Configuring Index Monitoring for an OpenSearch Cluster
Index monitoring helps you monitor the index status, statistics, and trends of a cluster, allowing you to promptly handle potential risks to ensure cluster reliability. By collecting index statistics, you can gain insights into various aspects of index performance and resource utilization, and make informed O&M decisions.
How the Feature Works
Index monitoring consists of two steps:
- Data ingestion
- Index stats (such as the number of documents, data storage, and shard status) are ingested periodically.
- Data is written into the monitoring-eye-css-* index, where a data aging mechanism is applied.
- The default data retention duration is seven days. Data is automatically deleted when this duration expires.
- Monitoring chart generation
- Preset dashboards and custom visualizations on OpenSearch Dashboards enable intuitive index monitoring.
- Time series analysis, trend analysis and comparison, and anomaly detection are supported.
Constraints
- Only OpenSearch 2.19.0 supports index monitoring.
- Indexes starting with monitoring-eye-css-* are identified as monitoring indexes and will not be monitored. Do not use this prefix for regular indexes.
- The index pattern of monitoring-eye-css-* must not be deleted while index monitoring is enabled. Otherwise, monitoring charts will become abnormal.
Logging In to OpenSearch Dashboards
Log in to OpenSearch Dashboards and go to the command execution page. OpenSearch clusters support multiple access methods. This topic uses OpenSearch Dashboards as an example to describe the operation procedures.
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > OpenSearch.
- In the cluster list, find the target cluster, and click Dashboards in the Operation column to log in to OpenSearch Dashboards.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Dev Tools.
The left part of the console is the command input box, and the triangle icon in its upper-right corner is the execution button. The right part shows the execution result.
Enabling Index Monitoring
- Run the following command to enable index monitoring:
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "css.monitoring.index.enabled": "true" } } - To monitor a specified index, run the following command to set the monitoring period, target index name, and monitoring index retention duration.
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "css.monitoring.index.enabled": "true", "css.monitoring.index.interval": "30s", "css.monitoring.index.indices": ["index_name"], "css.monitoring.history.duration": "3d" } }Table 1 Parameters for index monitoring Parameter
Type
Description
css.monitoring.index.enabled
Boolean
Whether to enable index monitoring. Setting this parameter to true enables index monitoring.
Default value: false
css.monitoring.index.interval
Time
Index monitoring period.
Minimum value: 1s
Default value: 10s
css.monitoring.index.indices
String
Name of an index to be monitored. By default, all indexes are monitored. You can configure specific indexes or a specific type of indexes to monitor.
Example:
- "css.monitoring.index.indices": ["index_name"] indicates only index_name is monitored.
- "css.monitoring.index.indices": ["log_*"] indicates that only indexes starting with log_ are monitored.
- "css.monitoring.index.indices": ["index1", "index2"] indicates that index1 and index2 are monitored.
Default value: * (indicating that all indexes are monitored)
css.monitoring.history.duration
Time
Retention period of the monitoring index monitoring-eye-css-*. The default period is one week.
Minimum value: 1d
Default value: 7d
Checking the Read and Write Traffic of Indexes
After index monitoring is enabled for a cluster, you can check the read/write traffic of this cluster's indexes during specific periods of time.
- Run the following command to check the read and write traffic of all indexes:
GET /_cat/monitoring
- Run the following command to check the read and write traffic of a specified index:
GET /_cat/monitoring/{indexname}{indexName} indicates the name of the index whose read and write traffic you want to check.
- Run the following command to check the read and write traffic of an index during specified periods of time:
GET _cat/monitoring?begin=1650099461000 GET _cat/monitoring?begin=2022-04-16T08:57:41 GET _cat/monitoring?begin=2022-04-16T08:57:41&end=2022-04-17T08:57:41
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
indexname |
String |
Index name. You cannot check the traffic of system indexes, whose names start with a period (.). |
|
begin |
Date |
Start time (UTC time) of the monitoring data you want to view. Time format: strict_date_optional_time|epoch_millis The default start time is 5 minutes before the current time. |
|
end |
Date |
End time (UTC time) of the monitoring data you want to view. Time format: strict_date_optional_time|epoch_millis The default end time is the current time. |
Information similar to the following is displayed:
index begin end status pri rep init unassign docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size delete.rate indexing.rate search.rate test 2022-03-25T09:46:53.765Z 2022-03-25T09:51:43.767Z yellow 1 1 0 1 9 0 5.9kb 5.9kb 0/s 0/s 0/s
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
index |
Index name |
|
begin |
Start time of the monitoring data you queried. |
|
end |
End time of the monitoring data you queried. |
|
status |
Index status within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
pri |
The number of index shards within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
rep |
The number of index replicas within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
init |
The number of initialized indexes within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
unassign |
The number of unallocated indexes within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
docs.count |
The number of documents within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
docs.deleted |
The number of deleted documents within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
store.size |
Index storage size within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
pri.store.size |
Size of the primary index shard within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
delete.rate |
Number of indexes deleted per second within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
indexing.rate |
Number of indexes written per second within the queried monitoring interval. |
|
search.rate |
Number of indexes queried per second within the queried monitoring interval. |
Checking Index Monitoring Data in OpenSearch Dashboards Charts
You can check preconfigured index monitoring charts on the Dashboard and Visualizations pages of OpenSearch Dashboards. You can also customize tables and charts.
- Check index monitoring results in preconfigured dashboards.
- On the OpenSearch Dashboards console, expand the menu in the upper-left corner, and choose Dashboards.
- Click [Monitoring] Index monitoring Dashboard to check preconfigured dashboards.
Figure 1 Preconfigured dashboards
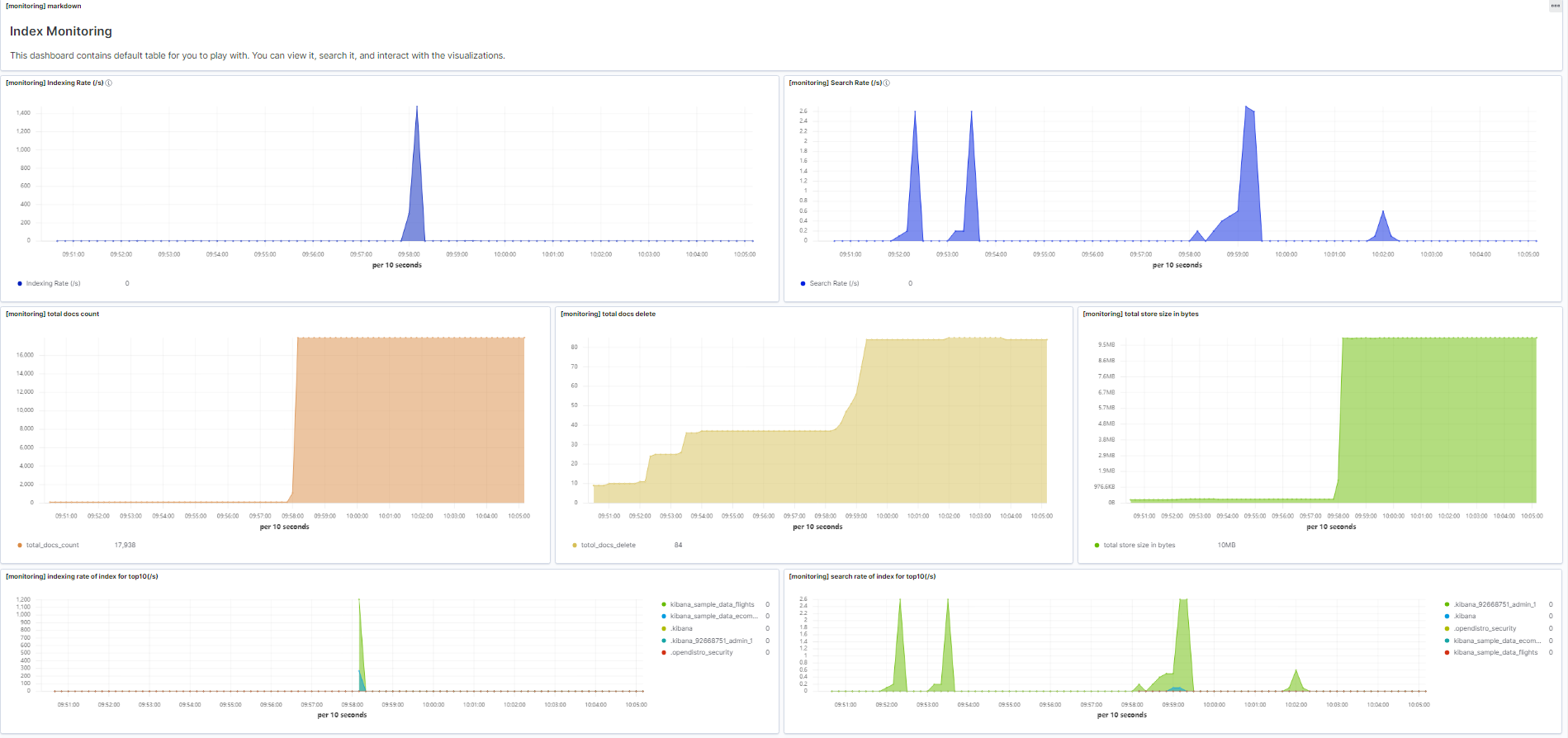
The preconfigured dashboard displays the number of read and write operations per second in the cluster and the top 10 indexes that have the most read and write operations per second.
Table 4 Preconfigured charts Chart Name
Description
[monitoring] markdown
Markdown chart, which briefly describes the dashboard content.
[monitoring] Indexing Rate (/s)
Number of documents written to a cluster per second.
[monitoring] Search Rate (/s)
Average number of queries per second in a cluster.
[monitoring] indexing rate of index for top10
Top 10 indexes with the most documents written per second.
[monitoring] search rate of index for top10
Top 10 indexes with the most queries per second.
[monitoring] total docs count
Total number of documents in a cluster.
[monitoring] total docs delete
Total number of deleted documents in a cluster.
[monitoring] total store size in bytes
Total storage space occupied by documents in a cluster.
[monitoring] indices store_size for top10
Top 10 indexes that occupy the largest storage space.
[monitoring] indices docs_count for top10
Top 10 indexes that store the largest number of documents.
[monitoring] indexing time in millis of index for top10(ms)
Top 10 indexes with the longest document write latency in a unit time (ms).
[monitoring] search query time in millis of index for top10(ms)
Top 10 indexes with the longest index query time in a unit time (ms).
[monitoring] segment count of index for top10
Top 10 indexes with the largest number of index segments.
[monitoring] segment memory in bytes of index for top10
Top 10 indexes with the largest heap memory usage of index segments.
- Check index monitoring results in custom visualizations.
The index monitoring module periodically stores the index/stats information in the monitoring-eys-css index. You can create custom charts on OpenSearch Dashboards to visualize the information.
The following procedure describes how to check the trend of document quantities in a chart as an example.
- Click Visualize in the navigation tree on the left of the OpenSearch Dashboards console.
- Click Create visualization and select TSVB.
- Set chart parameters and view the visualizations.
On the Data tab page, set the parameters as needed.
- Select Max for Aggregation, and select index_stats.primaries.docs.count in Field, indicating the number of documents in a primary shard.
- Select Derivative from Aggregation to indicate differences between aggregation buckets. Set Units to 1s to visualize network rates as "per second".
- Set Aggregation to Positive Only to prevent negative numbers after resetting.
- To show statistics by index, set Group by to Terms and By to index_stats.index. Statistics will be grouped by index name.
- To view data in different time segments, set the aggregation interval, or the displayed data will be incomplete. On the Panel options tab page, set Interval to 1m or 30m to adjust the interval of timestamp.
Figure 2 TSVB page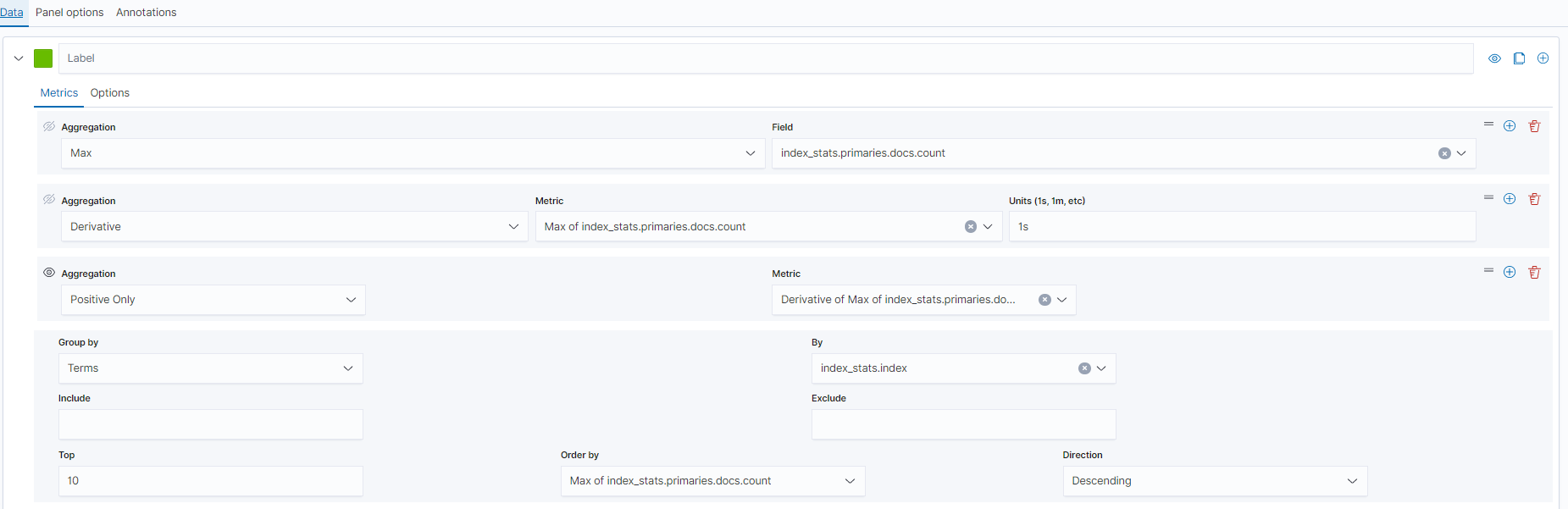 Figure 3 Setting the interval
Figure 3 Setting the interval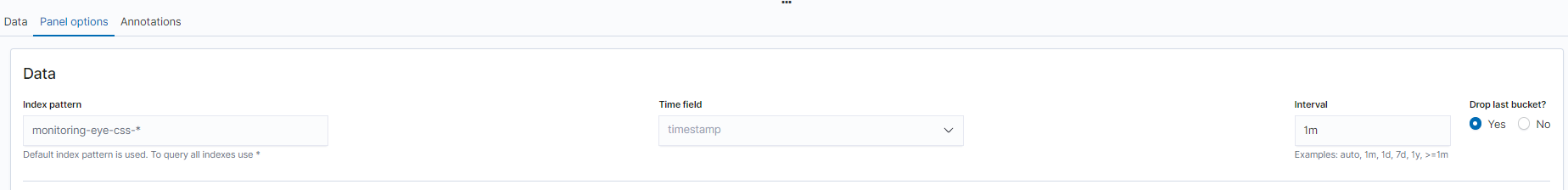
FAQ: What Do I Do If Index Monitoring Charts Are Not Displayed?
Symptom: The cluster's preset dashboards and visualizations are not displayed.
Solution:
- In the cluster list, check whether the security mode is enabled for the cluster.
Figure 4 Checking whether the security mode is enabled

- If Security Mode is Enabled, switch to the Global space.
On OpenSearch Dashboards, click the username in the upper right corner and choose Switch tenants. On the Select your tenant page, switch the space and click Confirm. Then, check whether the charts are now displayed properly. If they are still not, go to the next step.
- If Security Mode is Disabled, go to the next step.
- If Security Mode is Enabled, switch to the Global space.
- In the cluster list, check whether the image version of the cluster is 2.19.0_25.9.0_xxx or later.
- If the cluster image version is 2.19.0_25.9.0_xxx or later, go to the next step to restart index monitoring.
- If the cluster image version is earlier than 2.19.0_25.9.0_xxx, restart all cluster nodes and then restart index monitoring. For details, see Restarting an OpenSearch Cluster.
- Restart index monitoring.
Set css.monitoring.index.enabled to false and then to true. Wait for approximately 5 minutes. The index monitoring charts will be automatically displayed.
PUT _cluster/settings { "persistent": { "css.monitoring.index.enabled": "true" } }If the problem persists, contact technical support.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





