):009:0> quit
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot