Cross-Cloud Active-Active DR
If critical application systems are deployed in an IDC or another cloud environment and need to be deployed on Huawei Cloud for active-active DR, a cross-cloud active-active DR solution is required to provide high availability. Assuming the systems in the IDC or other cloud already have 99.9% availability, using Huawei Cloud DR can bring it up to 99.99%.
A typical architecture for cross-cloud applications includes a frontend stateless application layer and a backend database layer. The frontend application layer uses VMs or containers (using services like Huawei Cloud CCE), while the backend database layer uses MySQL databases (like you get with Huawei Cloud RDS for MySQL) to support cross-cloud active-active DR.
The recommended deployment on Huawei Cloud is as follows.
|
Item |
Solution |
|---|---|
|
Redundancy |
Deploy cloud services like ELB, CCE, DCS, Kafka, RDS, and DDS, to ensure high availability. |
|
Backup |
Enable automated backup for RDS and DDS databases. When a data fault occurs, the latest backup can be used to restore data, meeting availability requirements. |
|
DR |
Deploy applications across AZs. If an AZ fails, applications can be automatically recovered. Use cross-cloud active-active DR to switch workloads to Huawei Cloud quickly if an IDC or another cloud environment fails. |
|
Monitoring |
Monitor and check site statuses and instance workloads. If a site fails or a CCE, DCS, Kafka, RDS, or DDS instance is overloaded, an alarm is reported. |
|
Auto scaling |
Use CCE clusters with auto scaling of workloads. |
|
Change error prevention |
Use canary or blue-green deployment for software updates. Canary and blue-green deployments can be completed automatically and rolled back if an update does not go smoothly. |
|
Emergency recovery |
Develop an emergency response system and designate emergency personnel to make decisions quickly and recover services. Provide solutions for common application and database issues, as well as upgrade and deployment failures. Conduct periodic drills to promptly identify and address potential problems. |
A typical deployment architecture is as follows.
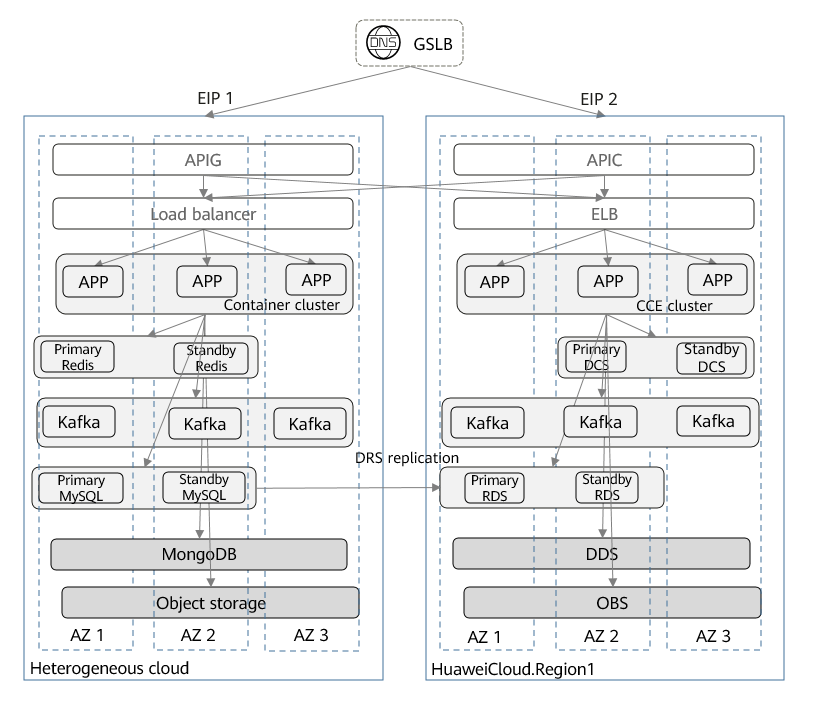
The architecture has the following features:
- The application system uses a multi-layered architecture featuring stateless applications and stateful databases.
- The application system is deployed on both another cloud platform and Huawei Cloud. On Huawei Cloud, the system is distributed across AZs to facilitate active-active DR at the application level between different data centers. Data from other clouds is deployed in separate units and can be synchronized to Huawei Cloud in real-time. If there is a failure on a third-party cloud, the active-active DR solution enables workloads to be rapidly switched over to Huawei Cloud.
- Access Layer (external GSLB and API Gateway): The external GSLB handles domain name resolution and traffic load balancing. Both clouds operate simultaneously, and if a third-party cloud fails, service traffic is automatically redirected to Huawei Cloud. API Gateway ensures traffic is correctly routed to the appropriate service units.
- Application Layer (load balancers, application software, and containers): Load balancers are used to detect faults and distribute loads for stateless applications, while containers enable elastic scaling.
- Middleware layer: Redis and Kafka clusters are deployed across AZs for high availability.
- Data layer: MySQL databases are deployed across multiple AZs for high availability. DRS is used to implement cross-cloud database replication and DR switchover.
- To ensure data reliability, database data is automatically backed up periodically, enabling quick restoration in the event of data loss.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





