Configuring HTTPS Password
Background
As shown in the following figure, developer Sam uses a new IAM account to develop the Test_Repo repository of the Test_Project.
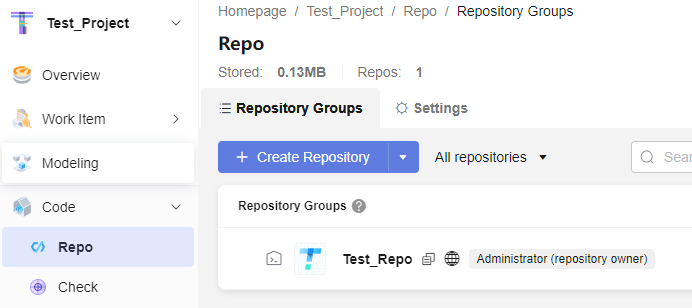
When Sam pushes code to or pulls code from CodeArts Repo, CodeArts Repo needs to verify his identity and permissions. HTTPS password is an authentication mode for remote access to CodeArts Repo. This case describes how Sam configures the HTTPS password for the first time, changes the HTTPS password, clones code files from CodeArts Repo on Windows, and uploads code files to CodeArts Repo.
Preparations
Developers need to configure the Git client (later than 2.30) on a local PC and configure the username and email address. For details, see Installing and Configuring Git Client.
Configuring an HTTPS Password for the First Time
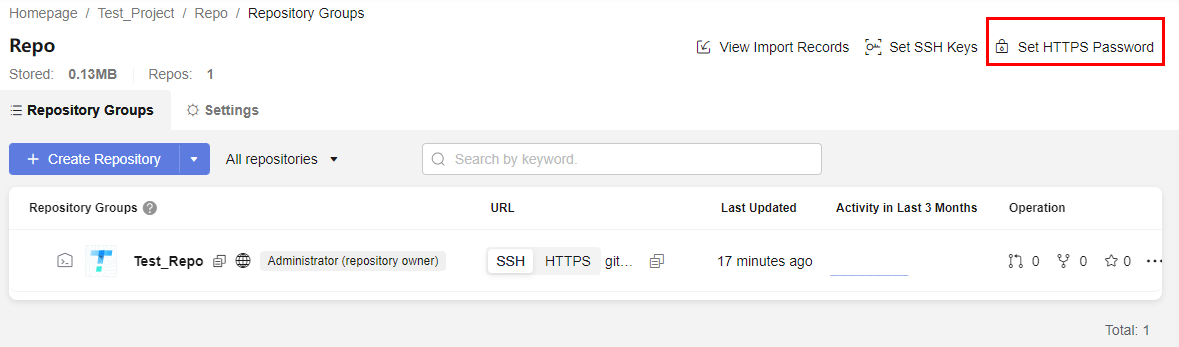
- Sam logs in to the CodeArts Repo homepage for the first time and clicks Set HTTPS Password in the upper right corner of the page.
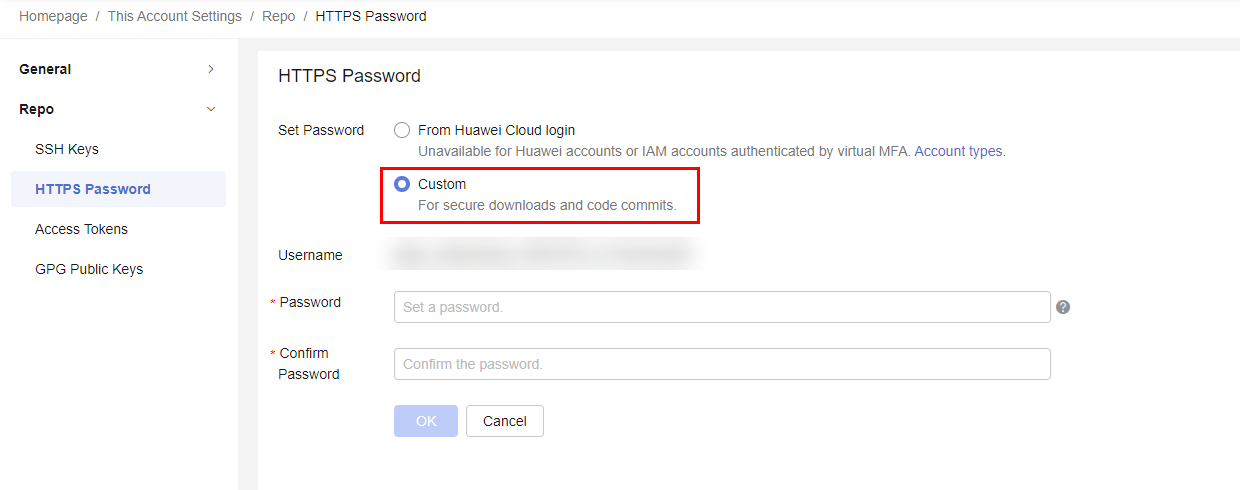
- By default, Sam's tenant name or IAM username is the account name, and the password is the login password of Sam's account. To ensure information security, Sam selects Custom, resets and saves the new password RepoNewPassword.
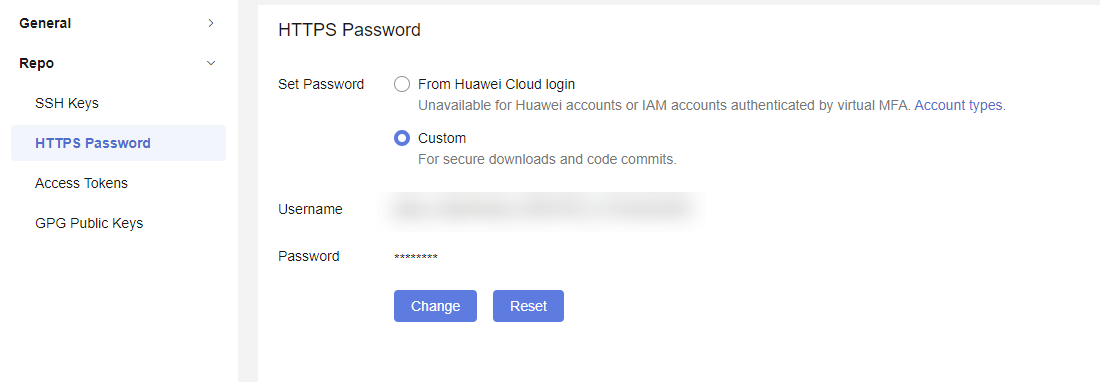
- A dialog box is displayed in the upper right corner, indicating that Sam successfully sets the custom password. The custom password page is displayed. Sam copies and saves the username and password on the local PC.
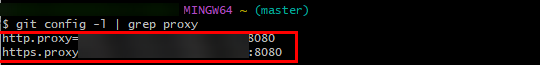
- Sam has already configured a proxy on the local PC previously and now he runs the following command to view the configured Git proxy:
git config -l | grep proxy
The command output indicates that the HTTP and HTTPS proxies of Git have been configured.
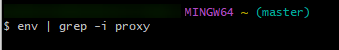
- Sam runs the following command to check the proxy of the environment:
env | grep -i proxy
If the command output is empty, no proxy is configured for the environment.
- Sam runs the following command to cancel the global HTTP and HTTPS proxies of Git:
git config --global --unset http.proxy git config --global --unset https.proxy
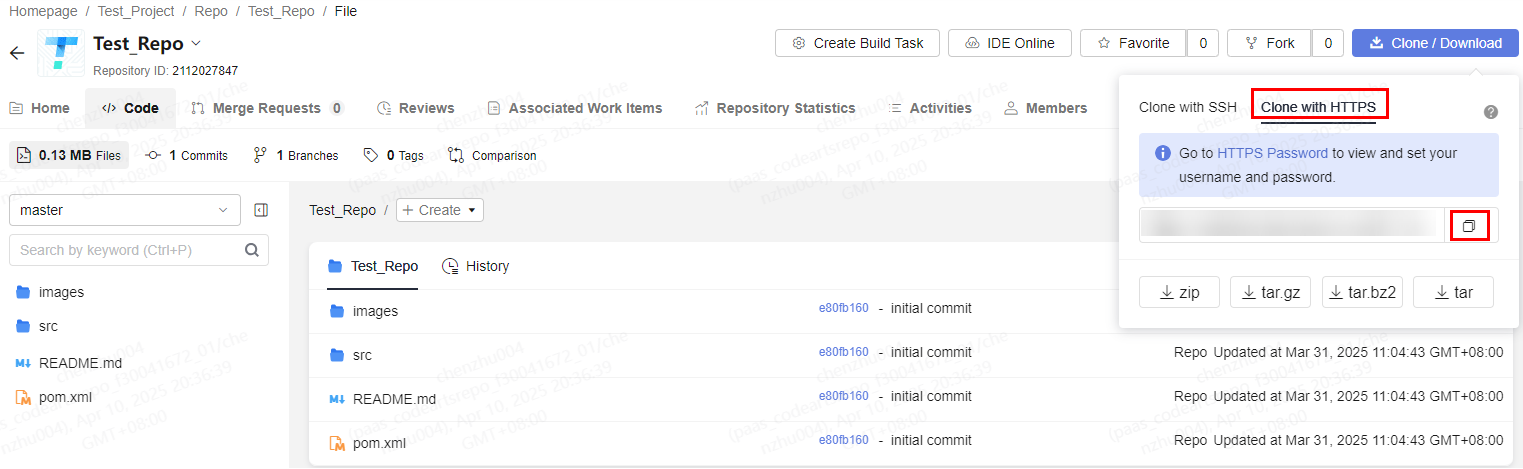
- Sam copies the HTTPS address and clones the repository to the local host for development.
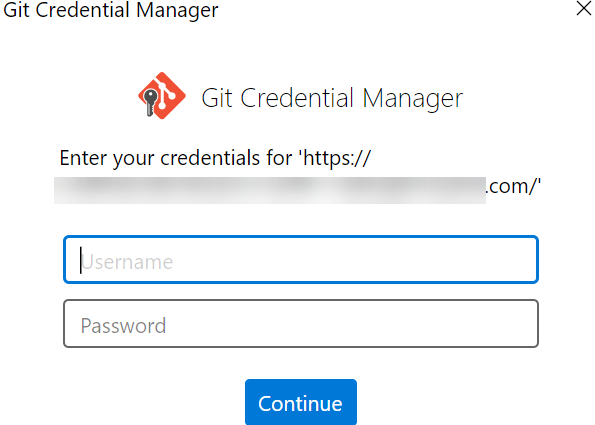
- Sam runs the following command to check whether the configured HTTPS password is valid. https//example.git is the address of the repository to be cloned.
git clone https://example.git
- As shown in the following figure, Sam enters the account name and password copied and saved in 3.
- After Sam enters the account and password, the repository fails to be cloned, and the error message "remote: <CH.00905401> HTTP Basic: Access denied. Request-id is sQIEbze60W. fatal: Authentication failed for 'https://example.com/Test_Repo.git/" is displayed, indicating that the authentication fails.
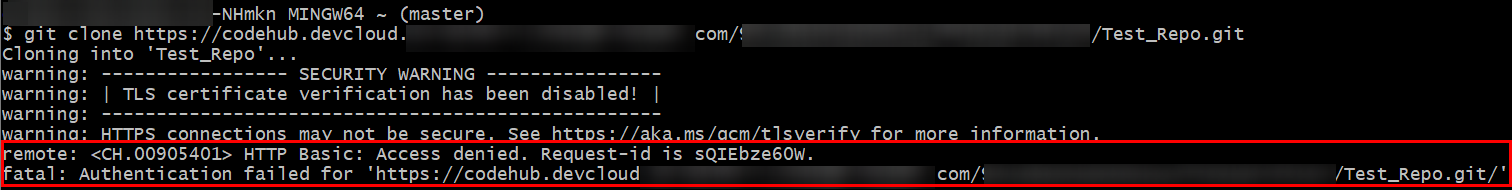
- Sam contacts the tenant administrator to add permissions for Sam. After logging in to the console, the administrator clicks the profile image in the upper right corner and chooses Identity and Access Management, as shown in the following figure.
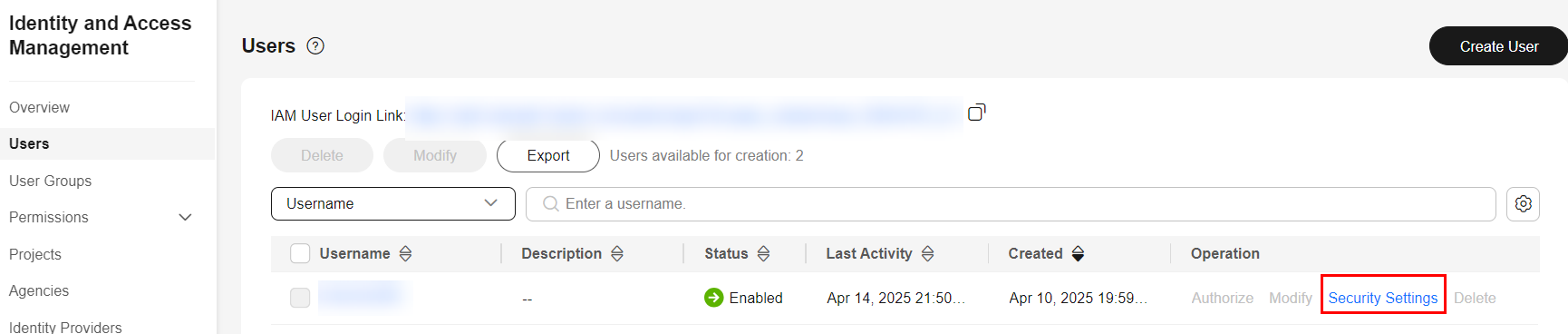
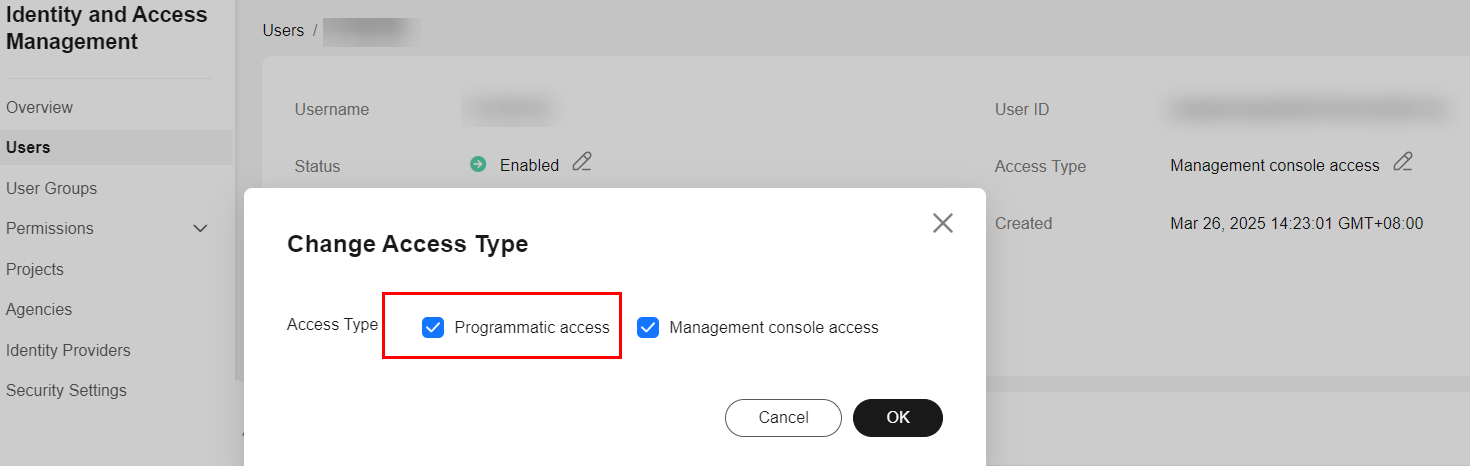
- After clicking User, the administrator locates Sam's account and clicks Security Settings in the Operation column to select Programmatic access for Sam. After the administrator adds the permission, Sam will be notified to clone the repository again.
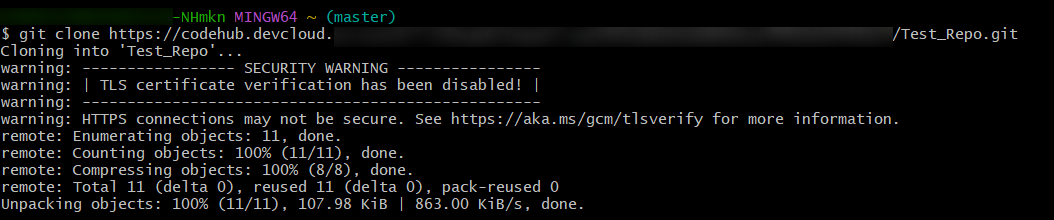
- Sam runs the Git clone command again on the local host and the repository is successfully cloned to the local host, as shown in the following figure.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





