Combining WAF and HSS to Improve Web Page Tampering Protection
Application Scenarios
Web tampering is a type of cyberattack that exploits vulnerabilities in web applications to tamper with web application content or to insert hidden links. Web tampering attacks are often used to spread malicious information, incite unrest, and steal money.
Links to pornographic or otherwise illegal content may be inserted into normal web pages. Tampered web pages can permanently damage the brand image of your organization.
This topic describes how to use the combination of WAF and HSS to protect dynamic and static web pages from being tampered with.
Solution Architecture and Advantages
WAF examines HTTP/HTTPS requests. If an attacker attempts to tamper with web pages using attacks like SQL injection, WAF can identify and block the attacks in a timely manner, so they cannot sneak into or change anything in the OSs of your web servers.
Even if attacks bypass the first layer of protection, HSS WTP provides multi-level defenses. HSS WTP protects files in the web file directories from any unauthorized access. Only your website administrator can update the website content through the privileged process. Apart from that, HSS WTP also backs up web file directories locally and remotely. Once a file is tampered with, it can be quickly restored with backups. For dynamic web pages such as applications on web servers, HSS WTP uses Runtime Application Self-Protection (RASP) to monitor application access. It can detect tampering on dynamic data such as databases and prevent attackers from using applications to tamper with web pages in real time.
With HSS and WAF in place, you can stop worrying about web page tampering.
Resource and Cost Planning
|
Resource |
Description |
Monthly Fee |
|---|---|---|
|
Host Security Service (HSS) |
|
For details about billing rules, see Billing Description. |
|
Web Application Firewall |
Cloud - Standard edition
|
For details about pricing rules, see Billing Description. |
Step 1: Configure a Web Tamper Protection Rule in WAF
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner of the management console and select a region or project. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Web Application Firewall under Security & Compliance.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Web Application Firewall under Security & Compliance. - In the navigation pane on the left, click Policies.
- If you have enabled the enterprise project function, in the upper part of the navigation pane on the left, select your enterprise project from the Filter by enterprise project drop-down list. Then, WAF will display the related security data in the enterprise project on the page.
- Click the name of the target policy to go to the protection configuration page.
- Click the Web Tamper Protection configuration area and toggle it on or off if needed.
 : enabled.
: enabled. : disabled.
: disabled.
- In the upper left corner above the Web Tamper Protection rule list, click Add Rule.
- In the displayed dialog box, specify the parameters by referring to Table 3.
Figure 1 Adding a web tamper protection rule

Table 3 Rule parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Domain Name
Domain name of the website to be protected
www.example.com
Path
A part of the URL, not including the domain name
A URL is used to define the address of a web page. The basic URL format is as follows:
Protocol name://Domain name or IP address[:Port]/[Path/.../File name].
For example, if the URL is http://www.example.com/admin, set Path to /admin.
NOTE:- The path does not support regular expressions.
- The path cannot contain two or more consecutive slashes. For example, ///admin. If you enter ///admin, WAF converts /// to /.
/admin
Rule Description
A brief description of the rule. This parameter is optional.
None
- Click OK. You can view the rule in the list of web tamper protection rules.
Step 2: Enable HSS Web Tamper Protection
- Log in to the management console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Server Protection > Web Tamper Protection.
Figure 2 Web tamper protection
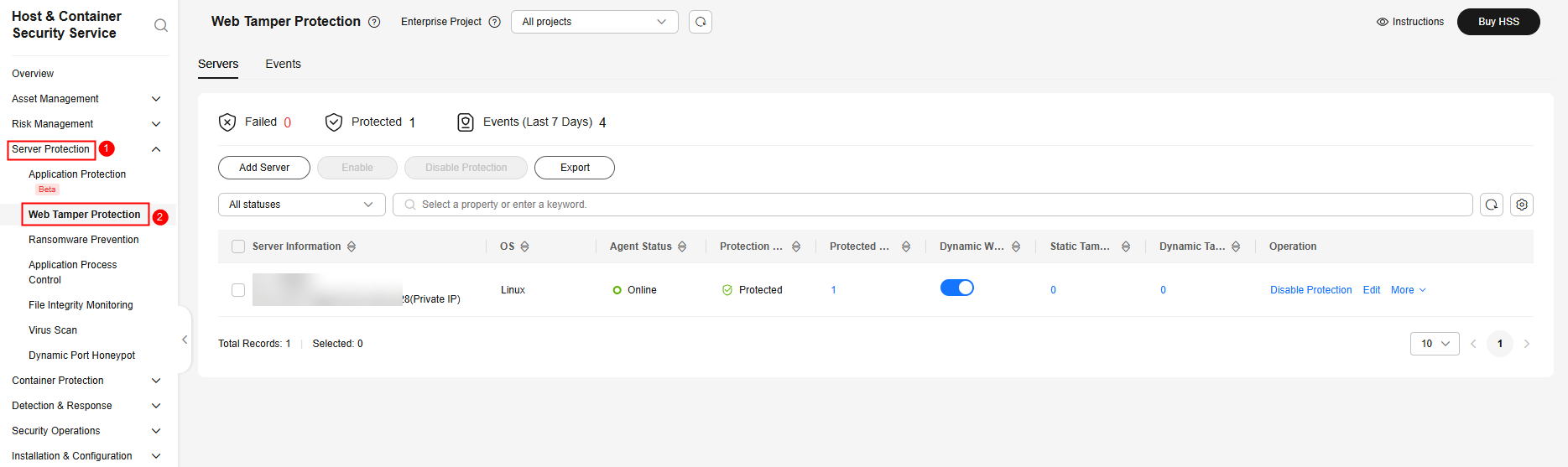
- On the Servers tab, click Add Server. The Add Server page is displayed.
- On the Add Server page, select servers and click Next. For more information, see Table 4.
Figure 3 Selecting servers

Table 4 Parameters for selecting protected servers Parameter
Description
Example Value
OS
Select the OS type of the server to be protected by WTP.
- Linux
- Windows
Linux
Select Servers
Select servers.
You can filter the servers by software type or other attributes.
-
Select Quota
The HSS WTP edition supports two billing modes, yearly/monthly and pay-per-use billing, to meet requirements in different scenarios.
- Yearly/Monthly billing is a prepaid mode in which you pay for the service before using it. Your bill is generated based on the required duration you specify in the order. The longer you use the service, the more discounts you got.
- Pay-per-use is a postpaid billing mode. You pay as you go and just pay for what you use. The HSS usage is calculated by the second but billed every hour. With the pay-per-use billing mode, you can easily adapt to resource requirement changes, reducing the risk of over-provisioning resources or lacking capacity. In this mode, there are no upfront commitments required.
When selecting the yearly/monthly billing mode, you can select a quota or retain the default value Select a quota randomly.
Yearly/Monthly
Agreement
Before enabling WTP, ensure that you have read the Host Security Service Disclaimer.
Select I have read and agree to the Host Security Service Disclaimer.
Selected
- On the Add Server page, configure policies. For more information, see Table 5.
Figure 4 Configuring policies
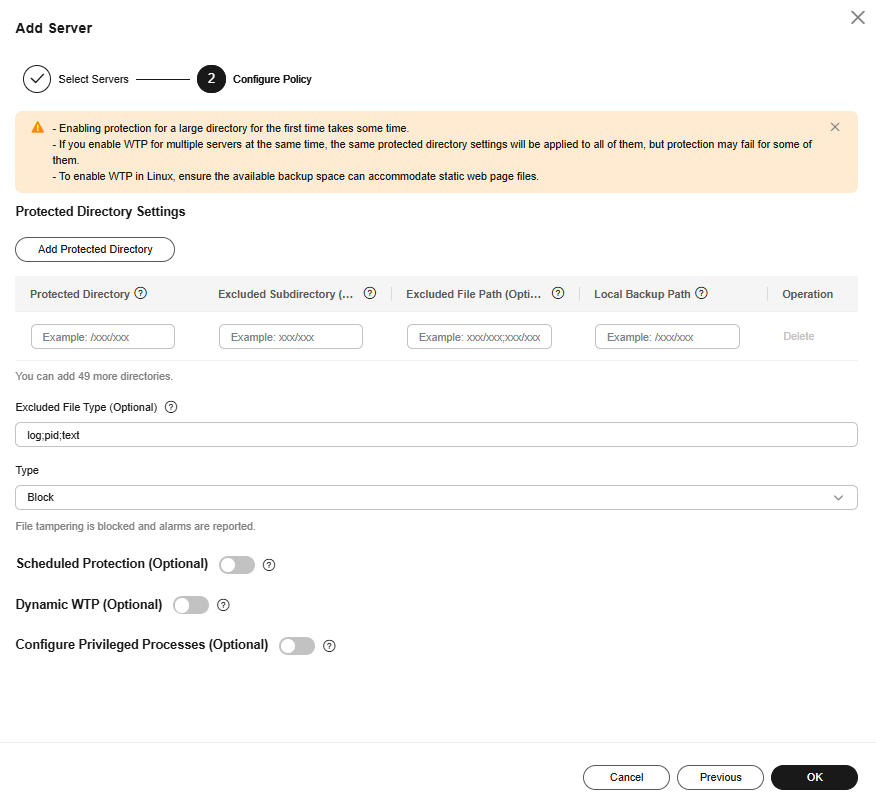
Table 5 Parameters for configuring rules Parameter
Description
Example Value
Protected Directory
WTP supports static and dynamic web page protection. Static WTP protects specified directories by locking files in the web file directory in the drive to prevent attackers from modifying the files.
Therefore, when configuring a protection policy, you need to specify the directories to be protected.
After a directory is protected, the files and folders in the directory will become read-only.
The requirements for adding a protected directory are as follows:
- For Linux,
- It cannot start with a space, end with a slash (/), or contain semi-colons (;). Up to 256 characters are allowed.
- A server can have up to 50 protected directories.
- The folder levels of a protected directory cannot exceed 100.
- The total folders in protected directories cannot exceed 900,000.
- For Windows,
- Up to 256 characters are allowed. The directory name cannot start with a space or end with a backslash (\). It cannot contain the following characters: ;/*?"<>|
- A server can have up to 50 protected directories.
- Linux: /etc/lesuo
- Windows: d:\web
Excluded Subdirectory (Optional)
If a protected directory contains subdirectories that do not need to be protected, you can exclude the subdirectories.
The requirements for adding a subdirectory are as follows:
- A subdirectory name must be a valid relative path of the protected directory.
- A subdirectory name cannot start or end with a slash (/), and can contain up to 256 characters.
- Up to 10 subdirectories can be added. Use semicolons (;) to separate multiple subdirectories.
- Linux: lesuo/test
- Windows: web\test
Excluded File Path (Optional)
This item is available only for Linux servers.
If a protected directory contains files that do not need to be protected, exclude the files.
The requirements for adding excluded file paths are as follows:
- A file path must be a valid relative path of the protected directory.
- A file path cannot start or end with a slash (/), and can contain up to 256 characters.
- Up to 50 file paths can be added. Use semicolons (;) to separate multiple file paths.
lesuo/data;lesuo/ma.txt
Local Backup Path
This item is available only for Linux servers.
Set a local backup path for a protected directory. After WTP is enabled, files in the protected directory are automatically backed up to the local backup path. Once the system detects that a file in the protected directory is tampered with, it immediately uses the local backup to restore the tampered file.
The requirements for adding local backup paths are as follows:
- A local backup path cannot contain semicolons (;), start with a space, or end with a slash (/). Up to 256 characters are allowed.
- Key system directories are a main attack target and cannot be used as backup paths, including but not limited to /etc/, /bin/, /usr/bin/, /var/spool/, /usr/sbin/, /sbin/, /usr/lib/, /lib/, /lib64/, /usr/lib64/, and their subdirectories.
Local backup rule description:
- The local backup path must be valid and cannot overlap with the protected directory path.
- Excluded subdirectories and types of files are not backed up.
- Generally, the backup completes within 10 minutes. The actual duration depends on the size of files in the protected directory.
/etc/backup
Excluded File Type
If a protected directory contains files of certain types that do not need to be protected, exclude these file types, for example, logs. You can exclude any type of files.
To record the running status of servers in real time, exclude the log files in the protected directory. You can set high permission requirements for log read and write, so that attackers cannot view or tamper with log files.
log
Type
Action taken when file tampering is detected.
- Alarm: Only alarms are reported.
- Block: An alarm is reported, and the file is restored to the status before being tampered with.
Block
Scheduled Protection (Optional)
You can schedule when to disable static WTP. In the unprotected period, you can modify, update, or release web pages.
Click
 to enable scheduled protection and configure the following parameters:
to enable scheduled protection and configure the following parameters:- Unprotected Time Range
A time range when WTP is disabled within a day, for example, 10:05 to 15:35.
Requirements:
- A time range must be at least 5 minutes.
- Time ranges (except for those starting at 00:00 or ending at 23:59) cannot overlap and must have at least a 5-minute interval.
- All time ranges are subject to the system time of the server.
- Unprotected Days of a Week
Static WTP is automatically disabled on specified days of a week, for example, Wednesday and Thursday.
 , 10:05-15:35, Wednesday
, 10:05-15:35, WednesdayDynamic WTP (Optional)
Dynamic WTP is mainly used to protect Tomcat applications on Linux. It can detect and prevent tampering with dynamic data, such as database data, in real time during application running.
Currently, dynamic WTP can protect Tomcat applications using JDK 8, JDK 11, and JDK 17.
To enable dynamic WTP, click
 and enter a complete Tomcat bin directory path, for example, /usr/workspace/apache-tomcat-8.5.15/bin. The system presets the setenv.sh script in the bin directory to configure the startup parameters of the anti-tamper program.
and enter a complete Tomcat bin directory path, for example, /usr/workspace/apache-tomcat-8.5.15/bin. The system presets the setenv.sh script in the bin directory to configure the startup parameters of the anti-tamper program. , /usr/workspace/apache-tomcat-8.5.15/bin
, /usr/workspace/apache-tomcat-8.5.15/binConfigure Privileged Processes (Optional)
A privileged process is a process authorized to modify a protected directory.
After WTP is enabled, all files in the protected directory will be set to read-only and cannot be modified. If anyone attempts to modify a file or website, the system will automatically restore it to the status before the modification.
You can add privileged processes and use them to modify the files in protected directories or update websites. Ensure the specified privileged processes, which are authorized to access protected directories, are secure and reliable.
This feature is compatible with Linux and Windows. For Linux, only the distributions using kernel versions 5.10 or later are supported.
Click
 to enable the privileged processes and configure the following parameters:
to enable the privileged processes and configure the following parameters:- Process File Path
Set one or multiple complete file paths of privileged processes. Put each privileged process file path on a separate line. Up to 10 privileged processes are allowed.
- Trust Subprocess
If Trust Subprocess is enabled, HSS will trust all the subprocesses up to five levels deep in the subdirectories of specified directories, and allow the subprocesses to modify protected directories, and allow the subprocesses to modify protected directories.
- Linux: /Path/Software.type
- Windows: C:\Path\Software.type
- For Linux,
- After the policy is configured, click OK.
- On the Servers tab, check the static and dynamic WTP status of the server.
The Protected status indicates protection has been enabled. After dynamic WTP is enabled, restart Tomcat to apply the settings.

- Before disabling WTP, perform a comprehensive detection on the server, handle known risks, and record operation information to prevent O&M errors and attacks on the server.
- If WTP is disabled, web applications are more likely to be tampered with. Therefore, you need to delete important data on the server, stop important services on the server, and disconnect the server from the external network in a timely manner to avoid unnecessary losses caused by attacks on the server.
- After you or disable WTP, files in the protected directory are no longer protected. You are advised to process files in the protected directory before performing these operations.
- If you find some files missing after disabling WTP, search for them in the local or remote backup path.
- The premium edition will be disabled when you disable WTP.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





