C#
Scenarios
To use C# to sign backend requests, obtain the C# SDK, import the project, and verify the backend signature by referring to the example provided in this section.
The C# SDK supports only HMAC backend service signatures.
Prerequisites
- A signature key has been created on the ROMA Connect console and bound to an API. For details, see Configuring Signature Verification for Backend Services.
- You have obtained the signature key and secret. For details, see Preparations.
- You have installed the C# development environment. For details, see Preparations.
Obtaining the SDK
Old version: Log in to the ROMA Connect console, choose API Connect > API Management > Signature Keys, and download the SDK.
New version: Log in to the ROMA Connect console, choose API Connect > Credentials > SDKs, and download the SDK.
Opening the Sample Project
Double-click csharp.sln in the SDK package to open the project. The project contains the following:
- apigateway-signature: Shared library that implements the signature algorithm. It can be used in the .Net Framework and .Net Core projects.
- backend-signature: Example of a backend signature. Modify the parameters as required. For details about the sample code, see Backend Signature Verification Example.
- sdk-request: Example of invoking the signature algorithm.
Backend Signature Verification Example
- This example demonstrates how to write an ASP.Net Core–based server as the backend of an API and implement an IAuthorizationFilter to verify the signature of requests sent from APIC.
- Signature information is added to requests sent to access the backend of an API only after a signature key is bound to the API.
- Write a controller that provides the GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE interfaces, and add the ApigatewaySignatureFilter attribute.
// ValuesController.cs namespace backend_signature.Controllers { [Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] [ApigatewaySignatureFilter] public class ValuesController : ControllerBase { // GET api/values [HttpGet] public ActionResult<IEnumerable<string>> Get() { return new string[] { "value1", "value2" }; } // POST api/values [HttpPost] public void Post([FromBody] string value) { } // PUT api/values/5 [HttpPut("{id}")] public void Put(int id, [FromBody] string value) { } // DELETE api/values/5 [HttpDelete("{id}")] public void Delete(int id) { } } } - Implement ApigatewaySignatureFilter by putting the signature key and secret in a Dictionary.
// ApigatewaySignatureFilter.cs namespace backend_signature.Filters { public class ApigatewaySignatureFilter : Attribute, IAuthorizationFilter { private Dictionary<string, string> secrets = new Dictionary<string, string> { // Directly writing AK/SK in code is risky. For security, encrypt your AK/SK and store them in the configuration file or environment variables. // In this example, the AK/SK are stored in environment variables for identity authentication. Before running this example, set environment variables HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK1, HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK1, and HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK2, HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK2. {Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK1"), Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK1")}, {Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_AK2"), Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("HUAWEICLOUD_SDK_SK2")}, }; public void OnAuthorization(AuthorizationFilterContext context) { //Signature verification code ... } } } - The OnAuthorization function is the signature verification code. The verification process is as follows: Use a regular expression to parse the Authorization header. Obtain the key and signedHeaders.
private Regex authorizationPattern = new Regex("SDK-HMAC-SHA256\\s+Access=([^,]+),\\s?SignedHeaders=([^,]+),\\s?Signature=(\\w+)"); ... string authorization = request.Headers["Authorization"]; if (authorization == null) { context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult(); return; } var matches = authorizationPattern.Matches(authorization); if (matches.Count == 0) { context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult(); return; } var groups = matches[0].Groups; string key = groups[1].Value; string[] signedHeaders = groups[2].Value.Split(';');For example, for Authorization header:
SDK-HMAC-SHA256 Access=signature_key1, SignedHeaders=host;x-sdk-date, Signature=e11adf65a20d1b82c25419b5********8d0ba12fed1ceb13ed00
The parsing result is as follows:
signingKey=signature_key1 signedHeaders=host;x-sdk-date
- Find secret based on key. If key does not exist, the authentication failed.
if (!secrets.ContainsKey(key)) { context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult(); return; } string secret = secrets[key]; - Create an HttpRequest, and add the method, URL, query, and signedHeaders headers to the request. Determine whether the body needs to be set.
The body is read if there is no x-sdk-content-sha256 header with value UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD.
HttpRequest sdkRequest = new HttpRequest(); sdkRequest.method = request.Method; sdkRequest.host = request.Host.Value; sdkRequest.uri = request.Path; Dictionary<string, string> query = new Dictionary<string, string>(); foreach (var pair in request.Query) { query[pair.Key] = pair.Value; } sdkRequest.query = query; WebHeaderCollection headers = new WebHeaderCollection(); string dateHeader = null; bool needBody = true; foreach (var h in signedHeaders) { var value = request.Headers[h]; headers[h] = value; if (h.ToLower() == "x-sdk-date") { dateHeader = value; } if (h.ToLower() == "x-sdk-content-sha256" && value == "UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD") { needBody = false; } } sdkRequest.headers = headers; if (needBody) { request.EnableRewind(); using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream()) { request.Body.CopyTo(ms); sdkRequest.body = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(ms.ToArray()); } request.Body.Position = 0; } - Check whether the signature has expired. Obtain the time from the X-Sdk-Date header, and check whether the difference between this time and the server time is within 15 minutes. If signedHeaders does not contain X-Sdk-Date, the authentication failed.
private const string BasicDateFormat = "yyyyMMddTHHmmssZ"; ... if(dateHeader == null) { context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult(); return; } DateTime t = DateTime.ParseExact(dateHeader, BasicDateFormat, CultureInfo.CurrentCulture); if (Math.Abs((t - DateTime.Now).Minutes) > 15) { context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult(); return; } - Invoke the verify method to verify the signature of the request, and check whether the verification is successful.
Signer signer = new Signer(); signer.Key = key; signer.Secret = secret; if (!signer.Verify(sdkRequest, groups[3].Value)) { context.Result = new UnauthorizedResult(); } - Run the server to verify the code. The following example uses the HTML signature tool in the JavaScript SDK to generate a signature.
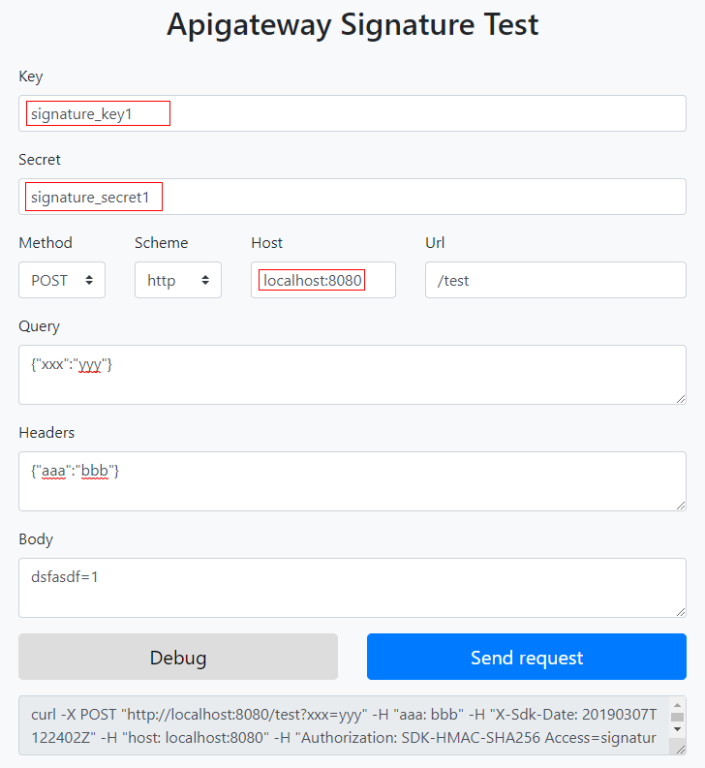
Set the parameters according to the following figure, and click Send request. Copy the generated curl command, execute it in the CLI, and check whether the server returns 200.
If an incorrect key or secret is used, the server returns 401, which means authentication failure.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





