Using ROMA Connect for Service Integration
Overview
ROMA Connect encapsulates APIs, data sources, and custom functions into RESTful APIs and opens them to external systems, manages the whole API lifecycle, and protects APIs in multiple layers.
This chapter provides a configuration example to help you get familiar with the service integration process.
The steps for integrating services with ROMA Connect are as follows:
Prerequisites
Before performing this operation, complete the following preparations:
- An EIP has been bound to the ROMA Connect instance, and the network where the local PC is located can communicate with the EIP network.
- The Postman tool has been downloaded and installed on your local PC.
Step 1: Create an API Group
Each open API belongs to an API group. Before creating an API, create an API group.
- Log in to the ROMA Connect console. On the Instances page, click View Console of an instance.
- Create an integration application.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Integration Applications. In the upper right corner of the page, click Create Integration Application.
- In the dialog box displayed, set Name and Description, and click OK.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose API Connect > API Groups. In the upper right corner of the page, click Create API Group and select Create Directly.
- In the Create API Group dialog box, enter the group-related parameters and click OK.
Figure 1 API group configuration
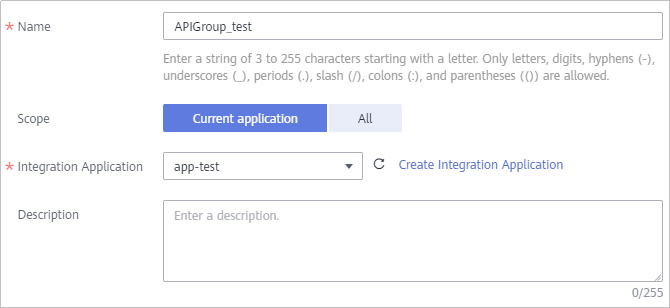
Table 1 Parameters for creating an API group Parameter
Description
Name
Enter an API group name. Using naming rules facilitates future search.
Scope
Specify whether the API group is available on the current application or on all applications. Select Current application.
Integration Application
Select the integration application created in 2. If none is available, click Create Integration Application on the right to create one.
Description
Enter a brief description of the API group.
Step 2: Create an API
Create an API on ROMA Connect and associate it with the backend service.
- In the left navigation pane on the instance console, choose API Connect > APIs. In the upper right corner, click Create API.
- On the page displayed, configure the frontend definition of the API.
Figure 2 Frontend configuration
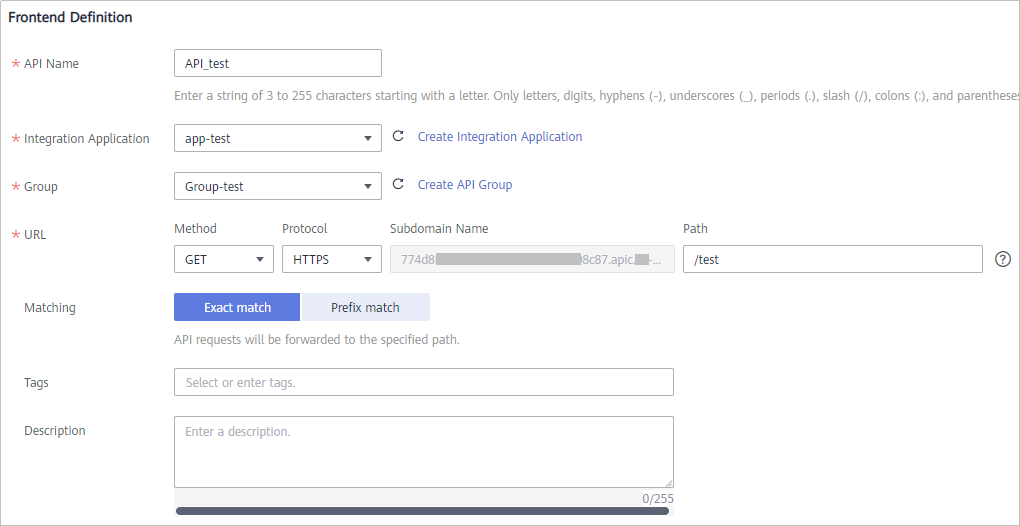
Table 2 Parameters for defining an API frontend Parameter
Description
API Name
Enter an API name. Using naming rules facilitates future search.
Integration Application
Select the integration application created in Step 1: Create an API Group. If none is available, click Create Integration Application on the right to create one.
Group
Select the API group created in Step 1: Create an API Group.
URL
Configure the API access address.
- Method: request method of the API. Set this parameter to GET here.
- Protocol: request protocol of the API. Set this parameter to HTTPS here.
- Path: request path of the API, in /getUserInfo/{userId} format. Set this parameter to /test here.
Matching
Matching mode of the API request path. Set this parameter to Exact match here.
Tags
Skip this parameter.
Description
Skip this parameter.
- Configure API security information.
Figure 3 Security configuration

Table 3 Security parameters Parameter
Description
Visibility
Specifies whether the API can be released to the marketplace. Retain the default value Public, which indicates that the API can be released to the marketplace.
Authentication Mode
Security authentication mode used by the API. In this example, select None.
CORS
Specifies whether CORS is supported. You do not need to enable this option.
- Configure the request parameters of the API. You can skip this step and click Next.
- Set the backend type. In this example, select Mock to return specified response.
- Configure API backend information.
Figure 4 Backend configuration
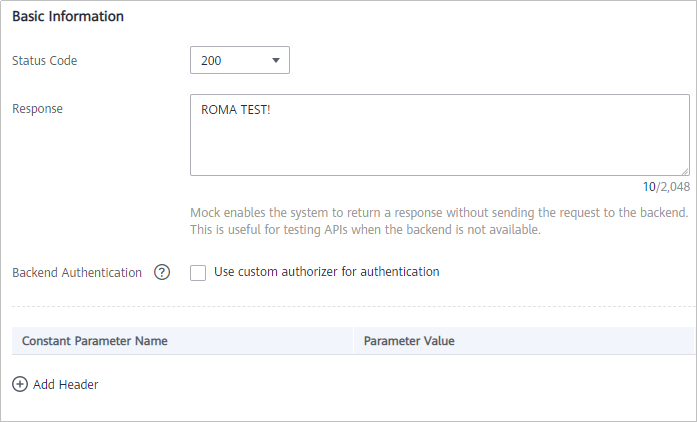
Table 4 Parameters for defining an API backend Parameter
Description
Status Code
Select the HTTP status code returned by the API. Use 200 here.
Response
Enter the response result of the API. In this example, set this parameter to ROMA TEST!. Once you call the API, ROMA TEST! is returned.
Backend Authentication
Specify whether to use a custom authorizer for authentication. Skip this parameter.
Add Header
Customize the header parameters of the API response. Skip this parameter.
- Configure response examples to help API callers understand the responses to an API request.
Figure 5 Response configuration
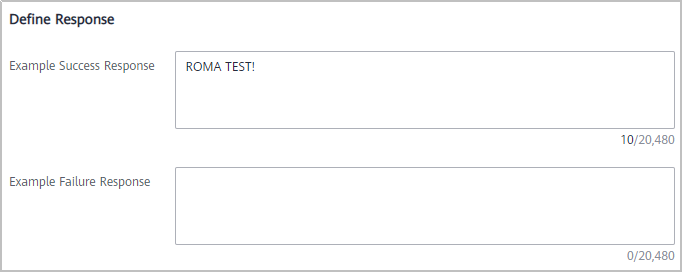
Table 5 Response parameters Parameter
Description
Example Success Response
Example of a system response when an API is called successfully. In this example, set this parameter to ROMA TEST!.
Example Failure Response
Example of a system response when an API cannot be called. Skip this parameter.
- Click Finish. After the API is created, the API details page is displayed.
Step 3: Debug the API
After you create an API, debug it to ensure that the API functions properly.
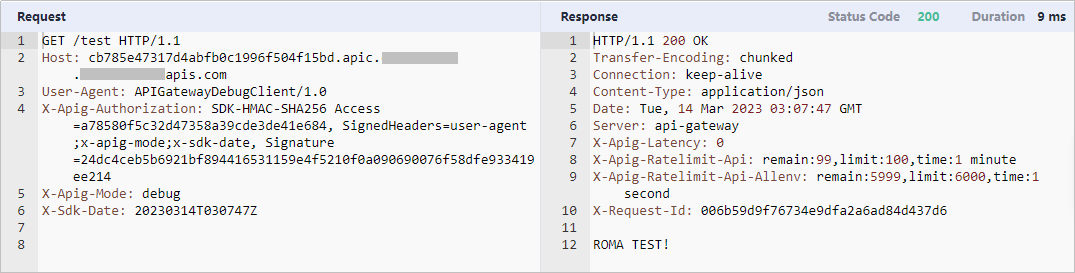
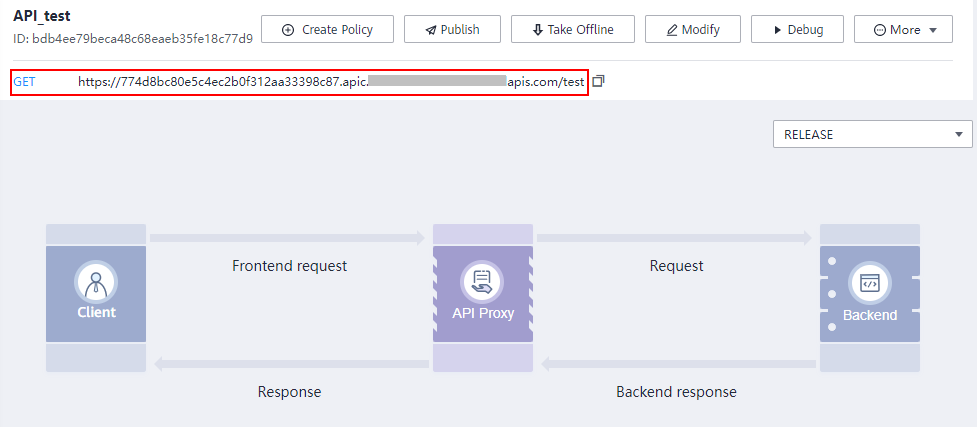
- On the details page of the API created in Step 2: Create an API, click Debug in the upper right corner.
- Click Debug next to the API's access address. Request parameters are not required in this example because none has been set in previous steps.
- View the request and response for API calling.
- Click
 on the right of Debug to return to the APIs details page after debugging.
on the right of Debug to return to the APIs details page after debugging.
Step 4: Publish the API
Once the API is tested normal, publish it to an environment so that it can be called by other users.
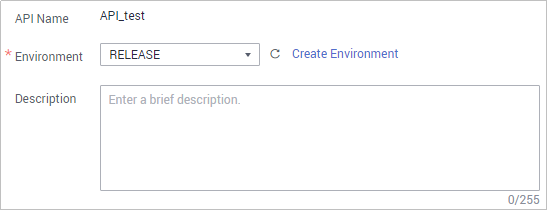
- On the API details page, click Publish in the upper right corner.
- On the page displayed, set Environment to RELEASE and click Publish.
Figure 7 Publishing the API
Step 5: Call the API
In this example, Postman is used to call the API.
- Obtain request information of the API.
- Call the API.
Use Postman to call the API obtained in 1.
After the API is successfully called, check whether the response is the same as the test result in Step 3: Debug the API.
Figure 9 API calling response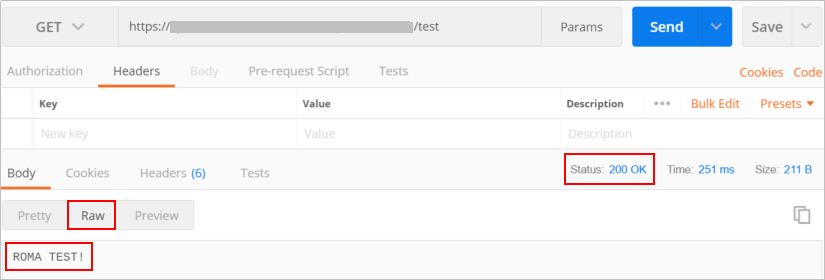
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot