MRS Cluster Metadata Storage in an External Data Source
Metadata is data that describes other data, providing details such as its structure, storage location, and access permissions. In an MRS cluster, component metadata is stored by default within the local GaussDB database of the cluster. Deleting a cluster will also delete its metadata. To retain the metadata, you need to manually save it in advance.
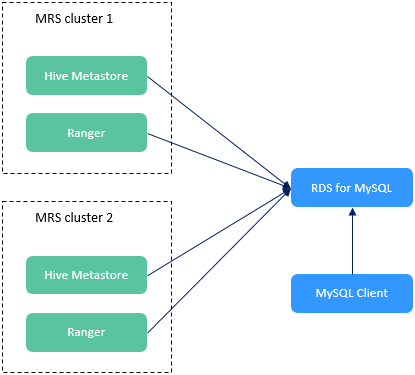
MRS provides the data connection management function. This function allows metadata of components (such as Hive and Ranger) to be stored in external data sources, decoupling the data storage layer (such as HDFS) from compute engines (such as Spark and Flink).
For example, Hive metadata can be stored in an external relational database and will not be deleted when the current MRS cluster is deleted. In addition, multiple MRS clusters can share the same metadata.
External Data Connections Supported by MRS
|
Data Connection Type |
Description |
Applicable Version |
Supported Engine |
|---|---|---|---|
|
RDS PostgreSQL database |
RDS for PostgreSQL is designed for enterprise online transactional processing (OLTP) scenarios requiring complex SQL processing. It supports NoSQL data types (such as JSON, XML, and HStore) and geographic information system (GIS) data types, and is renowned for its reliability and data integrity. It is suitable for internet websites, location-based applications, and complex data object processing. For more information, see What Is RDS for PostgreSQL? |
|
Hive |
|
RDS MySQL database |
RDS for MySQL is fully compatible with native MySQL, combining stability, reliability, and high performance. It features intelligent operations and maintenance, robust security, out-of-the-box usability, and automatic scaling. For more information, see What Is RDS for MySQL? |
|
|
|
GaussDB(for MySQL) |
GaussDB is a distributed relational database developed by Huawei. It supports distributed transactions and intra-city deployment across AZs for zero data loss, storage for petabytes of data, and scale-up to more than 1,000 nodes. For more information, see What Is GaussDB? |
MRS cluster versions: MRS 3.1.2-LTS.3, MRS 3.1.5, and MRS 3.3.0-LTS |
|
|
LakeFormation |
LakeFormation is a one-stop enterprise-class data lake and warehouse construction service. It provides APIs and a GUI for unified management of data lake metadata, and is compatible with Hive metadata and Ranger permission models. LakeFormation can connect to multiple compute engines and big data cloud services seamlessly to ensure quick building and easy operations of data lakes and unleash rich value of service data. LakeFormation is a serverless service that uses underlying resources to implement cross-AZ deployment, high reliability, auto scaling, unified metadata management, association between metadata and file directories, and interconnection with multiple compute engines. For more information, see What Is LakeFormation? |
MRS cluster version: MRS 3.3.0-LTS or later |
|
Notes and Constraints
- When Hive metadata is switched between different clusters, MRS synchronizes only the permissions in the metadata database of the Hive component. The permission model on MRS is maintained on MRS Manager. Therefore, when Hive metadata is switched between clusters, the permissions of users or user groups cannot be automatically synchronized to MRS Manager of another cluster.
- The VPC and subnet of the service for which an external data connection will be created must be the same as those of the MRS cluster to be interconnected.
- The RDS database instance interconnected with the MRS cluster cannot be deleted. Otherwise, the cluster will be abnormal.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





