Functions
BCS provides the following functions to help you quickly deploy blockchains featuring security, high efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Instance Deployment
You can purchase resources when deploying a blockchain system, without a need to prepare resources required by the system in advance.
- The blockchain network configuration and deployment are completed in minutes, instead of days.
- Underlying technological details are masked. You do not need to care about the underlying technology implementation and platform construction.
- You can create consortium or private blockchains.
Instance Management
You can view the running statuses of your BCS instances and perform operations on them, for example, adding organizations, upgrading, and obtaining client configurations.
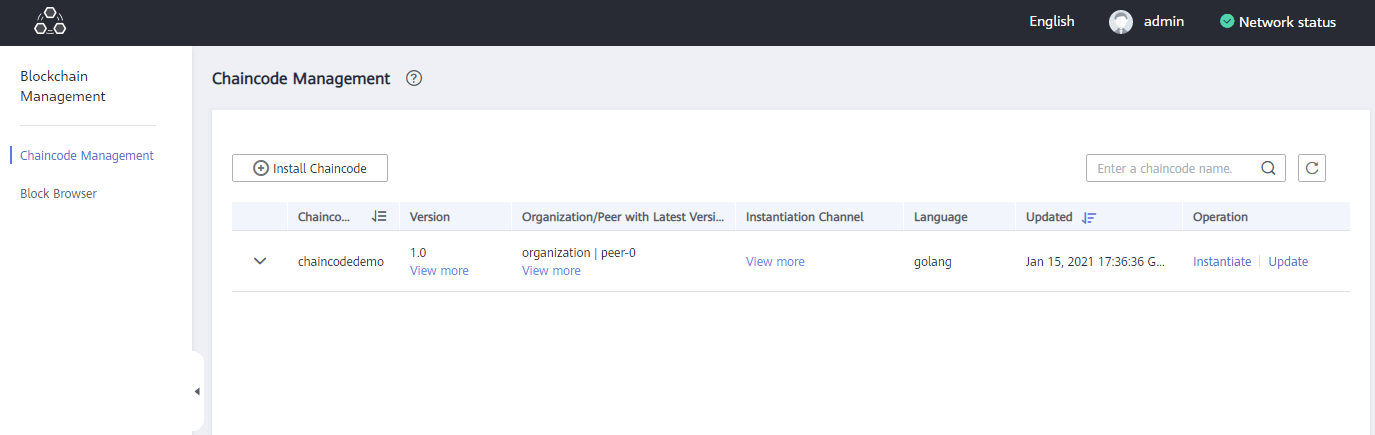
Chaincode Management
You can manage chaincodes on the graphical user interface (GUI) throughout the entire chaincode lifecycle, including coding, debugging, installation, instantiation, and upgrade.
Block Browser
In the block browser, you can query the block and transaction quantities and details, peer statuses, and performance data for blockchain maintenance.

Ledger Storage
File database (GoLevelDB) and NoSQL (CouchDB) are available for ledger storage.
- File database: Historical transaction data is stored in the blockchain, and status data is stored in LevelDB.
- NoSQL: Transaction and status data are stored in CouchDB.

Consensus Algorithms
BCS supports two consensus algorithms for different scenarios.
- Raft (CFT): A crash fault tolerance (CFT) algorithm that tolerates faults at a maximum of (N – 1)/2 orderers, where N indicates the total number of orderers. It also supports Fabric v2.2.
- FBFT: The fast Byzantine fault tolerance (FBFT) algorithm. It requires 4 to 10 orderers for transaction ordering and tolerates faults at a maximum of (N – 1)/3 orderers, where N indicates the total number of orderers. It also supports Fabric v2.2.

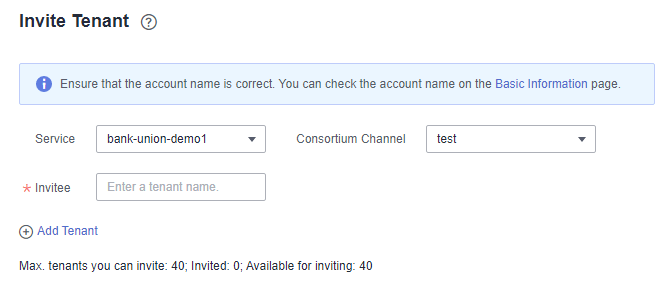
Consortium Member and Organization Management
- A consortium initiator can dynamically invite other tenants to conveniently and quickly set up a consortium blockchain. Peers of each consortium member run in a separate virtual private cloud (VPC) for independent management, ensuring security and controllability.
- You can dynamically add peer organizations to a BCS instance.
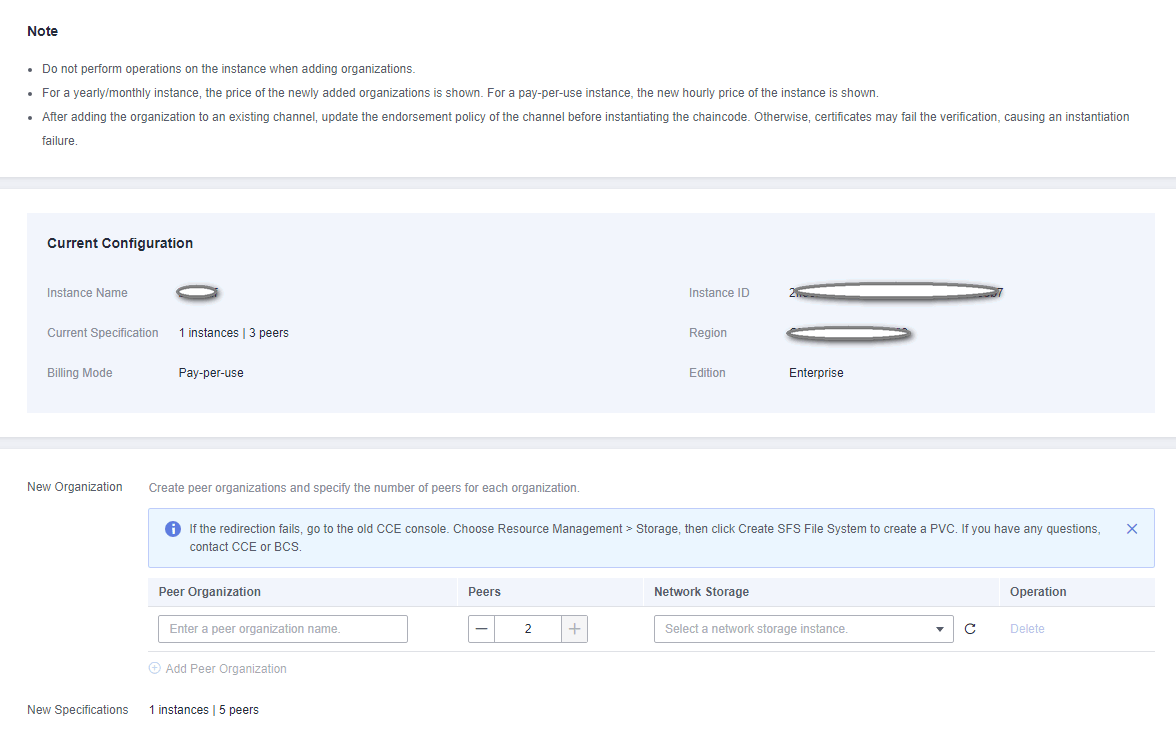
Auto Scaling of Nodes
You can scale nodes as required, without rebooting systems.
Contract Scan
Automatic analysis tools are provided to ensure the smart contract safety from the source. Based on the vulnerabilities and issues commonly found in consortium blockchain smart contracts, the check reports and solutions are generated to help users and developers audit code security, detect risks, and resolve problems.
Privacy Protection
- In each channel, members are assigned different access permissions to certain data, ensuring the data privacy of members within a channel.
- Different channels are also isolated from each other, protecting block data of all members in a channel from other channels.
Application Access
Applications can access blockchain networks using software development kits (SDKs) and RESTful APIs.
- SDK configuration files can be downloaded. After simple configuration, an application can be connected to a blockchain network.
- Applications can invoke chaincodes through RESTful APIs. The policy of multi-organization endorsement is supported.
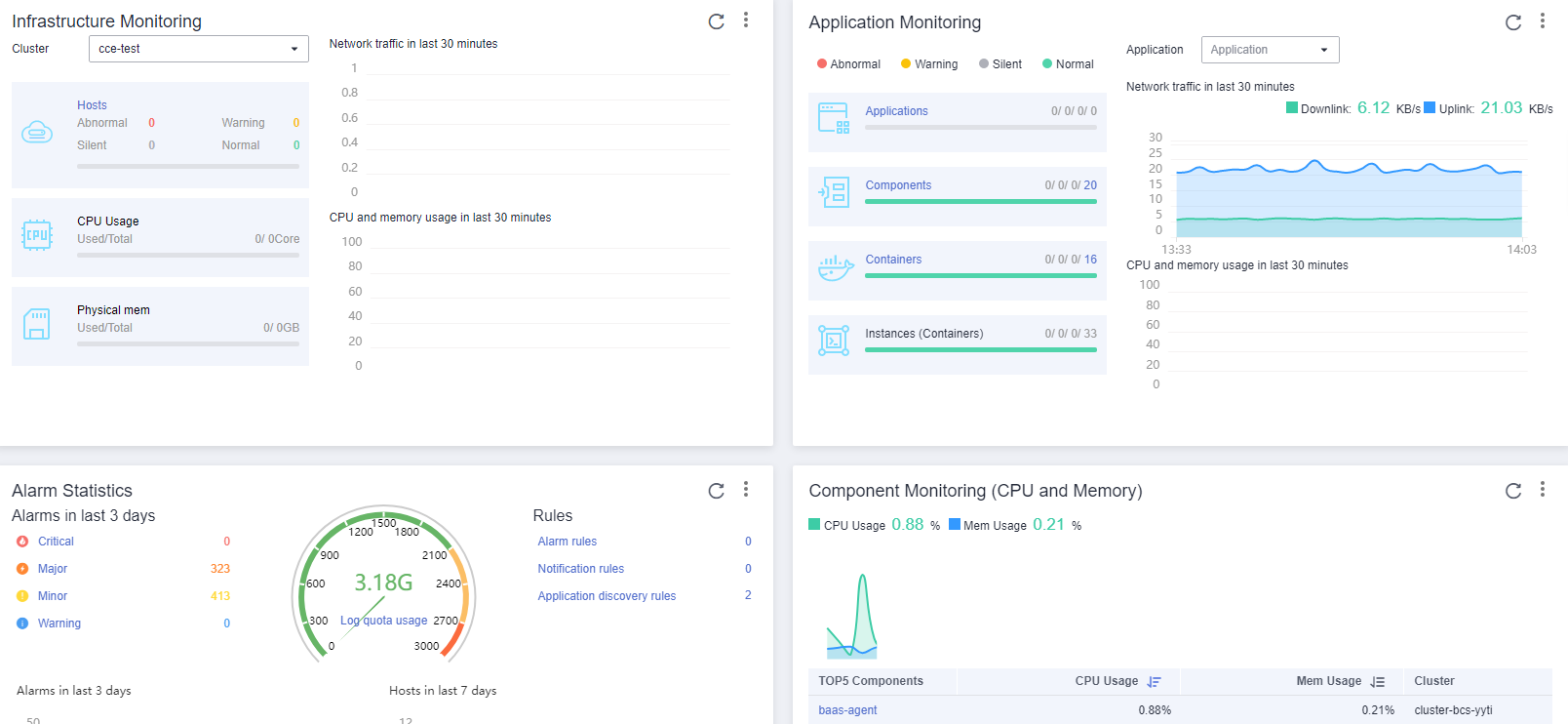
Monitoring and O&M
BCS connects to the monitoring platform to monitor data and resources in real time and generate alarms and notifications when necessary.
- Automated O&M: BCS actively upgrades the underlying blockchain platform and updates patches to seamlessly integrate with the Huawei Cloud O&M system.
- Enterprise-grade monitoring: Multi-dimensional monitoring is performed on clusters 24/7, and user-defined alarms can be reported through multiple channels.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





