What Do I Do If an Application Fails to Be Delivered to an Edge Node?
Symptom
An application cannot be delivered to an edge node.
Fault Locating
Troubleshooting methods are sorted based on the occurrence probability of the possible causes. You are advised to check the possible causes from high probability to low probability to quickly locate the cause of the problem.
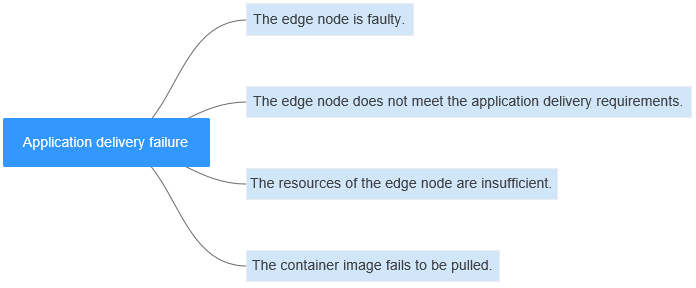
|
Possible Cause |
Solution |
|---|---|
|
The edge node is faulty. |
Log in to the IEF console, choose Managed Resources > Edge Nodes, and check the edge node status. If the edge node is faulty, rectify the fault by referring to What Do I Do If an Edge Node Is Faulty?. |
|
The edge node does not meet the application delivery requirements. |
Edge Node Does Not Meet the Application Delivery Requirements |
|
The resources of the edge node are insufficient. |
|
|
The container image fails to be pulled. |
For details, see What Do I Do If a Container Image Fails to Be Pulled?. |
Edge Node Does Not Meet the Application Delivery Requirements
- Check the resource information of the edge node.
- If the application needs to use NPU and GPU resources, check whether the type of the edge node is correctly selected.
- Run the docker ps command on the edge node to check whether the NPU container (npu-device-plugin) and GPU container (gpu-device-plugin) are running properly.
If you manage the edge node for the first time, rectify the fault by following the procedure described in What Do I Do If a Containerized Application Fails to Be Started on an Edge Node?.
- Check whether the GPU and NPU resources are used by any application running on the edge node and whether the node has remaining GPU and NPU resources.
- Check whether the edge node specifications (CPU and memory) displayed on the IEF console are correct. If the memory size is displayed as 0, check whether the edge node uses the OS of the Chinese edition. IEF supports only the OS of the English edition. If the OS of the Chinese edition is used, IEF cannot obtain memory information or deliver applications to the edge node. In this case, you need to reinstall the OS and manage the edge node again.

Before the OS reinstallation, securely store the installation package and certificate file you downloaded from IEF. If they are not stored, you must delete the edge node and register a new edge node.
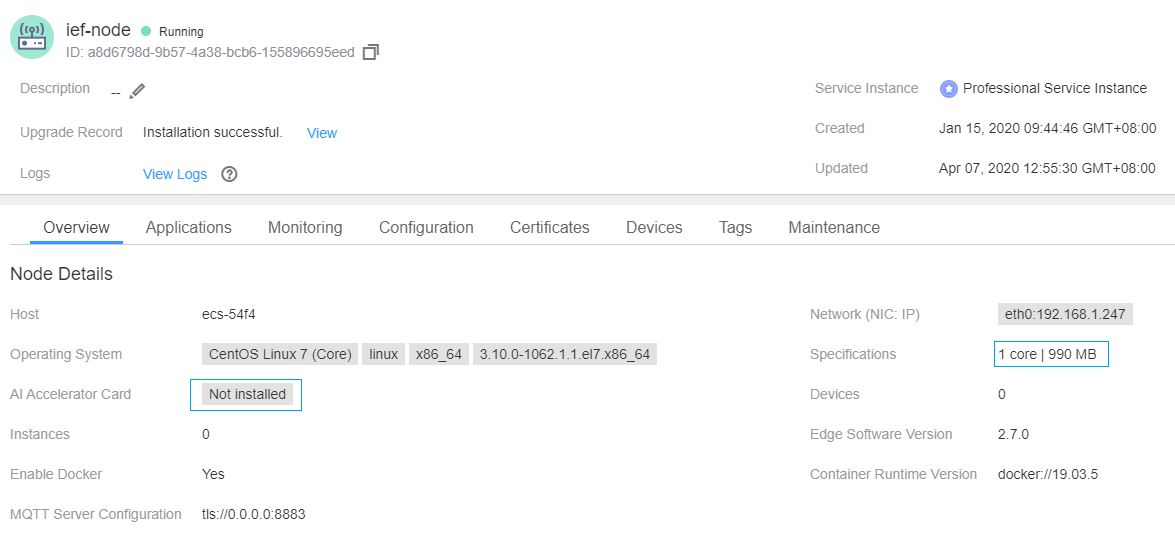
- If you want to deliver a containerized application, check whether a container engine is enabled on your edge node. If a container engine is not enabled, the containerized application cannot be delivered.
Edge Node Resources Are Sufficient
- Check the cause of the container exception.
Hover the cursor over the
 icon next to the instance status to view the cause of the application delivery failure.Figure 2 Instance list
icon next to the instance status to view the cause of the application delivery failure.Figure 2 Instance list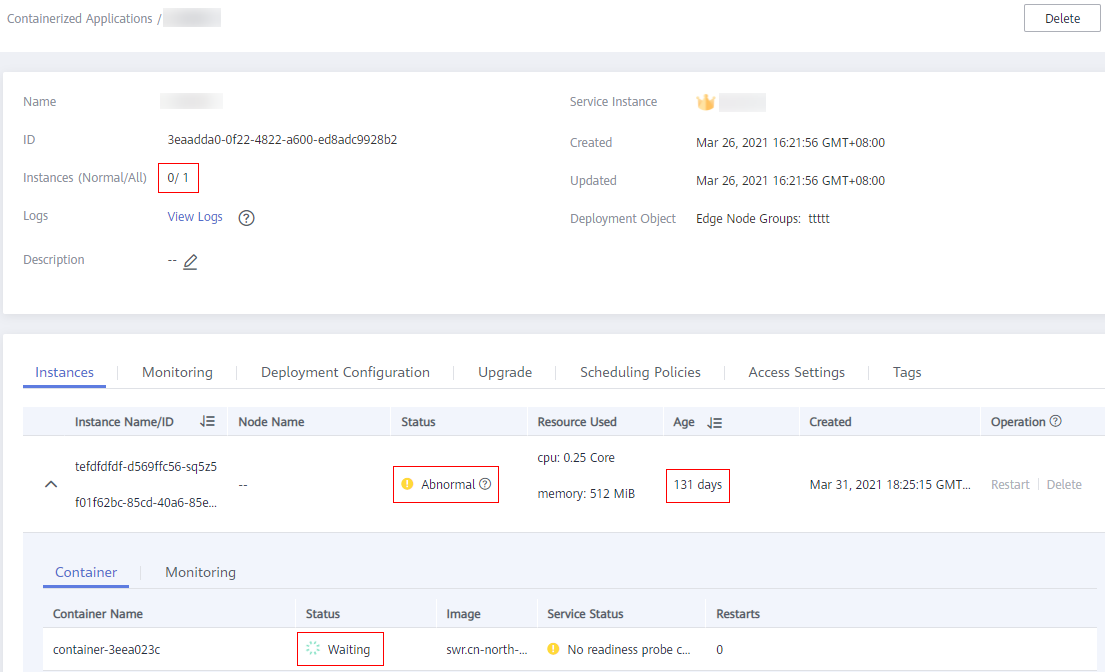
- Check the size of the resources requested by the application.
Check whether the available resources on the edge node meet the resources requested by the application. Ensure that the edge node resources are sufficient.
Figure 3 shows how to check the amount of resources requested by the application.
- Check whether a port conflict occurs. If a port conflict occurs, the application instance cannot be started.
Go to the application details page, click the Access Settings tab, and check whether the port mapping or host network of the specified port is configured for the application.
Figure 4 Access settings
- For a single-instance application:
Set the access mode to Bridged Network, and change the port number to an available port on the current node Alternatively, you can set it to assign ports automatically, and IEF will select an available port for the application.
- For a multi-instance application:
If external access is required for a multi-instance application, you can use the automatic scheduling deployment mode. The application will select a node with an unused port from the edge node group to deploy the instance.
Alternatively, you can set it to assign ports automatically, and IEF will select an available port for the application to avoid port conflicts.
- For a single-instance application:
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






