Creating a Custom Graph
- Log in to the GES console and click Create Graph in the upper right corner of the Overview page.
- Select the Region where the cluster works from the drop-down list in the upper left corner of the page.
- On the Create Graph page, click the Customize Graph tab and set the following parameters:
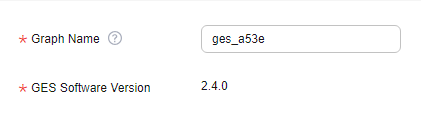
- In the Configure step, set the graph name and software version.
Figure 1 Graph name and software version
Parameter
Description
Graph Name
You can set a name or use the default name. After a graph is created, its name cannot be changed.
The graph name must:
- Contain 4 to 50 characters and start with a letter.
- Be case-insensitive.
- Contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_).
GES Software Version
The system uses the latest version by default, and only the default version is available.
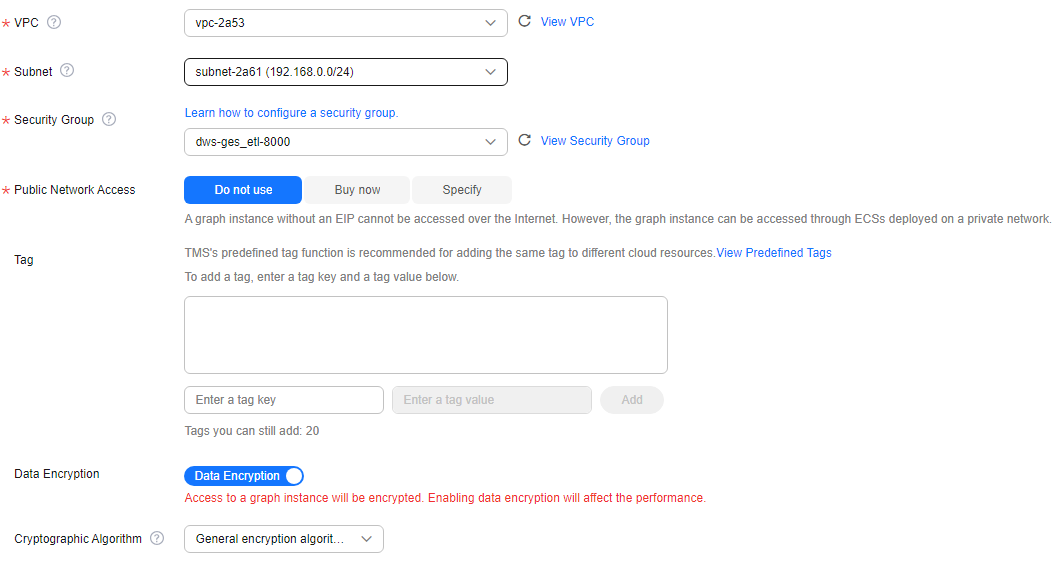
- Set network parameters, including VPC, Subnet, Security Group, Enterprise Project, and Public Network Access.
Figure 2 Network information
Parameter
Description
VPC
A VPC is a secure, isolated, and logical network environment.
Select the VPC for which you want to create the graph and click View VPC to view the name and ID of the VPC.
NOTE:If your account has VPCs, a VPC will be automatically selected. You can change it as needed. If no VPC is available, you need to create a VPC. After the VPC is created, it will be automatically selected.
Subnet
A subnet provides dedicated network resources that are logically isolated from other networks for network security.
Select the subnet for which you want to create the graph to enter the VPC and view the name and ID of the subnet.
Security Group
A security group implements access control for ECSs that have the same security protection requirements in a VPC.- Click Learn how to configure a security group. to get instructions.
- Click View Security Group to learn security group details.
Public Network Access
The public network access to the graph. Set this parameter as you need.
Do not use: A graph instance without an elastic IP (EIP) cannot be accessed over the Internet. However, the graph instance can be accessed through ECSs deployed on a private network.
Buy now: GES automatically allocates an EIP with exclusive bandwidth to the graph instance so that the graph instance can be accessed over the Internet using the EIP. In addition, GES uses the tenant permission to automatically create an agency with the prefix of ges_agency_default in the project to support EIP binding.
Specify: Select an EIP to allow the graph instance to be accessed over the Internet.
Click Create EIP to access the VPC management console and create an EIP.
Enterprise Project
Centrally manages cloud resources and members by project.
Click Create Enterprise Project to go to the Enterprise Project Management page.
Tag
Tags for a resource. Enter a tag key and value, and click Add to add the tag.
You can view the added tag in the graph details and search for graphs by tag on the Graph Management page.
Figure 3 Viewing tag details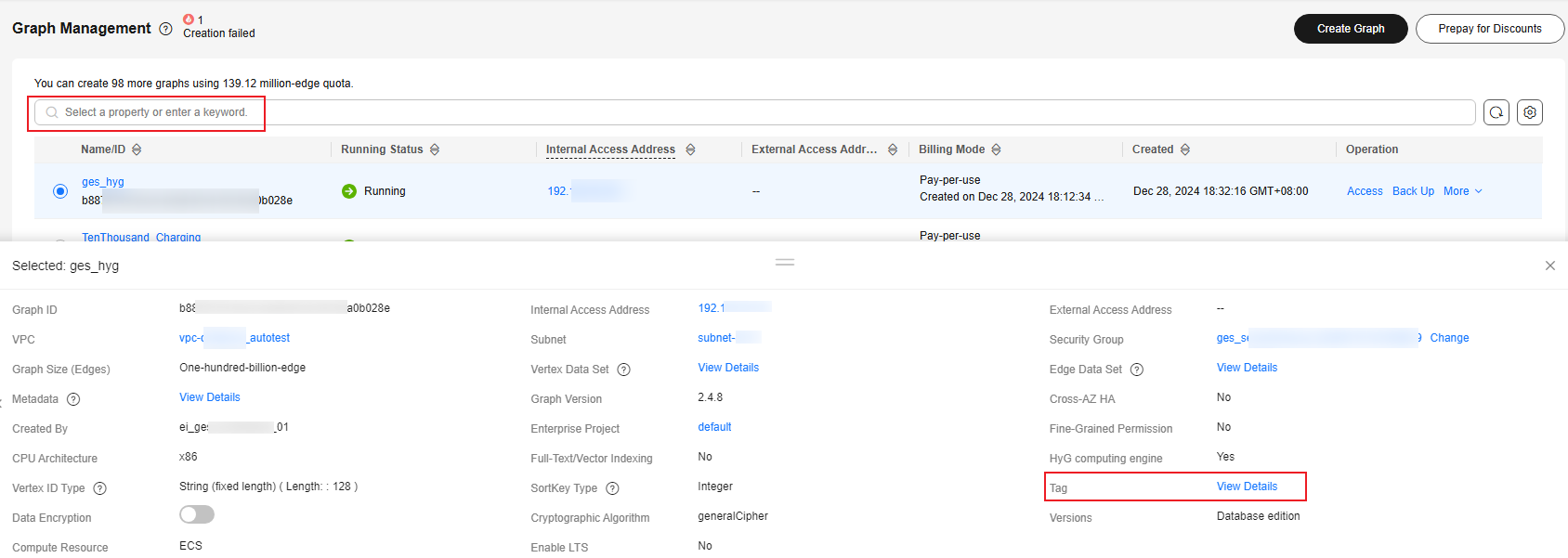 NOTE:
NOTE:It is recommended that you use TMS's predefined tag function to add the same tag to different cloud resources.
Security Mode
If you enable the security mode, communications will be encrypted when you access a graph instance, and only HTTPS can be used when you call APIs. This function affects GES performance.
Cryptographic Algorithm
Available values are as follows:- General cryptographic algorithms (SM series cryptographic algorithms not supported) are used by all components to store and transmit sensitive data. These algorithms that do not have special requirements.
- SM series cryptographic algorithms (compatible with the international general algorithm) are supported. Sensitive data of all components is stored using this algorithm. The SM series cryptographic algorithms and international algorithms can be used for data transmission.
- Set graph parameters.
Figure 4 Graph parameters
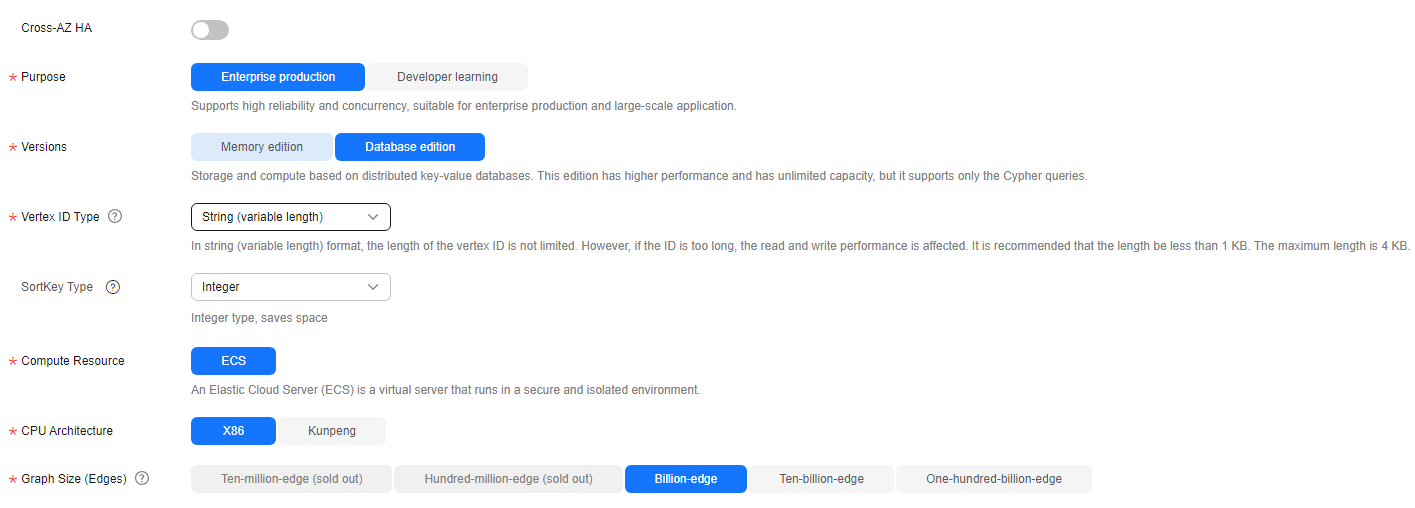
Parameter
Description
Cross-AZ HA
Whether to support cross-AZ cluster.
If this function is enabled, graph instances are distributed in different AZs to enhance reliability.
Purpose
Purpose of the graph to be created.
Enterprise production: High reliability and concurrency are supported, suitable for production and large-scale applications.
Developer learning: A complete function experience is offered, suitable for developer learning.
Versions
GES editions.
- Memory edition: The capacity is limited and a maximum of 10 billion edges are supported. Storage and compute based on memory storage. This edition is preset with a variety of algorithms, and Gremlin and Cypher query languages are supported.
- Database edition: The storage capacity is unlimited. Storage and compute based on distributed key-value databases. This edition has higher performance and has unlimited capacity, but it supports only the Cypher queries.
Vertex ID Type (This parameter is available only when you choose the database edition.)
The options include String (fixed length), String (variable length), and Hash.
- String (fixed length): Vertex IDs are used for internal storage and compute. Specify the length limit. If the IDs are too long, the query performance can be reduced. Specify the length limit based on your dataset vertex IDs. If you cannot determine the maximum length, set the ID type to hash.
- String (variable length): The length of the vertex IDs written by the user is not limited. However, if the IDs are too long, the read and write performance is affected. It is recommended that the length be within 1 KB bytes, with a maximum of 4 KB bytes.
- Hash: Vertex IDs are converted into hash code for storage and compute. There is no limit on the ID length. However, there is an extremely low probability, approximately 10^(-43), that the vertex IDs will conflict.
NOTE:If you cannot determine the maximum length of a vertex ID, set this parameter to Hash.
SortKey Type (This parameter is available only when you choose the database edition.)
Different SortKey values are configured to distinguish duplicate edges (edges with the same source vertex, end vertex, and label). The options include:
- Integer: The value is an integer, which saves space.
- String (byte length less than or equal to 40)
- String (variable length): The length is not limited. However, if the value is too long, the read and write performance is affected. It is recommended that the length be within 1 KB bytes, with a maximum of 2 KB bytes.
Compute Resource
Type of compute resources.
An elastic cloud server (ECS) is a computer system that has complete hardware, an operating system (OS), and network functions and runs in a secure, isolated environment.
CPU Architecture
Currently, GES supports x86 and Kunpeng.
Graph Size (Edges)
Available options based on your resource quota.
Different graph specifications are displayed for Enterprise production and Developer learning.
- Development learning: Currently, there is only Ten-thousand-edge graphs are available for this purpose, regardless of the edition.
- Enterprise production: The specifications vary depending on the edition.
- Memory edition: The options are Million-edge, Ten-million-edge, Hundred-million-edge, Billion-edge, Billion-edge-pro, and Ten-billion-edge.
- Database edition: The options are Billion-edge, Ten-billion-edge, and Hundred-billion-edge.
NOTE:Graph size, which is based on the number of edges. The value is not accurate. If there are a large number of vertices and properties, you are advised to apply for graphs with a larger size.
- Advanced Settings: Set this parameter to Default or Custom.
- Default: Use the default values.
- Custom:
- When you set Versions to Memory edition, you need to set the following custom parameters: Fine-Grained Permission.
Figure 5 Advanced settings for the memory edition
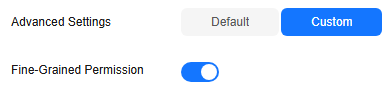
Parameter
Description
Fine-Grained Permission
Traverse, read, and write permissions can be set for specific properties of a label.
After enabling this function, you must create a graph permission policy, set up a user group, and assign the policy to that group. Users in the group will then be able to access the graph data.
- If you choose the database edition, you can enable or disable HyG computing engine and Fine-Grained Permission.
Figure 6 Advanced settings for the database edition
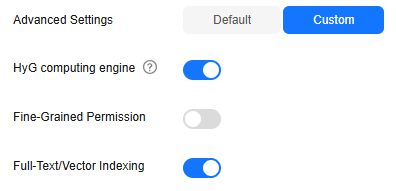
Parameter
Description
HyG computing engine
HyG is a high-performance distributed graph computing framework that supports many graph analysis algorithms. HyG engine is suitable for complex graph analysis.
Fine-Grained Permission
Traverse, read, and write permissions can be set for specific properties of a label.
After enabling this function, you must create a graph permission policy, set up a user group, and assign the policy to that group. Users in the group will then be able to access the graph data.
Full-Text/Vector Indexing
After enabling this function, the created graph supports both full-text indexing and vector indexing.
Either fine-grained permission control or full-text/vector indexing can be enabled.
- When you set Versions to Memory edition, you need to set the following custom parameters: Fine-Grained Permission.
- In the Configure step, set the graph name and software version.
- Click Next. The Confirm page is displayed.
- Confirm the information and click Submit to create the graph.
- Once the submission is successful, the Finish tab page is displayed. You can click Back to Instance to view the status and result of the created graph.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





