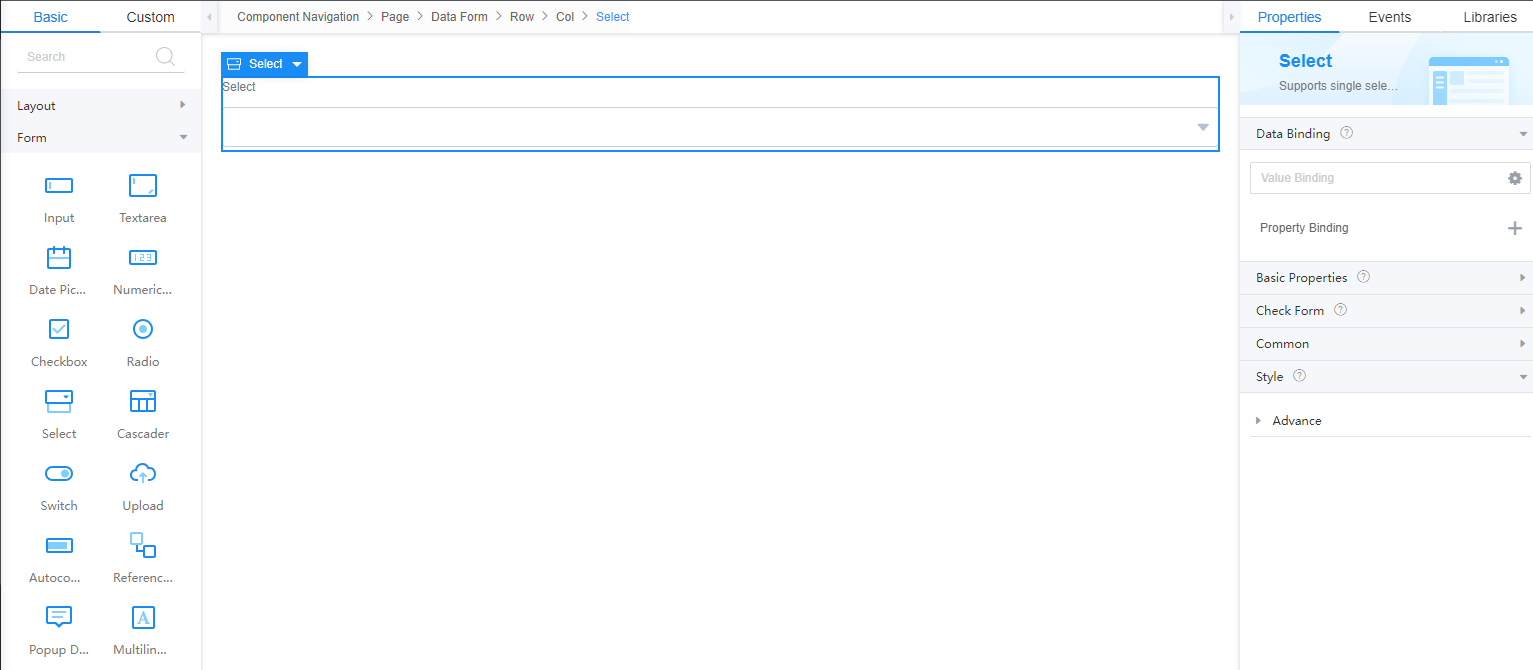
Setting Properties of the Select Widget
The select widget provides options from the drop-down list and supports the single-option selection, multi-option selection, search, and keyboard shortcut operations.
Data Binding
- Value binding: Value binding is similar to the v-model of the Vue. Bidirectional data binding is created on the widget. Value binding automatically selects the correct method to update the element based on the widget type. In addition, it checks events that cause binding data changes to update data.
- In the Data Binding area, click
 in the value binding area. The Select Model dialog box is displayed.
in the value binding area. The Select Model dialog box is displayed. - Click New.
- Set Model Name and Source, and click Next.
Figure 2 Defining a model
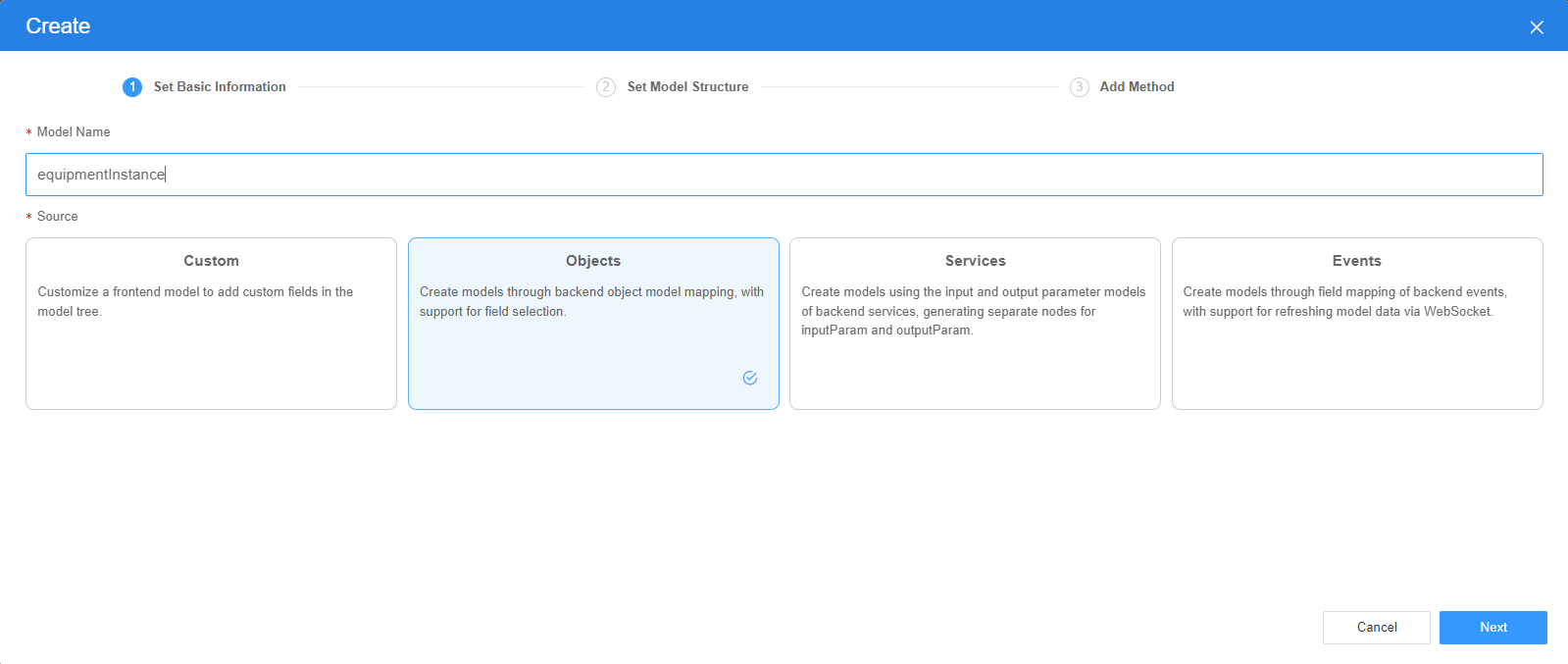
There are four types of models: Custom, Objects, Services, and Events. Each type of model contains parameter definitions and method definitions. Methods are APIs defined on models. In general, these APIs are called in event scripts (such as page loading events and mouse click events) associated with frontend widgets to implement certain logic.
Table 1 Model types Type
Model Description
Model Parameter Description
Model Method Description
API Calling Method
Custom
Models defined by developers.
Defined by developers. Subnodes can be added.
Developer-defined method.
$model.ref("modelName").actionName();
Objects
Object models are generated based on the mapping of the object table. For details about the object model, see Objects.
The system automatically obtains all fields of an object. Developers can select some fields as parameters.
The system automatically generates four methods: query, save, delete, and count.
- Query: $model.ref("modelName").query(param);
- Save: $model.ref("modelName").save();
- Delete: $model.ref("modelName").delete();
- Statistics: $model.ref("modelName").count();
Services
Service models are generated by mapping backend services. Currently, service models can only be mapped to flows or scripts. For details about the service model, see Flows and Scripts.
The parameters are mapped to the inputParam and outputParam sections based on the input and output parameters of backend services.
The run method is automatically generated to execute a flow or a script associated with the model.
$model.ref("modelName").run();
Events
For event models, data binding is created based on fields of a backend event. Model data can be updated based on the web socket.
Parameters are generated by mapping fields of backend events.
Directly use.
Directly use.
In addition to the methods defined in models, the platform provides the following standard APIs for all models:
- Obtaining model data: $model.ref("modelName").getData();
- Setting model data: $model.ref("modelName").setData();
- Setting model field values: $model.ref("modelName").setValue(key,value);
- On the Settings page of the new model, perform the following operations:
- If Source is set to Custom in the previous step, you need to add customized parameters and types of subnodes.
- If Source is set to Objects in the previous step, you need to configure the object and fields associated with the model.
- If Source is set to Services in the previous step, you need to configure the backend service associated with the model. The backend service can be a script, flow, or public API.
- If Source is set to Events in the previous step, you need to configure the event and event fields associated with the model.
- Click Next.
Generally, you do not need to add a method. If you need to add or modify a method, refer to the method generated by the object and service by default.
- Click OK.
- In the Data Binding area, click
- Property Binding: Binds a property of a container widget, such as hiding, style, and elastic layout, to a specific model field. Once bound, these properties automatically update in sync with the model field's value, functioning in a manner akin to Vue's v-bind directive.
- In the Data Binding area, click + next to Property Binding.
- Select a property of the container from the Properties drop-down list.
- Under Field, click
 . The model selection page is displayed.
. The model selection page is displayed. - Click New.
- Set Model Name and Source, and click Next.
There are four types of models: Custom, Objects, Services, and Events. Each type of model contains parameter definitions and method definitions. Methods are APIs defined on models. In general, these APIs are called in event scripts (such as page loading events and mouse click events) associated with frontend widgets to implement certain logic. For details, see Table 1.Figure 3 Defining a model
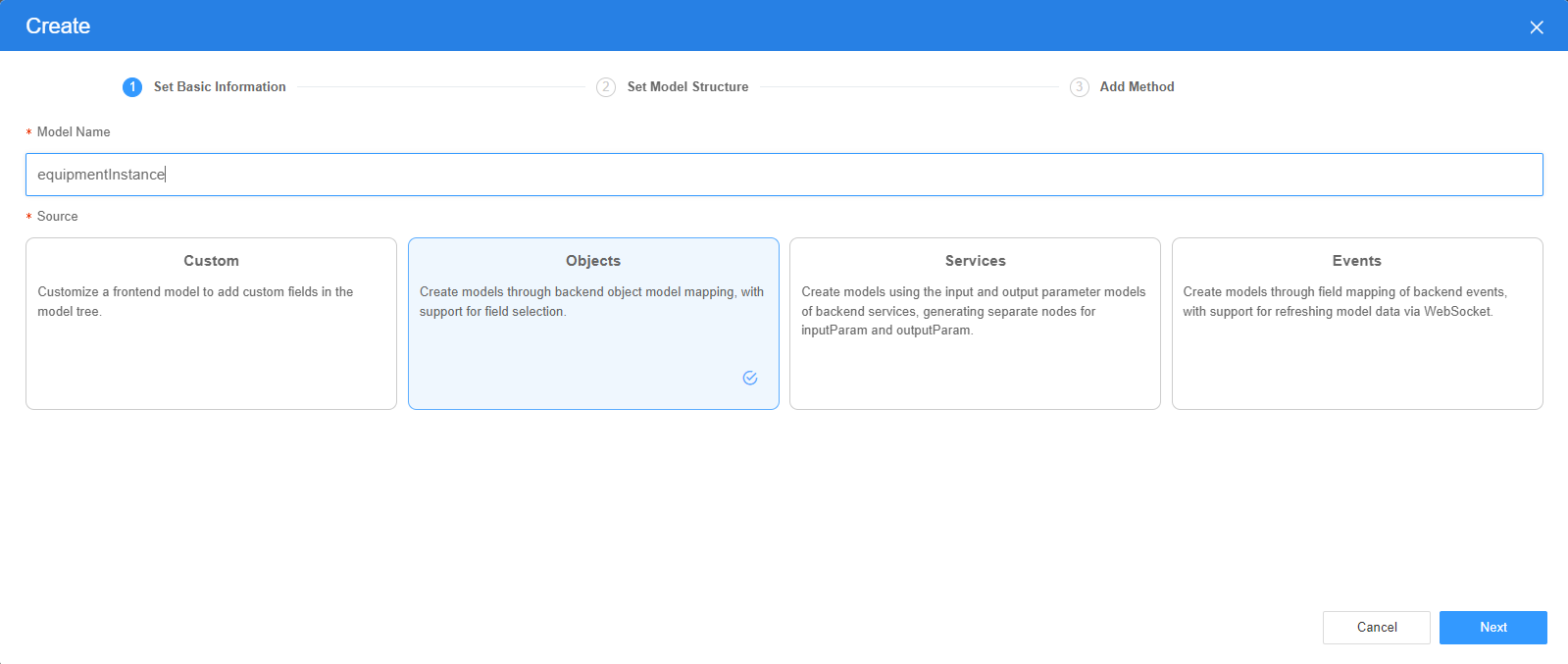
- On the Settings page of the new model, perform the following operations:
- If Source is set to Custom in the previous step, you need to add customized parameters and types of subnodes.
- If Source is set to Objects in the previous step, you need to configure the object and fields associated with the model.
- If Source is set to Services in the previous step, you need to configure the backend service associated with the model. The backend service can be a script, flow, or public API.
- If Source is set to Events in the previous step, you need to configure the event and event fields associated with the model.
- Click Next.
Generally, you do not need to add a method. If you need to add or modify a method, refer to the method generated by the object and service by default.
- Click OK.
Basic Properties
- Label: Label of the drop-down list box. This property is valid only when the drop-down list box is placed in a form.
- Placeholder: Message displayed to a user when no option is selected in the drop-down list box.
- Options: Options that can be selected from the drop-down list box. If Options is bound to a model field in value binding, when you preview a page, the value binding is preferred and the option content is displayed.
The input data must be in JSON format. The following is an example: [{"value": "1","display": "male"},{"value": "0","display": "female"}] - Picklist: Click
 and select a picklist configured in the system. Options and Picklist. Only one of them can be configured.
and select a picklist configured in the system. Options and Picklist. Only one of them can be configured.
If Options is bound to a model field in value binding, when you preview a page, the value binding is preferred and the option content is displayed.
- Unique Option Value: The option value is a unique identifier. After this property is enabled, the rendering performance is improved.
- Multi-Select: Indicates whether the drop-down list box provides the capability of selecting multiple options.
- Clearable: Indicates whether to display a delete icon for the user to clear the selected option in the drop-down list box.
- Append Layer body: When the option value area is not completely displayed and some content is hidden, the complete option value can be displayed after this property is enabled.
- Filterable: Indicates whether the drop-down list box provides the filter capability.
- Remote Search: Indicates whether to call the customized API to query data based on the entered keyword. This property is used together with the on-remote-search event.
- Initial Load: Indicates whether the drop-down list box is initially loaded.
- AUI Style: Once enabled, the style of the drop-down list icon is different.
- Max. Width: maximum width of the widget.
Form Verification
- Mandatory: Indicates whether an option of a drop-down list box must be selected.
- Mandatory Error: Information displayed to indicate that the mandatory drop-down list box has no value when the drop-down list box is bound to an object model and placed in a form widget.
- Custom Validation: indicates whether to perform custom validation. Once enabled, you need to set the validation JavaScript code. The setting takes effect only when the text box is in the form widget.
- Verification Method: Enter the JavaScript code to define the validation rule. The return value of the code must be of the Boolean type or object type.
- Boolean type: If false is returned, the verification fails. To configure an error message, set the Custom Validation parameter. If true is returned, the verification is successful.
- Object type: If "{result:false, message:'error message'}" is returned, the verification fails and the message value is an error message. If "{result:true}" is returned, the verification is successful and no message is displayed.
An example is as follows:
- Example 1: The input option length for verification cannot exceed 10 characters.
return value.length <= 10
The value variable is defined in the system and indicates the input content variable. You can use it directly.
- Example 2: The options for verification can contain only letters.
Object type:
var reg = new RegExp("^[A-Za-z]+$"); if (reg.test(value)) { return true; } else { return {result: false, message:'The content does not comply with the rules. Only uppercase letters and lowercase letters are allowed.'}; }
- Error message verification: error information displayed when the verification fails.
Common
- Name: name of the current widget.
- Hid: indicates whether to hide the widget. In this mode, the widget is statically hidden. You can also set the attribute value of the widget to a model field of the Boolean type. In this way, you can control the value of the model field in the customized JavaScript code to determine whether to hide the widget. This dynamic setting has the highest priority.
- Disable: indicates whether to disable the widget.
- Read-only: indicates whether the value is read-only.
Style
Set the CSS style class name used by the widget in . The class name can be referenced in CSS code.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





