Creating a Supplementary Network Interface
Scenarios
Supplementary network interfaces can be attached to network interfaces of an iMetal server for flexible and high-availability network configuration.
Constraints
- Supplementary network interfaces must be in the same VPC as the network interface they are attached to, but they can be in different subnets.
- After supplementary network interfaces are created, you need to create VLAN sub-interfaces on the network interface of the iMetal server and configure corresponding rules by referring to Configuring a Supplementary Network Interface.
Creating a Supplementary Network Interface
- Go to the supplementary network interface list page.
- In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Supplementary Network Interface.
- Configure the parameters based on Table 1.
Table 1 Parameter descriptions Parameter
Description
Example Value
Region
Region where the supplementary network interface will be created. Select the region nearest to you to ensure the lowest latency possible.
CN-Hong Kong
Network Interface
Network interface that you want the supplementary network interface to attach to.
Select an elastic network interface from the drop-down list.
--(172.16.0.145)
VPC
VPC where the supplementary network interface will be created. The VPC of the network interface that the supplementary network interface is attached to is selected by default.
vpc-A
CloudDCN Subnet
CloudDCN subnet where the supplementary network interface will be created. The supplementary network interface and its network interface can be in different subnets.
subnet-clouddcn-01
Quantity
Number of supplementary network interfaces to be created.
1
Private IP Address
Whether to assign a private IPv4 address to the supplementary network interface.
This parameter cannot be deselected in the current version.
-
IPv4 Address
How a private IPv4 address will be assigned to the supplementary network interface. There are two options:- Automatically assign IP address: The system assigns an IP address from the subnet you have selected.
- Manually specify IP address: You can specify an IP address.
If you select Manually specify IP address, enter a private IPv4 address.
Automatically assign IP address
Description (Optional)
Description of the supplementary network interface.
The description can contain a maximum of 255 characters and cannot contain angle brackets (< or >).
-
Tag (Optional)
Optional
Tags that are used to identify, classify, and search for supplementary network interfaces.
For details, see Managing Supplementary Network Interface Tags.
Tag key: test
Tag value: 01
- Click Create Now.

To use a supplementary network interface, you need to create a VLAN sub-interface by referring to Configuring a Supplementary Network Interface.
Configuring a Supplementary Network Interface
After a supplementary network interface is created, you need to create a VLAN sub-interface for the network interface of the iMetal server and configure a private IP address and default routes for the supplementary network interface.
Before doing so, you need to obtain:
- The information described in Table 2 when you configure a supplementary network interface for a Linux iMetal server.
- The information described in Table 2 and Table 3 when you configure a supplementary network interface for a Windows iMetal server.
Table 2 Information about the supplementary network interface and CloudDCN subnet Item
How to Obtain
VLAN ID
MAC address
Private IP address
CloudDCN subnet mask
- In the supplementary network interface list, locate the target supplementary network interface and click the CloudDCN subnet name in the Network column.
The Summary page of the subnet is displayed.
- On the displayed page, check and record the following information:
- CloudDCN subnet mask: subnet mask of the IPv4 CIDR block. For example, if the IPv4 CIDR block is 192.168.0.0/24, the mask is 24.
- CloudDCN subnet gateway: In the Gateway and DNS Information area, check the gateway address.
Gateway address
Table 3 Information about the network interface and CloudDCN subnet to which the supplementary network interface belongs Item
How to Obtain
Private IP address
- In the iMetal server list, view and record the private IP address of the network interface.
- On the Network Interfaces tab of the iMetal server details page, expand the details and view the MAC address.
MAC address
CloudDCN subnet mask
- In the network interface list, locate the target network interface and click the CloudDCN subnet name in the Network column.
The Summary page of the subnet is displayed.
- On the displayed page, check and record the following information:
- Subnet mask: subnet mask of the IPv4 CIDR block. For example, if the IPv4 CIDR block is 192.168.0.0/24, the mask is 24.
- Subnet gateway: In the Gateway and DNS Information area, check the gateway address.
Gateway address
- In the supplementary network interface list, locate the target supplementary network interface and click the CloudDCN subnet name in the Network column.
Configuring a Supplementary Network Interface for a Linux iMetal Server
- VLAN ID: 1937
- MAC address: fa:16:3e:6d:c5:5a
- Private IP address: 192.168.0.149
- Subnet mask: 24
- Subnet gateway address: 192.168.0.1
- Log in to the iMetal server.
For details, see iMetal Server Login Methods.
- Run the following command to view and record the network interface name of the iMetal server:
Information similar to the following is displayed. In this example, the network interface name is eth0.
[root@imetal-subeni-linux ~]# ifconfig eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 inet 192.168.0.125 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.0.255 inet6 fe80::f816:3eff:fe6d:c542 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link> ether fa:16:3e:6d:c5:42 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet) RX packets 78131 bytes 111604802 (106.4 MiB) RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0 TX packets 8686 bytes 1422159 (1.3 MiB) TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0 ... - Run the following command to create a VLAN sub-interface on the network interface:
ip link add link <network-interface-name> name <VLAN-sub-interface-name> type vlan id <VLAN-ID-of-the-supplementary-network-interface>
Variables in the preceding command are as follows:- network-interface-name: the network interface name queried in 2. In this example, the name is eth0.
- VLAN-sub-interface-name: Name the sub-interface in the format of <network-interface-name>.<VLAN-ID-of-the-supplementary-network-interface>. In this example, the VLAN sub-interface name is eth0.1937.
- VLAN-ID-of-the-supplementary-network-interface: In this example, the ID is 1937.
Example command:
ip link add link eth0 name eth0.1937 type vlan id 1937
- Run the following command to create a namespace:
namespace-name: Name it in the format of ns<supplementary-network-interface-VLAN-ID>. In this example, the name is ns1937.
Example command:
ip netns add ns1937
- Run the following command to add the VLAN sub-interface to the namespace:
ip link set <VLAN-sub-interface-name> netns <namespace-name>
Example command:
ip link set eth0.1937 netns ns1937
- Run the following command to change the MAC address of the VLAN sub-interface to that of the supplementary network interface:
ip netns exec <namespace-name> ifconfig <VLAN-sub-interface-name> hw ether <MAC-address-of-the-supplementary-network-interface>
Example command:
ip netns exec ns1937 ifconfig eth0.1937 hw ether fa:16:3e:6d:c5:5a
- Run the following command to enable the VLAN sub-interface:
ip netns exec <namespace-name> ifconfig <VLAN-sub-interface-name> up
Example command:
ip netns exec ns1937 ifconfig eth0.1937 up
- Run the following command to configure a private IP address for the VLAN sub-interface:
ip netns exec <namespace-name> ip addr add <private-IP-address> dev <VLAN-sub-interface-name>
private-IP-address: private IP address of the supplementary network interface/subnet mask. In this example, the value is 192.168.0.149/24.
Example command:
ip netns exec ns1937 ip addr add 192.168.0.149/24 dev eth0.1937
- Run the following command to configure the default route for the VLAN sub-interface:
ip netns exec <namespace-name> ip route add default via <gateway-address-of-the-subnet-where-the-supplementary-network-interface-is-created>
Example command:
ip netns exec ns1937 ip route add default via 192.168.0.1
- Check whether the supplementary network interface has worked.
- Run the following command to verify the connectivity between network interface eth0 and the test iMetal server:
ping <private-IP-address-of-the-test-iMetal-server>
Plan the same VPC for the test iMetal server and the iMetal server with network interface eth0 attached, so that the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other by default.
Example command:
ping 192.168.0.133
If information similar to the following is displayed, the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other. If the communication is normal, proceed with 10.b.[root@imetal-subeni-linux ~]# ping 192.168.0.133 PING 192.168.0.133 (192.168.0.133) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.133: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.302 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.133: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.262 ms ... --- 192.168.0.133 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 999ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.262/0.282/0.302/0.020 ms
- Run the following command to verify the connectivity between the supplementary network interface and the test iMetal server.
ip netns exec <namespace-name> ping <private-IP-address-of-the-test-iMetal-server>
Plan the same VPC for the test iMetal server and the iMetal server that the supplementary network interface is attached to, so that the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other by default.
Example command:
ip netns exec ns1937 ping 192.168.0.133
If information similar to the following is displayed, the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other. This means the supplementary network interface has worked.
[root@imetal-subeni-linux ~]# ip netns exec ns1937 ping 192.168.0.133 PING 192.168.0.133 (192.168.0.133) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.133: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.420 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.0.133: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.233 ms ... --- 192.168.0.133 ping statistics --- 2 packets transmitted, 2 received, 0% packet loss, time 999ms rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.233/0.326/0.420/0.095 ms

The route configured above is a temporary route that is applied once configured, and will be lost once the iMetal server is restarted. To avoid network disruptions, take step 11 to configure permanent routes instead.
- Run the following command to verify the connectivity between network interface eth0 and the test iMetal server:
- Configure a permanent route for the supplementary network interface.
- Run the following command to open the /etc/rc.local file:
vi /etc/rc.local
- Press i to enter editing mode.
- Add the following content to the end of the file.
The parameters and values must be the same as those in steps 3 to 9.
ip link add link eth0 name eth0.1937 type vlan id 1937 ip netns add ns1937 ip link set eth0.1937 netns ns1937 ip netns exec ns1937 ifconfig eth0.1937 hw ether fa:16:3e:6d:c5:5a ip netns exec ns1937 ifconfig eth0.1937 up ip netns exec ns1937 ip addr add 192.168.0.149/24 dev eth0.1937 ip netns exec ns1937 ip route add default via 192.168.0.1
- Press ESC to exit and enter :wq! to save the configuration.
- Run the following command to assign execute permissions to the /etc/rc.local file:
chmod +x /etc/rc.local
If your operating system is Red Hat or EulerOS, run the following command after you perform 11.e:
chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
- Run the following command to restart the iMetal server:
- Check whether the permanent route has worked by referring to 10.
- Run the following command to open the /etc/rc.local file:
Configuring a Supplementary Network Interface for a Windows iMetal Server
- Supplementary network interface
- VLAN ID: 2242
- MAC address: fa:16:3e:6d:c5:db
- Private IP address: 192.168.0.22
- Subnet mask: 24 (255.255.255.0)
- Subnet gateway address: 192.168.0.1
- Network interface
- MAC address: fa:16:3e:6d:c5:d5
- Private IP address: 192.168.0.16
- Subnet mask: 24 (255.255.255.0)
- Subnet gateway address: 192.168.0.1
This example describes how to configure the supplementary network interface for the primary network interface of an ECS. If you want to do the same thing for the extended network interface of the ECS, follow the similar steps.
- Login to the iMetal server.
For details, see iMetal Server Login Methods.
- Enter Windows PowerShell in the search box in the lower left corner of the desktop and press Enter.
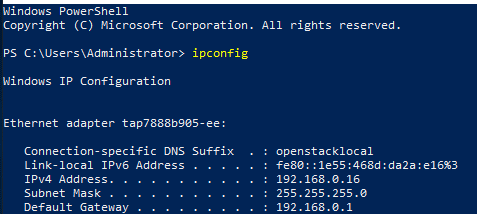
- On the displayed window, run the following command to query the Ethernet adapter information of the network interface:
Information similar to the following is displayed. In this example, the Ethernet adapter name is tap7888b905-ee.
- Create a bond group.
- Run the following command to create a bond group for the custom VLAN:
New-NetLbfoTeam -Name <bond-group-name> -TeamMembers "<Ethernet-adapter-name-of-the-network-interface>" -TeamingMode SwitchIndependent -LoadBalancingAlgorithm IPAddresses -Confirm:$false
Variables in the preceding command are as follows:
- bond-group-name: the bond group name of the custom VLAN. In this example, the bond group name is Team1.
- Ethernet-adapter-name-of-the-network-interface: information queried in 3. In this example, the name is tap7888b905-ee.
Example command:
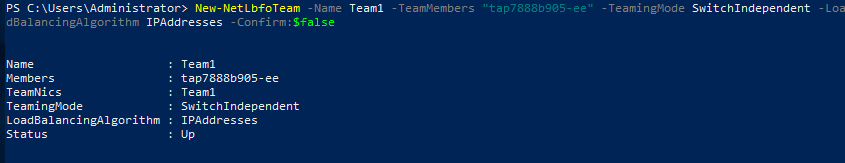
New-NetLbfoTeam -Name Team1 -TeamMembers "tap7888b905-ee" -TeamingMode SwitchIndependent -LoadBalancingAlgorithm IPAddresses -Confirm:$false
Information similar to the following is displayed:
- Run the following commands to query the bond group you have created:
Information similar to the following is displayed:
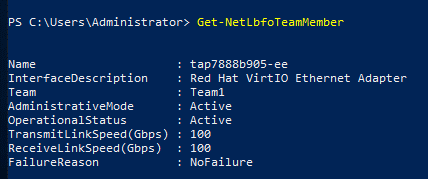
Get-NetAdapter
Information similar to the following is displayed:
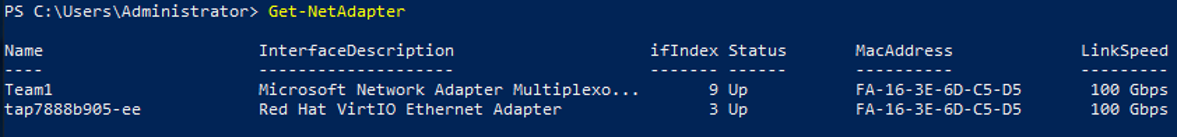
- Run the following command to create a bond group for the custom VLAN:
- Configure a custom VLAN network.
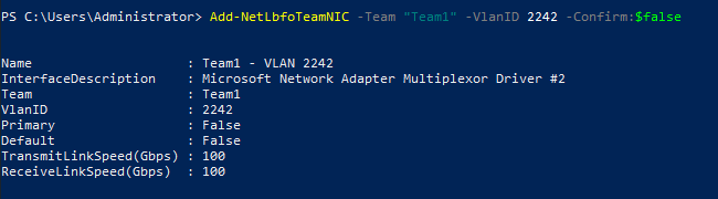
- Run the following command to create a VLAN sub-interface:
Add-NetLbfoTeamNIC -Team "<bond-group-name>" -VlanID <VLAN-ID-of-the-supplementary-network-interface> -Confirm:$false
Example command:
Add-NetLbfoTeamNIC -Team "Team1" -VlanID 2242 -Confirm:$false
Information similar to the following is displayed:
- Run the following command to open the Network Connections page:
ncpa.cpl
On the displayed page, Team1 is the bond group created in 4.a, and Team1 – VLAN 2242 is the VLAN sub-interface created in 5.a.
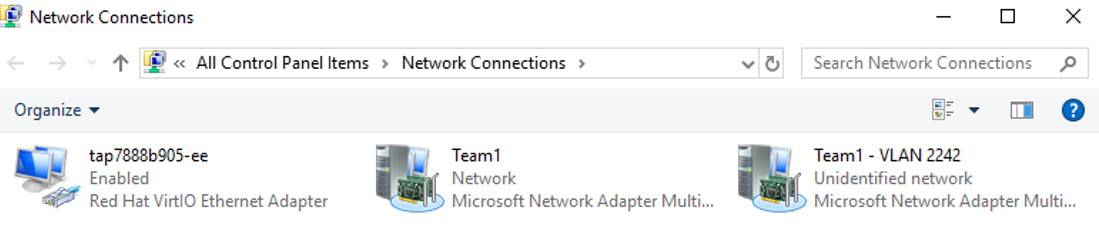
- Run the following command to create a VLAN sub-interface:
- Configure the network for the network interface.
- On the Network Connections page, double-click Team1.
The Team1 Status page is displayed.
- On the Team1 Status page, click Properties.
The Team1 Properties page is displayed.
- On the Team1 Properties page, click Configure....
The Microsoft Network Adapter Multiplexor Driver Properties page is displayed.
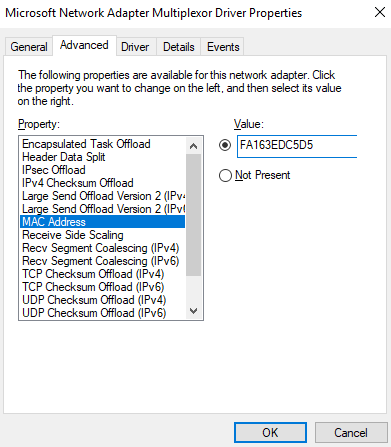
- On the Microsoft Network Adapter Multiplexor Driver Properties page, choose the Advanced tab, click MAC Address, enter the MAC address of the network interface, and click OK.
When entering the MAC address, remove the colons (:) and use the uppercase letters. For example, if the MAC address of the network interface is fa:16:3e:6d:c5:d5, enter FA163E6DC5D5.
- Return to the Team1 Properties page, double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties page is displayed.

- On the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties page, configure the network information of the network interface and click OK.
- Select Use the following IP address:.
- IP address: Enter the private IP address of the network interface. In this example, the private IP address is 192.168.0.16.
- Subnet mask: Enter the mask of the subnet where the network interface is created. In this example, the mask is 255.255.255.0.
- Default gateway: Enter the gateway of the subnet where the network interface is created. In this example, the gateway is 192.168.0.1.
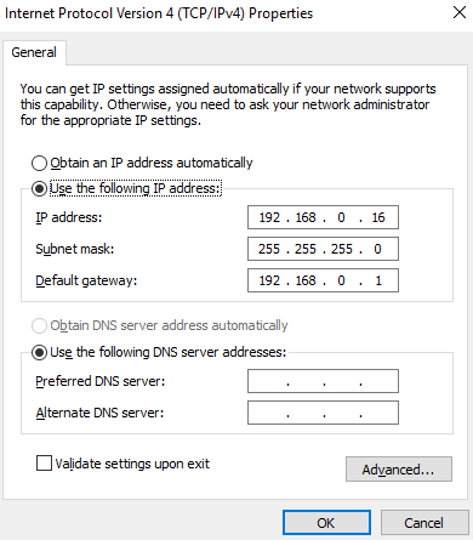
- On the Team1 Properties page, click OK to save the settings.
- Return to the Team1 Status page and click Details....
On the Network Connection Details page, check whether the following information is correctly configured:
- Physical Address: MAC address of the network interface.
- IPv4 Address: the private IP address of the network interface.
- IPv4 Subnet Mask: the mask of the subnet where the network interface is created.
- IPv4 Default Gateway: the gateway of the subnet where the network interface is created.
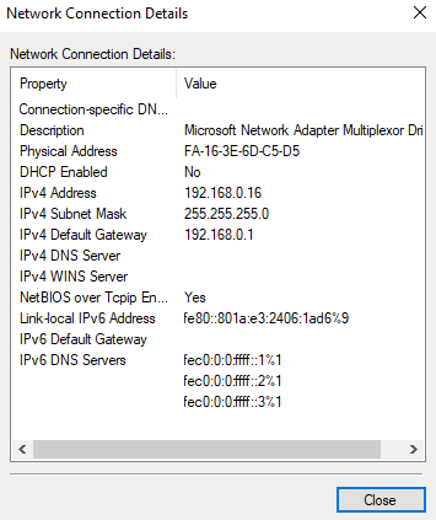
- Check the settings and click Close.
The Network Connections page is displayed.
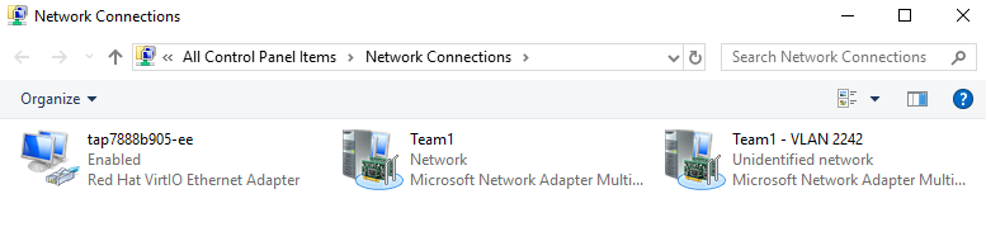
- On the Network Connections page, double-click Team1.
- Configure the network for the supplementary network interface.
- On the Network Connections page, double-click Team1 - VLAN 2242.
The Team1 - VLAN 2242 Status page is displayed.
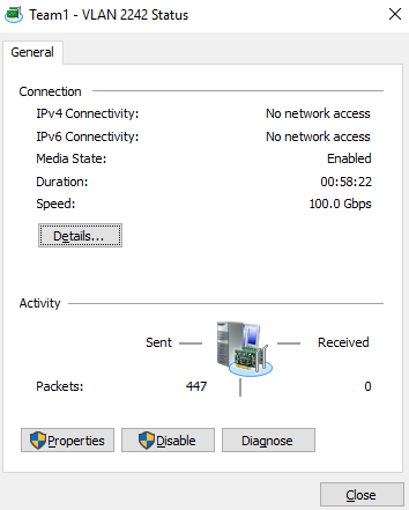
- On the Team1 - VLAN 2242 Status page, click Properties.
The Team1 - VLAN 2242 Properties page is displayed.
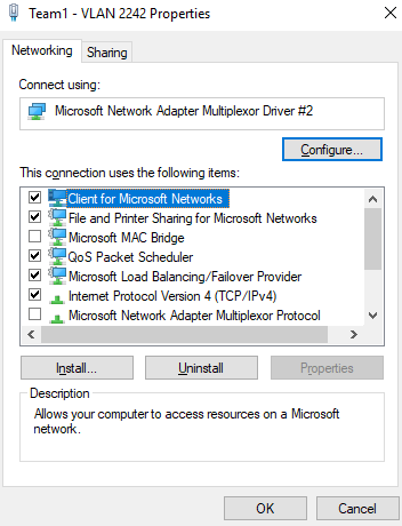
- On the Team1 - VLAN 2242 Properties page, click Configure....
The Microsoft Network Adapter Multiplexor Driver #2 Properties page is displayed.
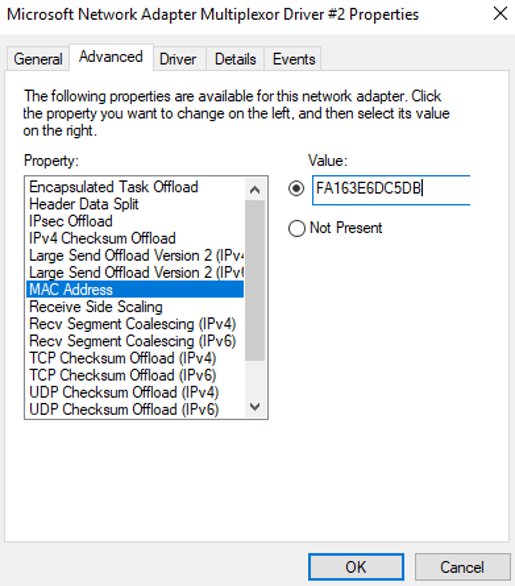
- On the Microsoft Network Adapter Multiplexor Driver #2 Properties page, choose the Advanced tab, click MAC Address, enter the MAC address of the supplementary network interface, and click OK.
When entering the MAC address, remove the colons (:) and use the uppercase letters. For example, if the MAC address of the supplementary network interface is fa:16:3e:6d:c5:db, enter FA163E6DC5DB.
- Return to the Team1 - VLAN 2242 Properties page, double-click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
The Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties page is displayed.
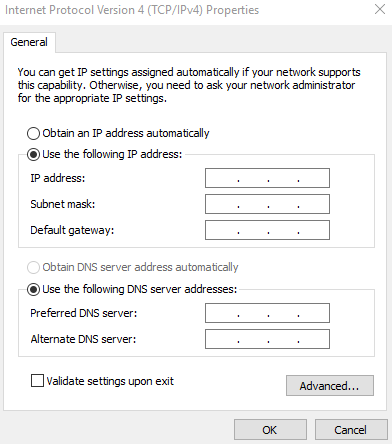
- On the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties page, configure the network information of the supplementary network interface and click OK.
- Select Use the following IP address:.
- IP address: Enter the private IP address of the supplementary network interface. In this example, the private IP address is 192.168.0.22.
- Subnet mask: Enter the mask of the subnet where the supplementary network interface is created. In this example, the mask is 255.255.255.0.
- Default gateway: Enter the gateway of the subnet where the supplementary network interface is created. In this example, the gateway is 192.168.0.1.
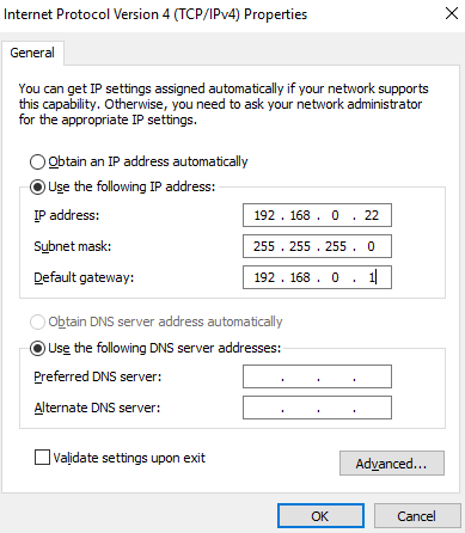
If the following warning is displayed, click Yes to close the dialog box.
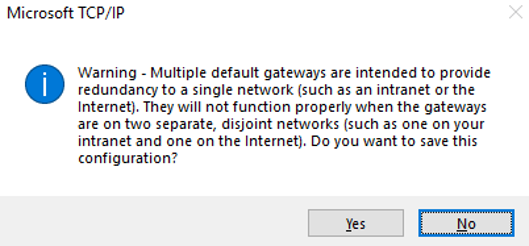
- On the Team1 - VLAN 2242 Properties page, click OK to save the settings.
- Return to the Team1 - VLAN 2242 Status page and click Details....
On the Network Connection Details page, check whether the following information is correctly configured:
- Physical Address: MAC address of the supplementary network interface.
- IPv4 Address: the private IP address of the supplementary network interface.
- IPv4 Subnet Mask: the mask of the subnet where the supplementary network interface is created.
- IPv4 Default Gateway: the gateway of the subnet where the supplementary network interface is created.
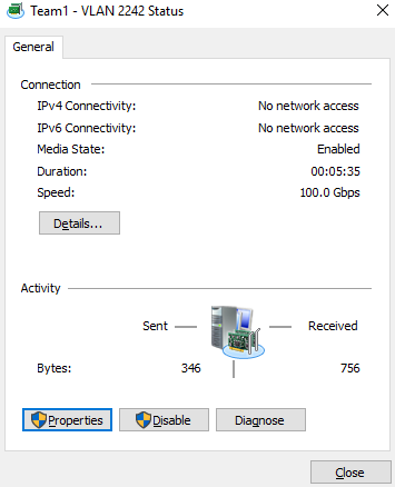
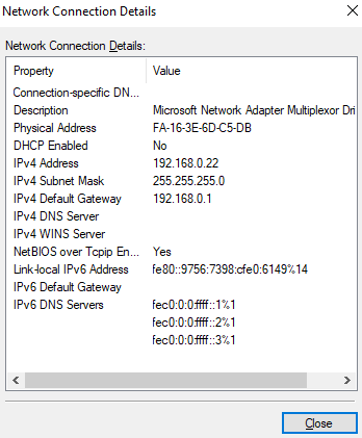
- Check the settings and click Close.
- On the Network Connections page, double-click Team1 - VLAN 2242.
- On the Windows PowerShell CLI page, check whether the network interface and supplementary network interface are connected to the test iMetal server.
- Run the following command to verify the network connectivity between the network interface and the test iMetal server.
Ping <private-IP-address-of-the-test-iMetal-server> -S <private-IP-address-of-the-network-interface>
Plan the same VPC for the test iMetal server and the iMetal server that the network interface is attached to, so that the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other by default.
Example command:
Ping 192.168.0.133 -S 192.168.0.16
If information similar to the following is displayed, the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other.
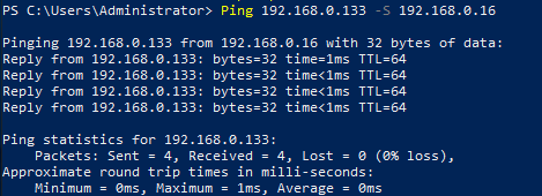
- Run the following command to verify the connectivity between the supplementary network interface and the test iMetal server.
Ping <private-IP-address-of-the-test-iMetal-server> -S <private-IP-address-of-the-supplementary-network-interface>
Plan the same VPC for the test iMetal server and the iMetal server that the supplementary network interface is attached to, so that the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other by default.
Example command:
Ping 192.168.0.133 -S 192.168.0.22
If information similar to the following is displayed, the two iMetal servers can communicate with each other.
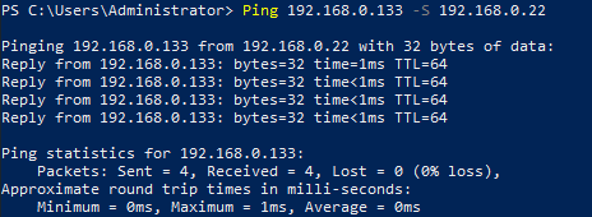
- Run the following command to verify the network connectivity between the network interface and the test iMetal server.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





