What Is Error Code 404, 502, or 504 Returned to Visitors After My Website or Application Is Connected to WAF?
If an error, such as 404 Not Found, 502 Bad Gateway, or 504 Gateway Timeout, occurs after your website or application is connected to WAF, use the following methods to locate the cause and remove the error:
404 Not Found
- A non-standard port is configured when a domain name is connected to WAF. No port is added or the origin server port instead of the non-standard port is used to access the website. For example, use https://www.example.com or https://www.example.com:80 to access the website.
Solution: Add the non-standard port to the URL and access the origin server again, for example, https://www.example.com:8080.
- No non-standard port is configured when a domain name is added to WAF. A non-standard port or the origin server port is used to access the website. For example, use https://www.example.com:8080 to access the website.
If no non-standard port is configured, WAF protects services on port 80/443 by default. To protect services on other ports, re-configure domain settings.
Solution: The domain name needs to be accessed directly. For example, https://www.example.com.
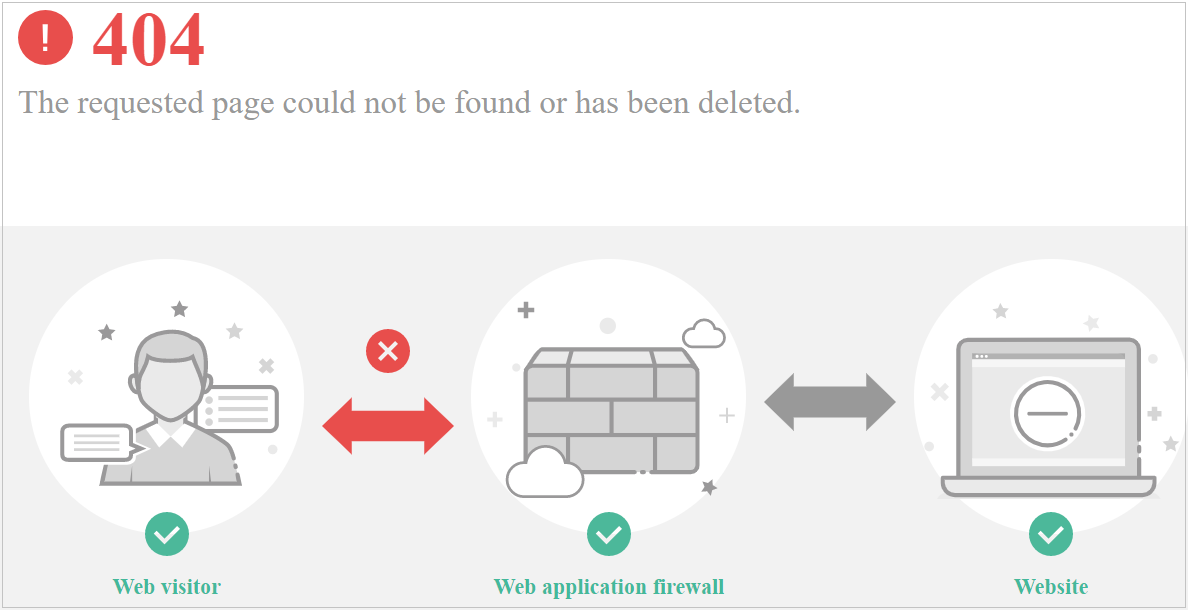
Scenario 2: When a visitor accesses your website, another 404 error page is displayed instead of the page shown in Figure 1.
Cause: The website does not exist or has been deleted.
Solution: Check your website.
502 Bad Gateway
If your web server is not deployed on the cloud, consult your server provider about whether the server has default block settings. If there are default block settings, ask the service provider to remove them.
Possible causes are as follows:
- Cause 1: Your website is using another security protection software. The software considers back-to-source IP addresses of WAF as malicious and blocks the requests forwarded by WAF. As a result, the site becomes inaccessible.
- Cause 2: Multiple backend servers are configured. However, one backend server is unreachable.
Perform the following steps to check whether the origin server configuration is correct:
- Log in to the management console, click Service List in the upper part of the page, and choose to go to the WAF console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Website Settings.
- In the Domain Name column, click the domain name. Its information is displayed.
- In the Server Information area, click
 . On the displayed page, check whether the client protocol, server protocol, origin server address, and port used by the origin server are correct.
Figure 2 Server configuration
. On the displayed page, check whether the client protocol, server protocol, origin server address, and port used by the origin server are correct.
Figure 2 Server configuration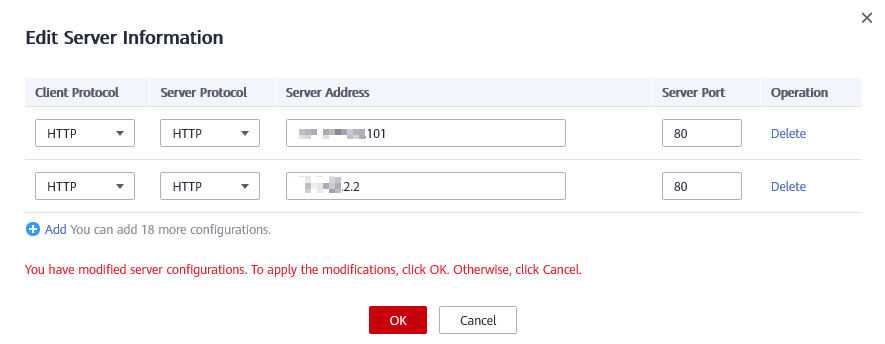
- Run the curl command on the host to check whether each origin server can be properly accessed.
curl http://xx.xx.xx.xx:yy -kvv
xx.xx.xx.xx indicates the IP address of the origin server. yy indicates the port of the origin server. xx.xx.xx.xx and yy must belong to the same origin server.
- The host where the curl command can be run must meet the following requirements:
- The network communication is normal.
- The curl command has been installed. curl must be manually installed on the host running a Windows operating system. curl is installed along with other operating systems.
- You can also enter http://origin server address:origin server port in the address bar of the browser to check whether the origin server can be properly accessed.
Figure 3 Command output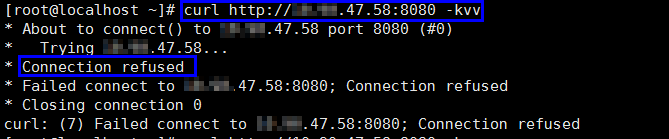
If connection refused is displayed, the origin server is unreachable and website cannot be accessed. Perform the following operations:
- Check whether the server is running properly. If it is not, restart the server.
- Add the WAF back-to-source IP address ranges to the whitelist of the firewall (hardware or software), security protection software, and rate limiting module.
- The host where the curl command can be run must meet the following requirements:
- Cause 3: Origin server performance
Solution: Contact your website owner to rectify the fault.
504 Gateway Timeout
Scenario: After the configuration of connecting a domain name to WAF is complete, your website works properly. However, with the increasing traffic volume, the number of 504 errors also increases. If you directly access the IP address of the origin server, the 504 error code is returned sometimes.
The possible causes are as follows:
- Cause 1: Backend server performance issues (such as too many connections or high CPU usage)
Solution:
- Optimize the server configuration, including TCP network parameters and ulimit parameters.
- To handle large-scale service increase, use method 1 or method 2 to perform the processing.
Method 1: Add a backend server group to the ELB load balancer.
Method 2: Create an ELB. Use the EIP of ELB as the IP address of the server to connect to WAF.- Log in to the management console, click Service List in the upper part of the page, and choose to go to the WAF console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Website Settings.
- In the Domain Name column, click the domain name. Its information is displayed.
- In the Server Information area, click
 . On the displayed page, click Add.
. On the displayed page, click Add.
- If the Client Protocol is HTTPS, you can use HTTPS on the WAF side. However, it is recommended that HTTP (Server Protocol) to forward the requests to your web server, lowering the computational demands on backend servers.
- Cause 2: The WAF back-to-source IP addresses are not whitelisted or your origin server port is not enabled.
Solution: Whitelist the WAF back-to-source IP addresses in the corresponding ECS security groups.
- Cause 3: The origin server has a firewall and the firewall blocks the WAF back-to-source IP addresses.
Solution: Whitelist the WAF back-to-source IP addresses in the corresponding ECS security groups or uninstall the firewall software except WAF.
- Cause 4: Connection timeout and read timeout
Solution
- Database queries are slow.
- Tune services to shorten the query duration and improve user experience.
- Modify the request interaction mode so that the persistent connection can have some data transmitted within 60 seconds, such as ACK packets, heartbeat packets, keep-alive packets, and other packets that can keep the session alive.
- It takes a long time to upload large files.
- Tune services to shorten the file upload time.
- An FTP server is recommended for file upload.
- Upload the file through an IP address or a domain name that is not protected by WAF.
- The default timeout for a dedicated WAF instance to respond origin servers is 180s.
- The origin server is faulty.
- Configure a timeout for connections between WAF and a website Server
Timeout duration for each request between WAF instance and origin server, include WAF-to-Server connection timeout (s), Read timeout (s), and Write timeout (s). For details, see Configuring a Timeout for Connections Between WAF and a Website Server.
- Database queries are slow.
- Cause 5: The bandwidth of the origin server exceeds the upper limit.
Solution: Increase the bandwidth of the origin server.
- Cause 6: In dedicated mode, the origin server port is not enabled in the security group of the origin server or the origin server subnet is not enabled in network ACLs.
Solution: Enable the security group ports, such as ports 80 and 443, and configure a network ACL to allow access from the origin server subnet.
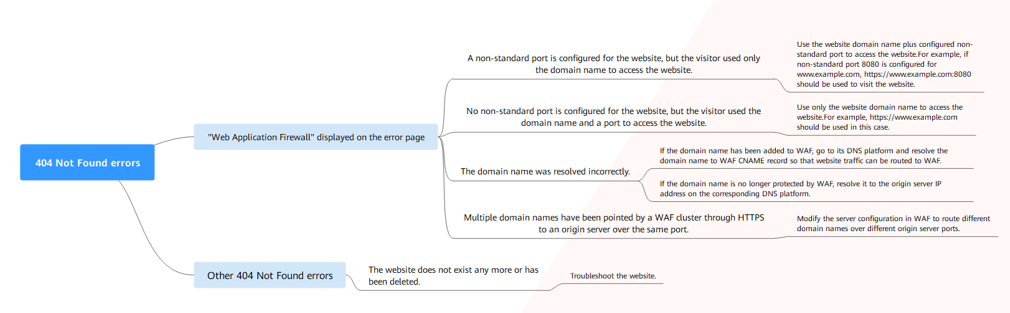
404 Not Found Troubleshooting Process and Suggestions
Refer to Figure 4 to fix the 404 Not Found error occurred after your website is connected to WAF.
- If the page shown in Figure 5 is displayed, the possible causes and solutions are as follows:
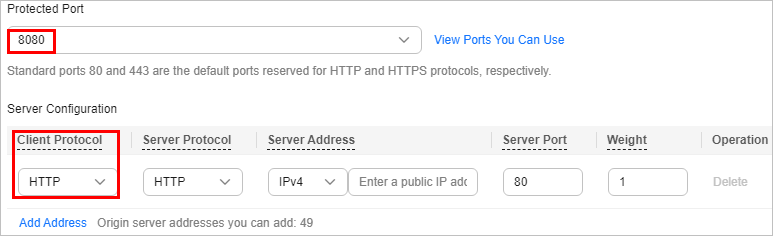
Cause 1: A non-standard port is configured when you add the domain name to WAF, but the visitors use the domain name and standard port or use only the domain name to access the website. For example, a non-standard port is configured as shown in Figure 6. A visitor uses https://www.example.com or https://www.example.com:80 to access the website. As a result, 404 error page is displayed.
Solution: Add the non-standard port to the URL and access the origin server again, for example, https://www.example.com:8080.
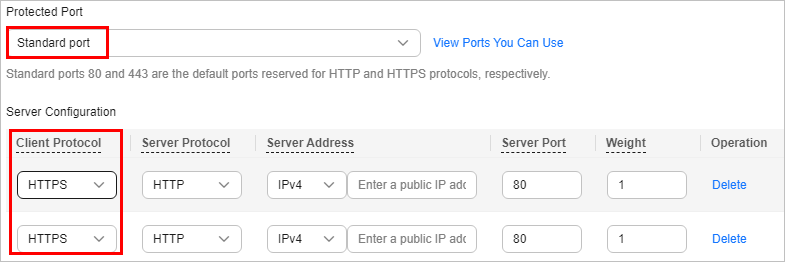
Cause 2: No non-standard port is configured when the domain name is added to WAF. The visitors use the domain name and a non-standard port or the non-standard port configured for origin server port to access the website. For example, access http://www.example.com:8080 when the protection service shown in Figure 7 is configured.
If no non-standard port is configured, WAF protects services on port 80/443 by default. To protect services on other ports, re-configure domain settings.
Solution: Use only the domain name to access the website. For example, https://www.example.com.
Cause 3: The domain name is incorrectly resolved.
Solution:- If the domain name has been added to WAF, resolve the domain name to WAF by referring to .
- If the domain name is no longer protected by WAF, resolve it to the origin server IP address on the DNS hosting platform.
Cause 4: If a WAF cluster pointed multiple domain names through HTTPS to an origin server over the same port, origin servers cannot tell which domain name a request originated from. This is because WAF uses persistent connections to forward requests to origin servers and Nginx identifies domain names based on Host and SNI. So, there might be a probability that requests destined for domain name A was mistakenly forwarded to domain name B, which causes 404 not found errors.
Solution: Modify the server configuration in WAF to route different domain names over different origin server ports.
- If the response page is not similar the one shown in Figure 5, the possible causes and solutions are as follows:
Cause: The website does not exist or has been deleted.
Solution: Check the website.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot