Can a Deleted CSS Cluster Be Restored?
For a deleted Elasticsearch or OpenSearch, if it still has snapshots stored in OBS, it can be restored using these snapshots. Otherwise, it cannot be restored. Therefore, exercise caution when deciding to delete a cluster.
To restore a deleted cluster using one of its snapshots stored in OBS, perform the following steps:
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, expand Clusters. Select a cluster type based on the target cluster. The cluster list is displayed.
- Click Create Cluster in the upper-right corner to create a cluster that is of the same type as the deleted cluster. Make sure that:
- The new cluster is in the same region as the deleted cluster.
- The cluster version is the same as or later than that of the deleted cluster.
- The number of nodes in the new cluster is greater than half of that in the deleted cluster. Ideally, they should have the same number of nodes. This is to prevent data restoration failures.
- Deselect Automatic Snapshot Creation.
- When the status of the new cluster changes to Available, enable cluster snapshots.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the new cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Click the Cluster Snapshots tab.
- Click Enable Snapshot. In the displayed dialog box, configure the necessary settings. Keep OBS Bucket and Backup Path consistent with those of the deleted cluster.
- Click OK.
- Above the cluster snapshot task list, click Synchronize OBS Backups. After data synchronization, manually refresh the list to show the updated snapshot information.
The snapshots of the deleted cluster are displayed in the cluster snapshot task list.
Figure 1 Synchronizing snapshots stored in OBS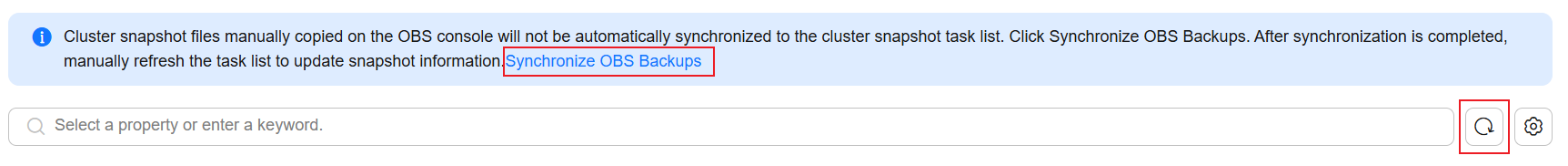
- Restore data from snapshots.
- In the cluster snapshot task list, locate the needed snapshot, and click Restore in the Operation column. In the displayed dialog box, configure index settings and select the current cluster in Cluster.
- Click OK. When the snapshot's Task Status changes to Restoration succeeded, data has been restored successfully.
If there are multiple snapshots, restore all of them in the right order to restore the data of the deleted cluster.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





