Using Spark SQL Statements Without Aggregate Functions for Correlated Subqueries
Scenarios
If you are using open-source Spark SQL, the aggregate function must be used for correlated subqueries. Otherwise, "Error in query: Correlated scalar subqueries must be aggregated" will be reported. MRS allows you to perform correlated subqueries without using aggregate functions.
Notes and Constraints
- This section applies only to MRS 3.3.1-LTS or later.
- SQL statements similar to select id, (select group_name from emp2 b where a.group_id=b.group_id) as banji from emp1 a is supported.
- SQL statements similar to select id, (select distinct group_name from emp2 b where a.group_id=b.group_id) as banji from emp1 a is supported.
Configuring Parameters
Spark SQL scenario:
- Install the Spark client.
For details, see Installing a Client.
- Log in to the Spark client node as the client installation user.
Modify the following parameters in the {Client installation directory}/Spark/spark/conf/spark-defaults.conf file on the Spark client.
Parameter
Description
Example Value
spark.sql.legacy.correlated.scalar.query.enabled
Whether Spark SQL supports correlated scalar subqueries without aggregate functions.
- true: Spark SQL supports correlated scalar subqueries without aggregate functions.
- false: Spark SQL does not support correlated scalar subqueries without aggregate functions.
true
Spark Beeline scenario:
- Log in to FusionInsight Manager.
For details, see Accessing FusionInsight Manager.
- Choose Cluster > Services > Spark, click Configurations and then All Configurations, and choose JDBCServer(Role) > Customization. Add the spark.sql.legacy.correlated.scalar.query.enabled parameter in the custom area and set its value to true.
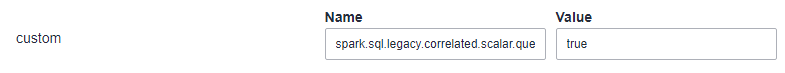
- Click Save and save the parameter settings as prompted. Click the Instances tab, select all JDBCServer instances, and choose More > Restart Instance to restart the JDBCServer instances as prompted.

If a correlated subquery uses multiple match predicates, an exception occurs.
Instances are unavailable during the restart, affecting upper-layer services in the cluster. To minimize the impact, perform this operation during off-peak hours or after confirming that the operation does not have adverse impact.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





