Deterministic Operations
Deterministic operations is a set of O&M concepts, methodologies, and best practices developed by Huawei Cloud based on years of cloud service O&M experience. It helps enterprises efficiently operate and maintain self-built and purchased service systems on the cloud, ensuring that these service systems can run continuously, efficiently, and stably on the cloud.
Deterministic operations is intended to create an O&M management system that makes risks avoidable, controllable, and manageable. It aims to minimize fault probability and strives for zero faults through high-quality product development and rigorous O&M processes and regulations. This also involves technical means to manage possible faults, ensuring that the occurrence interval, impact scope, and recovery time are avoidable, controllable, and manageable. In a word, the "uncertainty" brought by digital transformation and rapid service development can be managed through O&M.
Deterministic operations can help enterprises improve resource utilization through proper resource planning, allocation, and scheduling. In addition, deterministic operations can use automated, intelligent methods to help enterprises improve O&M efficiency, reduce O&M costs, and save a large number of resources.
Deterministic operations is a comprehensive system that involves quality culture, high-availability (HA) architecture, dynamic risk governance, and intelligent O&M tools, as shown in the following figure.
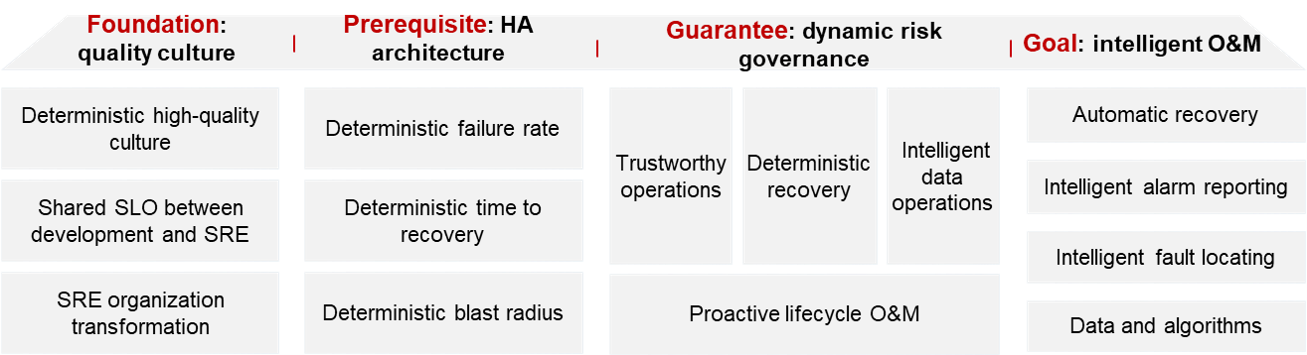
- Quality culture: the foundation
A quality culture is the cornerstone of deterministic operations. It can be a powerful tool to motivate team members to take responsibility for providing standardized and refined O&M. These are some best practices for building a high-quality culture:
- Emphasize quality from the top down and make it a core value.
- Establish shared quality goals and methods for R&D and O&M teams.
- Transform the O&M team and continuously improve their capabilities. Use software engineering methods to solve problems and move from reactive to proactive approaches.
- HA architecture: the prerequisite
An HA architecture is the prerequisite for deterministic operations. By designing and deploying a thoughtful architecture, you can minimize system failures, recover faster, and mitigate their impacts. To achieve this, you need to:
- Target at SLOs, design the architecture using scientific methods, and manage the selection and implementation time.
- Assign O&M teams rights and responsibilities during product planning, design, and launch, and set restrictions on the development and commercial-use plans to ensure the implementation of HA requirements.
- During O&M, verify the HA design as scheduled to ensure that the system meets the HA requirements.
- Dynamic risk control: the guarantee
Dynamic risk governance is crucial to responding to uncertainty and sudden events. It is essentially a process of identifying changes, fault modes, and service data to support proactive O&M throughout the lifecycle.
- For managing the risks involved in change jobs, you need comprehensive abilities, including creating version release architectures, managing account permissions, and automating changes.
- For managing known and unknown faults, you need to use scientific methods to create a fault mode library and develop rapid recovery capabilities. This involves contingency plans to quickly respond to sudden events and regular drills and reviews to verify the architecture's availability and the team's emergency response capabilities.
- Intelligent operations of service runtime data is essential for continuous improvement. A real-time data collection and operations system is required to support decision-making.
- Intelligent O&M: the goal
Intelligent O&M tools can help improve O&M efficiency and quality and reduce labor costs. Especially in the AI era, you can manage and maintain systems more efficiently by using automation and intelligence technologies.
- Select appropriate tools and technologies to ensure that they match service requirements and technology stacks, such as automatic deployment, fault prediction, and intelligent demarcation and locating.
- Integrate the tools into existing systems, and customize and optimize the tools to meet specific O&M requirements.
- Leverage new technologies to continuously update and upgrade intelligent O&M tools.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





