Precautions on Interface Implementation
Support for Thread Security Required
The decode and encode functions must ensure thread security. Therefore, member or static variables cannot be added to cache intermediate data.
Incorrect example: When multiple threads are started at the same time, the status of thread A is set to Failed while the status of thread B is set to Success. As a result, the status is incorrect, and the program running is abnormal.
public class ProtocolAdapter {
private String status;
@Override
public ObjectNode decode(finalbyte[] binaryData) throws Exception {
if (binaryData == null) {
status = "Failed";
return null;
}
ObjectNode node;
...;
status = "Success";
return node;
}
@Override
public byte[] encode(finalObjectNode input) throws Exception {
if ("Failed".equals(status)) {
status = null;
return null;
}
byte[] output;
...;
status = null;
return output;
}
}
Correct example: Encoding and decoding are performed based on the input parameters, and the encoding and decoding library does not process services.
public class ProtocolAdapter {
@Override
public ObjectNode decode(finalbyte[] binaryData) throws Exception {
ObjectNode node;
...;
return node;
}
@Override
public byte[] encode(finalObjectNode input) throws Exception {
byte[] output;
...;
return output;
}
}
Explanation of the mid Field
The IoT platform delivers orders in sequence. However, the IoT platform does not respond to the order execution results in the same sequence as the delivered orders. The MID is used to associate the order execution result response with the delivered order. On the IoT platform, whether the MID is implemented affects the message flow.
When the MID is implemented:
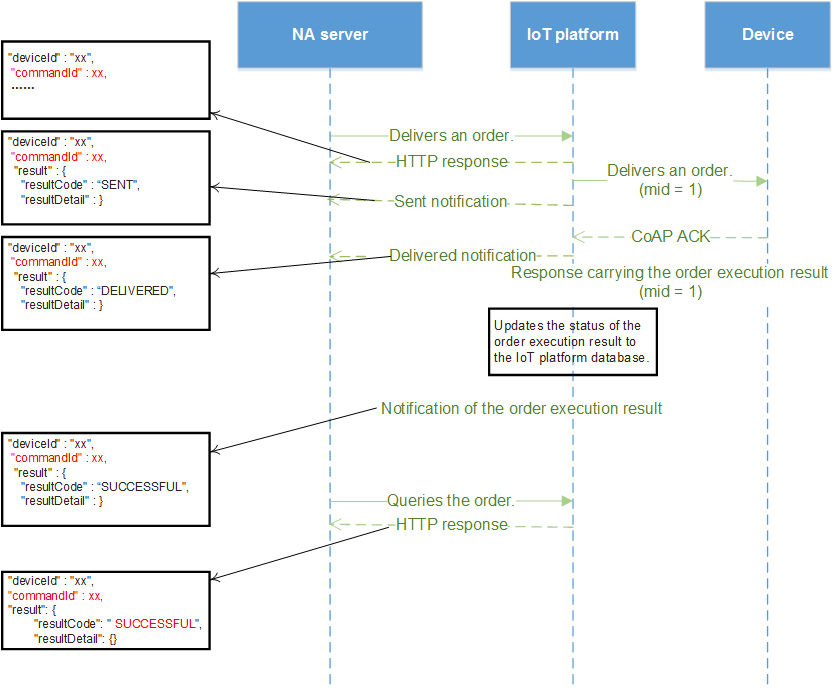
If the MID is implemented and the order execution result is reported successfully:
- The status (SUCCESSFUL/FAILED) in the order execution result is updated to the record of the order in the IoT platform database.
- The order execution result notification sent by the IoT platform to the NA server contains commandId.
- The query result of the NA server indicates that the status of the order is SUCCESSFUL/FAILED.
When the MID is not implemented:
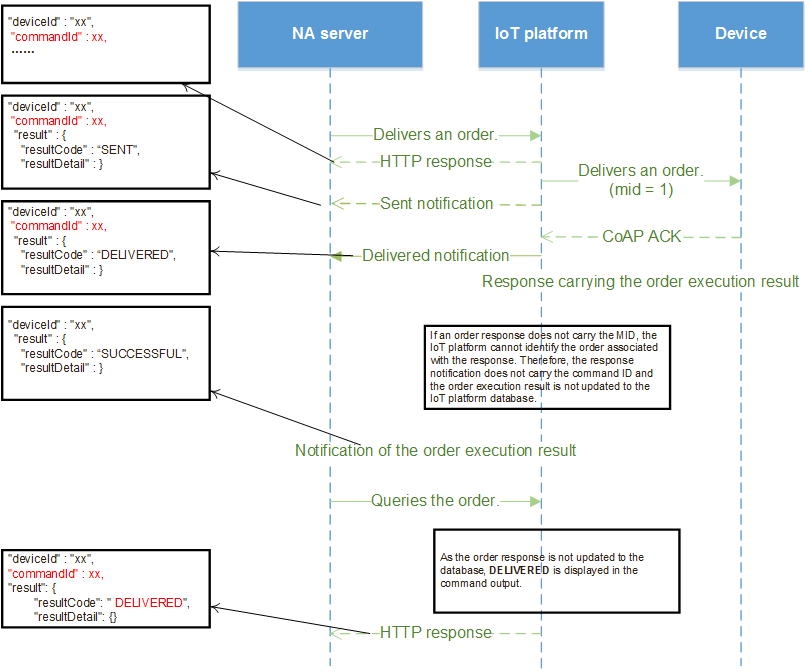
If the MID is not implemented and the order execution result is reported successfully:
- The status (SUCCESSFUL/FAILED) in the order execution result is not updated to the record of the order in the IoT platform database.
- The order execution result notification sent by the IoT platform to the NA server does not contain commandId.
- The query result of the NA server indicates that the final status of the order is DELIVERED.
- The preceding two message flows are used to explain the function of the mid field. Some message flows are simplified in the figures.
- In scenarios where whether orders are sent to the device is concerned but the order execution is not concerned, the device and codec plug-in do not need to process the MID.
- If the MID is not implemented after the vendor evaluation, the NA server cannot obtain the order execution result from the IoT platform. Therefore, the NA server needs to implement the solution by itself. For example, after receiving the order execution result response (without commandId), the NA server can do as follows:
- Match the response with the order according to the sequence in which orders are delivered. In this way, when the IoT platform delivers multiple orders to the same device at the same time, the order execution result is matched with the delivered order incorrectly if packet loss occurs. Therefore, it is recommended that the NA server deliver only one order to the same device each time. After receiving the order execution result response, the NA server delivers the next order.
- Identify the mapping between the order execution result response and the delivered order according to the information in the resultDetail field. The codec plug-in can add order-related information, such as an order code, to the resultDetail field of the order response to help identify the order.
Do Not Use DirectMemory
The DirectMemory field directly calls the OS interface to apply for memory and is not controlled by the JVM. Improper use of the DirectMemory field may cause insufficient memory of the OS. Therefore, the DirectMemory cannot be used in codec plug-in code.
Example of improper use: Use UNSAFE.allocateMemory to apply for direct memory.
if ((maybeDirectBufferConstructor instanceof Constructor))
{
address = UNSAFE.allocateMemory(1L);
Constructor<?> directBufferConstructor;
...
}
else
{
...
}
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





