Configuring a Dedicated Load Balancer for an OpenSearch Cluster
In big data processing scenarios, load balancers are essential for distributing traffic and improving the availability and performance of OpenSearch clusters. However, default shared load balancers have functional and performance limitations, making them inadequate for complex, high-concurrency data processing. Dedicated load balancers, with their richer features and superior performance, offer a more robust solution. This topic describes how to configure dedicated load balancers for more efficient and secure cluster access.
Overview
- A non-security cluster can also utilize the capabilities of the Elastic Load Balance (ELB) service.
- You can use custom certificates for HTTPS two-way authentication.
- Seven-layer traffic monitoring and alarm configuration are supported, allowing you to keep close track of the cluster status.
There are eight different ELB service forms for clusters in different security modes to connect to a dedicated load balancer. Table 1 describes the ELB capabilities for different cluster configurations. Table 2 describes the configurations for different ELB service forms.
|
Security Mode |
Service Form Provided by ELB for External Systems |
ELB Load Balancing |
ELB Traffic Monitoring |
ELB Two-way Authentication |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Non-security mode |
No authentication |
Supported |
Supported |
Not supported |
|
One-way authentication Two-way authentication |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
|
|
Security mode + HTTP |
Password authentication |
Supported |
Supported |
Not supported |
|
One-way authentication + Password authentication Two-way authentication + Password authentication |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
|
|
Security mode + HTTPS |
One-way authentication + Password authentication Two-way authentication + Password authentication |
Supported |
Supported |
Supported |
|
Security Mode |
Service Form Provided by ELB for External Systems |
ELB Listener |
ELB Listener |
ELB Listener |
Backend Server Group |
Backend Server Group |
Backend Server Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Frontend Protocol |
Frontend Port |
SSL Authentication |
Backend Protocol |
Health Check Port |
Health Check Path |
||
|
Non-security mode |
No authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
No authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
/ |
|
One-way authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
One-way authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
||
|
Two-way authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
Two-way authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
||
|
Security mode + HTTP |
Password authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
No authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
/_opendistro/_security/health |
|
One-way authentication + Password authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
One-way authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
||
|
Two-way authentication + Password authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
Two-way authentication |
HTTP |
9200 |
||
|
Security mode + HTTPS |
One-way authentication + Password authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
One-way authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
|
|
Two-way authentication + Password authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
Two-way authentication |
HTTPS |
9200 |
Constraints
- You are not advised to connect a load balancer that has been associated with a public IP address to a non-security mode cluster. Allowing public network access through such a load balancer may cause security risks because a non-security mode cluster can be accessed using HTTP without security authentication.
- HTTPS-enabled security-mode clusters do not support HTTP-based frontend authentication. If the frontend uses HTTP, disable security mode for your cluster first. For details, see Changing the Security Mode of an OpenSearch Cluster. Before changing the security mode, disable load balancing first. After the security mode is changed, enable load balancing again.
Prerequisites
- A dedicated load balancer has been created. For details, see Creating a Dedicated Load Balancer. This load balancer must meet the following requirements:
- Its VPC is the same as that of the CSS cluster. The network between the two is connected.
- IP as a Backend is enabled. This is necessary to connect a dedicated load balancer to a CSS cluster.
- Determine whether to configure an EIP based on service needs. A public IP address is displayed for the load balancer connecting the CSS cluster only if an EIP is configured. This will enable public network access to the cluster through this load balancer.
- If the ELB listener uses HTTPS, upload a server certificate or CA certificate to the ELB console. For details, see Adding a Certificate.
- If one-way authentication is used, upload a server certificate.
- If two-way authentication is used, upload a server certificate and a CA certificate.
Connecting a Cluster to a Load Balancer
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Click the Cluster Access tab, and then click the Load Balancing tab. On the OpenSearch tab, toggle on Load Balancing. In the displayed dialog box, set the parameters.
Table 3 Configuring load balancing Parameter
Description
Load Balancer
Select the dedicated load balancer you have created earlier.
To create a dedicated load balancer, see Creating a Dedicated Load Balancer.
Agency
To configure a load balancer, you must have the permission to access ELB resources. By configuring an IAM agency, you can authorize CSS to access its ELB resources through an associated account.- If you are configuring an agency for the first time, click Automatically Create IAM Agency to create css-elb-agency.
- If there is an IAM agency automatically created earlier, you can click One-click authorization to have the permissions associated with the ELB Administrator role or the ELB FullAccess system policy deleted automatically, and have the following custom policies added automatically instead to implement more refined permissions control.
"elb:loadbalancers:list", "elb:loadbalancers:get", "elb:certificates:list", "elb:healthmonitors:*", "elb:members:*", "elb:pools:*", "elb:listeners:*"
- To use Automatically Create IAM Agency and One-click authorization, the following minimum permissions are required:
"iam:agencies:listAgencies", "iam:roles:listRoles", "iam:agencies:getAgency", "iam:agencies:createAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgency", "iam:permissions:grantRoleToAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgencyOnProject", "iam:permissions:revokeRoleFromAgency", "iam:roles:createRole"
- To use an IAM agency, the following minimum permissions are required:
"iam:agencies:listAgencies", "iam:agencies:getAgency", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgencyOnProject", "iam:permissions:listRolesForAgency"
Figure 1 Enabling load balancing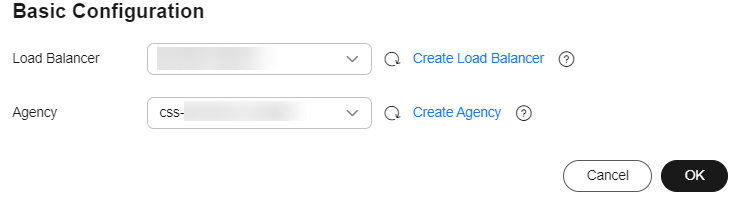
- Click OK to enable load balancing.
Load balancer information is displayed.
- In the Listener area, click
 to configure a listener to ensure proper accessibility of the CSS cluster.
to configure a listener to ensure proper accessibility of the CSS cluster.
Table 4 Listener configuration Parameter
Description
Frontend Protocol
Protocol used by the client and listener to distribute traffic.
Select HTTP or HTTPS.
Select this protocol based on your connectivity needs.
Frontend Port
Port used by the client and listener to distribute traffic.
Set this parameter based on site requirements.
SSL Authentication
Client authentication mode. Set this parameter only when Frontend Protocol is set to HTTPS.
Both one-way and two-way authentication are supported.
Select an authentication mode that suits your needs.
Server Certificate
The server certificate is used for SSL handshake. The certificate content and private key must be provided. It is required only when Frontend Protocol is set to HTTPS.
Select the server certificate created on ELB.
CA Certificate
Also called client CA public key certificate. It is used to verify the issuer of a client certificate. It is required only when SSL Authentication is set to Two-way authentication.
Select the CA certificate created on ELB.
When HTTPS two-way authentication is enabled, an HTTPS connection can be established only when the client can provide the certificate issued by a trusted CA.
Figure 2 Configuring a listener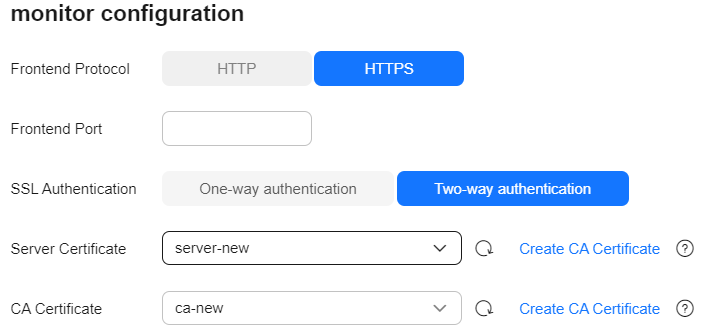
- (Optional) In the Listener area, click Configure next to Access Control to go to the listener list of the load balancer. Click Configure in the Access Control column of a listener to configure access control for that listener. You can specify IP addresses that are allowed to access your cluster for enhanced security. For more information, see What Is Access Control?.

Without access control policies, all IP addresses are allowed to access the CSS cluster through this load balancer, which may create security risks.
- In the Health Check area, you can check the health check results for each node IP address, ensuring that each node in the cluster is functioning properly.
Table 5 Health check result description Health Check Result
Description
Normal
The node IP address is connected.
Abnormal
The node IP address is disconnected.
- If the cluster no longer needs a dedicated load balancer, disassociate it to release resources.
Choose Load Balancing > OpenSearch, toggle off Load Balancing. In the displayed dialog box, click OK.

After the load balancer is disassociated, any listener or backend server group configurations will be permanently deleted.
Accessing a Cluster Through a Load Balancer by Executing cURL Commands
- In the left navigation pane on the CSS console, choose Clusters.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, click the name of the target cluster. The cluster information page is displayed.
- Click the Cluster Access tab, and then click the Load Balancing tab. On the OpenSearch tab, record the private or public IP address or IPv6 address of the load balancer, as well as the frontend protocol/port of the listener.

You are not advised to connect a load balancer that has been associated with a public IP address to a non-security mode cluster. Access from the public network using such a load balancer may cause security risks because a non-security mode cluster can be accessed using HTTP without security authentication.
- Run the following cURL commands on an ECS to check whether the dedicated load balancer can connect to the cluster.
Table 6 Commands for accessing different types of clusters Security Mode
Service Form Provided by ELB for External Systems
cURL Command for Accessing a Cluster
Non-security mode
No authentication
curl http://IP:port
One-way authentication
curl --cacert ./ca.crt https://IP:port
Two-way authentication
curl --cacert ./ca.crt --cert ./client.crt --key ./client.key https://IP:port
Security mode + HTTP
Password authentication
curl http://IP:port -u user:pwd
One-way authentication + Password authentication
curl --cacert ./ca.crt https://IP:port -u user:pwd
Two-way authentication + Password authentication
curl --cacert ./ca.crt --cert ./client.crt --key ./client.key https://IP:port -u user:pwd
Security mode + HTTPS
One-way authentication + Password authentication
curl --cacert ./ca.crt https://IP:port -u user:pwd
Two-way authentication + Password authentication
curl --cacert ./ca.crt --cert ./client.crt --key ./client.key https://IP:port -u user:pwd
Table 7 Variables Variable
Description
IP
IP address of a load balancer instance.
port
Frontend protocol and port configured for the listener.
user
Username of the cluster. This parameter is required only for a security-mode cluster.
pwd
Password of the username above. This parameter is required only for a security-mode cluster.
If cluster information is returned, the connection is successful.
Sample Code for Accessing a Cluster Using HTTPS Two-way Authentication Through a Load Balancer (Java)
This section provides sample code that can be used on a Java client to access a cluster using HTTPS two-way authentication through a load balancer.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





