Creating an SFS or SFS Turbo File System
Scalable File Service (SFS) is a network attached storage (NAS) service that provides scalable, high-performance file storage. With the service, shared file access can be achieved among multiple Elastic Cloud Servers (ECSs), Bare Metal Servers (BMSs), and containers created on Cloud Container Engine (CCE). For more information about SFS, see SFS Overview.
In the SAP HANA system, if the backup volume is provided by SFS, you can create an SFS file system to provide a shared path for SAP HANA ECSs.
Two SFS file systems are created and attached to the active and standby SAP HANA nodes, respectively. You need to create one SFS file system and mount it to /sapcd on the active and standby SAP S/4HANA nodes, and create two SFS Turbo file systems and respectively mount them to /sapmnt and /usr/sap/trans on the active and standby SAP S/4HANA nodes. For the details about the parameter configurations for creating SFS and SFS Turbo file systems, see Getting Started with SFS.
Procedure
- Click
 in the navigation pane on the left, and choose Scalable File Service under Storage.
in the navigation pane on the left, and choose Scalable File Service under Storage.
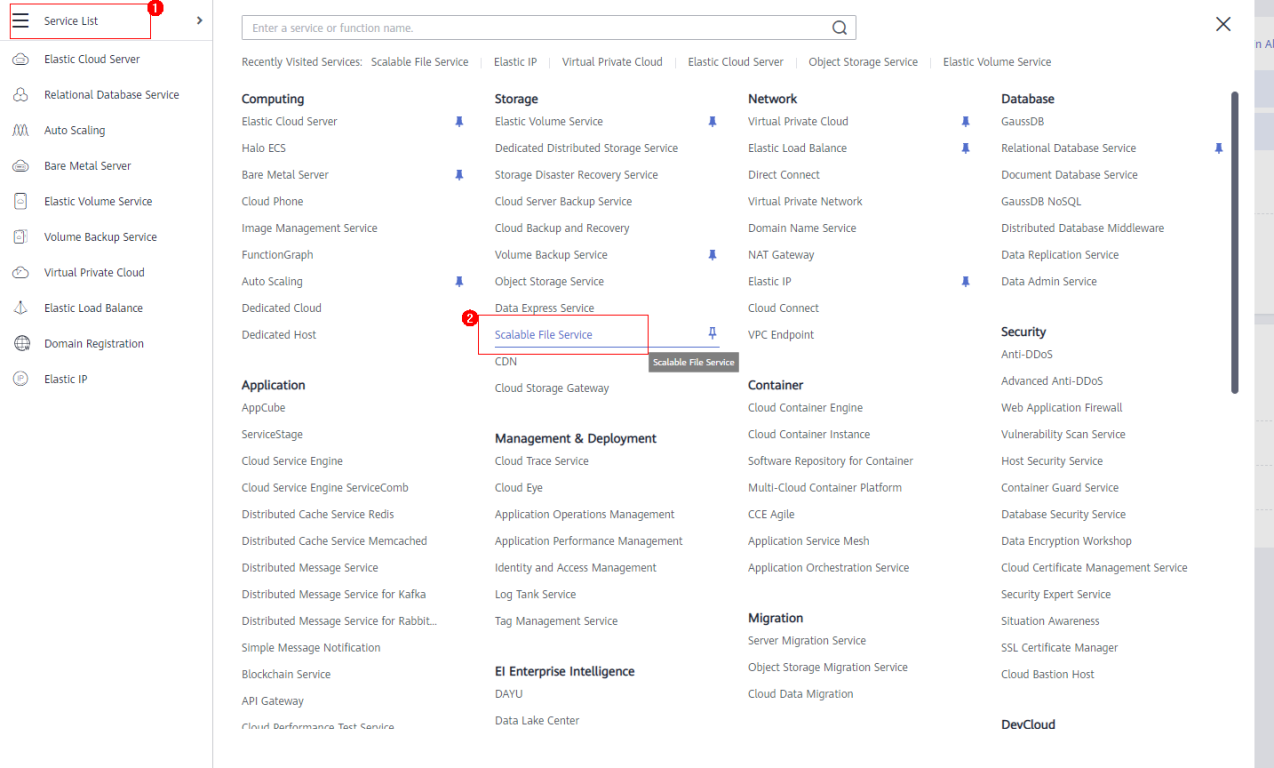
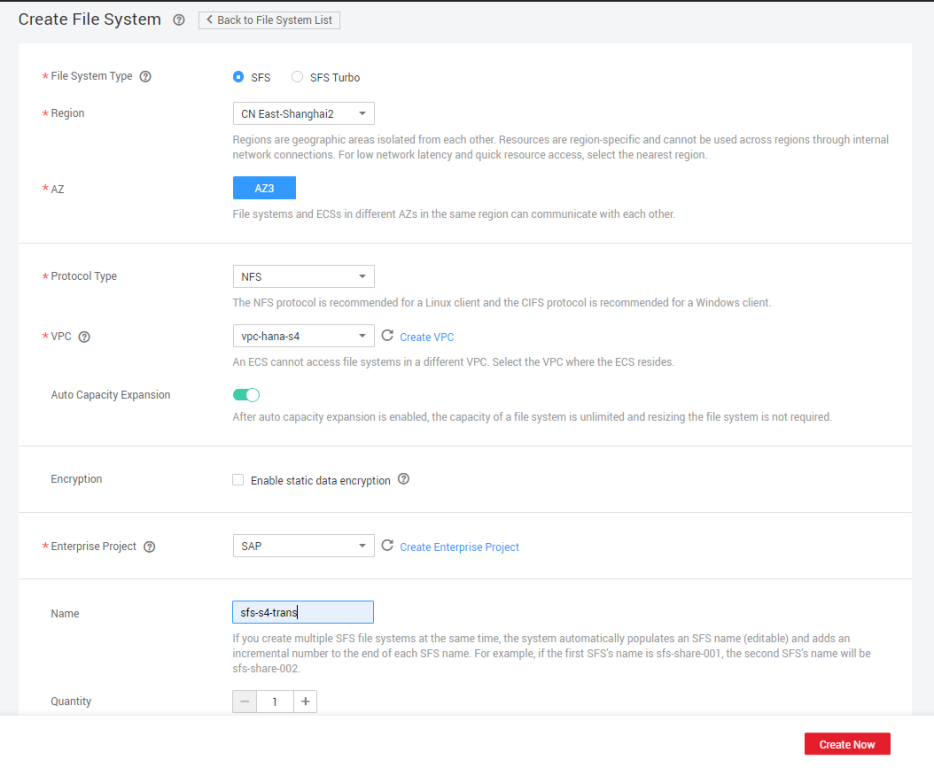
- Click Create File System. Set required parameters on the displayed page based on Table 1.
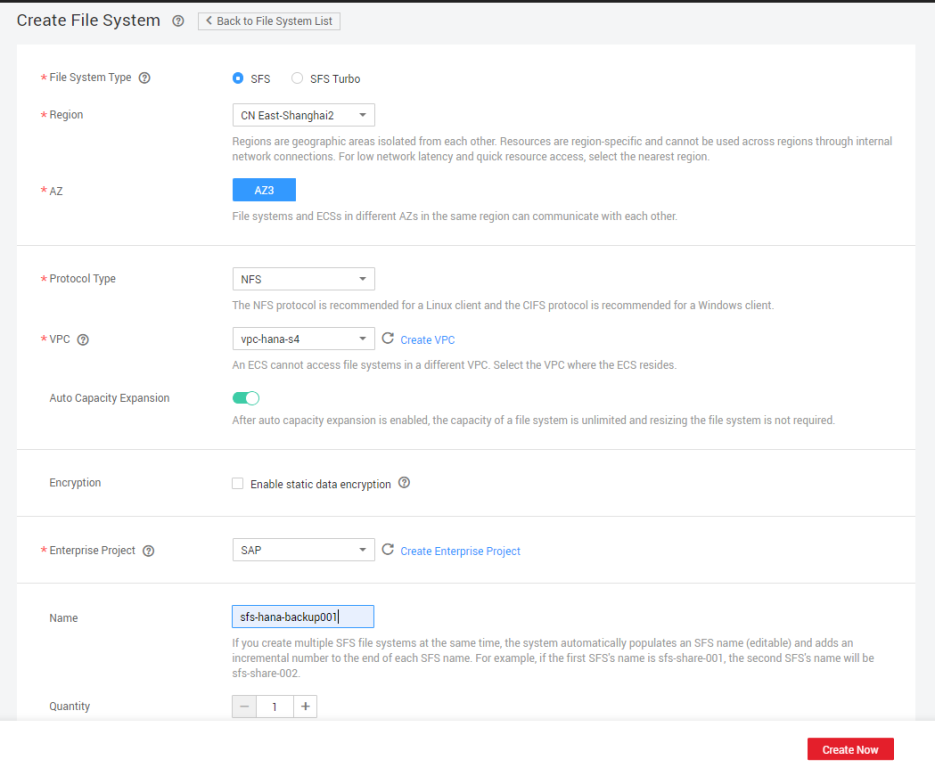
Table 1 Parameter description Parameter
Description
File System Type
Select the type of the file system to be created.
Region
Select the target region.
AZ
Specifies the AZ where the file system is located. Select your desired AZ.
Protocol Type
Specifies the protocol type. Select NFS.
VPC
Select vpc-hana-s4 for SAP HANA.
Auto Capacity Expansion
This function is enabled by default. When it is enabled, you do not need to manually adjust the capacity of the file system. You can determine whether to enable the function based on the site requirements.
Maximum Capacity
This parameter shows after Automatic Capacity Expansion is disabled. Specifies the maximum capacity of a single file system.
Encryption
Optional.
Specifies whether a file system is encrypted. You can create a file system that is encrypted or not, but you cannot change the encryption settings of an existing file system. If you select Enable static data encryption, follow the instructions described in Getting Started with SFS.
Enterprise Project
Select the target project.
Name
Specifies the file system name.
Quantity
Select the quantity based on the site requirements.
- Click Create Now. Confirm the file system information and click Submit on the displayed page. You can locate the created file system using its name in the file system list. In the Shared Path column, query the shared path.
- Repeat 2 and 3 to create other SFS file systems.
- Create an SFS file system sfs-hana-backup002 and mount it to the /hana/backup directory on the standby SAP HANA node.

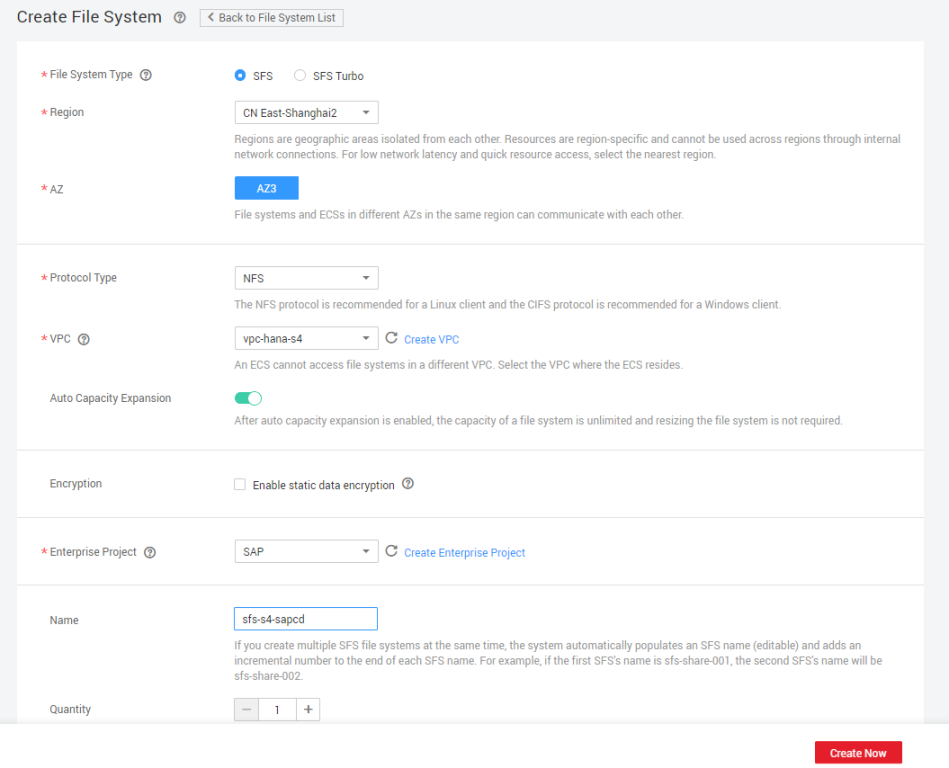
- Create a 40 GB SFS Turbo file system sfs-turbo-s4-sapmnt and mount it to the /sapmnt directory on the active and standby SAP S/4HANA nodes.
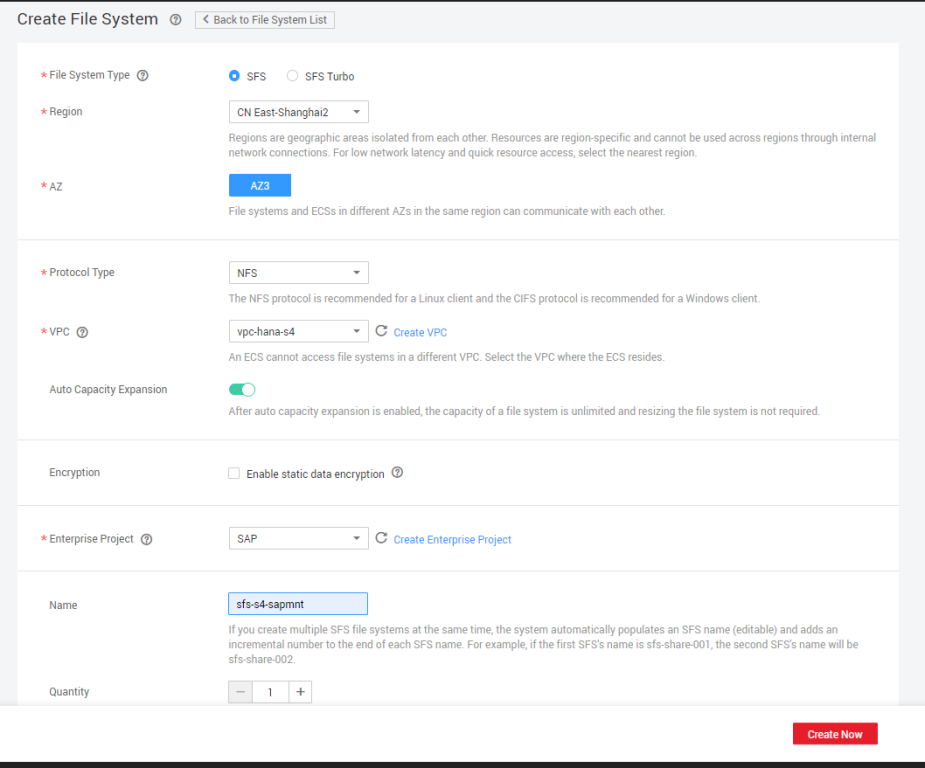
- Create an SFS file system sfs-s4-sapcd and mount it to the /sapcd directory on the active and standby SAP S/4HANA nodes.
- Create a 60 GB SFS Turbo file system sfs-turbo-s4-trans and mount it to the /usr/sap/trans directory on the active and standby SAP S/4HANA nodes.
- Create an SFS file system sfs-hana-backup002 and mount it to the /hana/backup directory on the standby SAP HANA node.
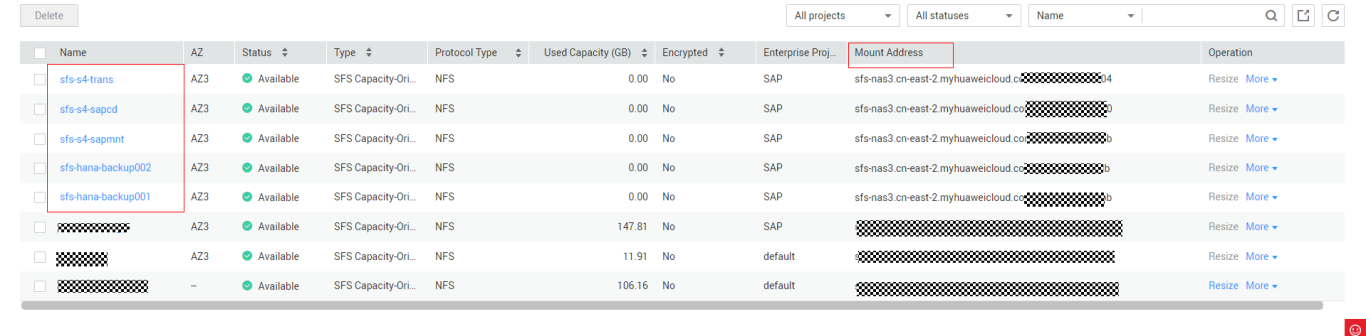
- The following figure shows the details about the created SFS file systems.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





