Mounting a File System to Linux ECSs as a Non-root User
Scenarios
By default, a Linux ECS allows only the root user to use the mount command to mount file systems, but you can grant the permissions of user root to other users. Such users can then use the mount command to mount file systems. The following describes how to mount a file system to a Linux ECS as a common user. EulerOS is used in this example.
Prerequisites
- A non-root user has been created on the ECS.
- A file system has been created and can be mounted to the ECS as root.
- The shared path of the file system has been obtained.
Procedure
- Log in to the ECS as user root.
- Assign the root permissions to a non-root user.
- Run chmod 777 /etc/sudoers to make the sudoers file editable.
- Use the which command to view the mount and umount command paths.
Figure 1 Viewing command paths
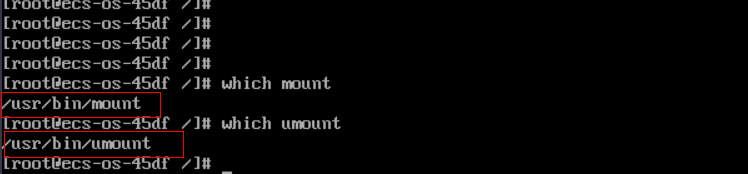
- Run vi /etc/sudoers to edit the sudoers file.
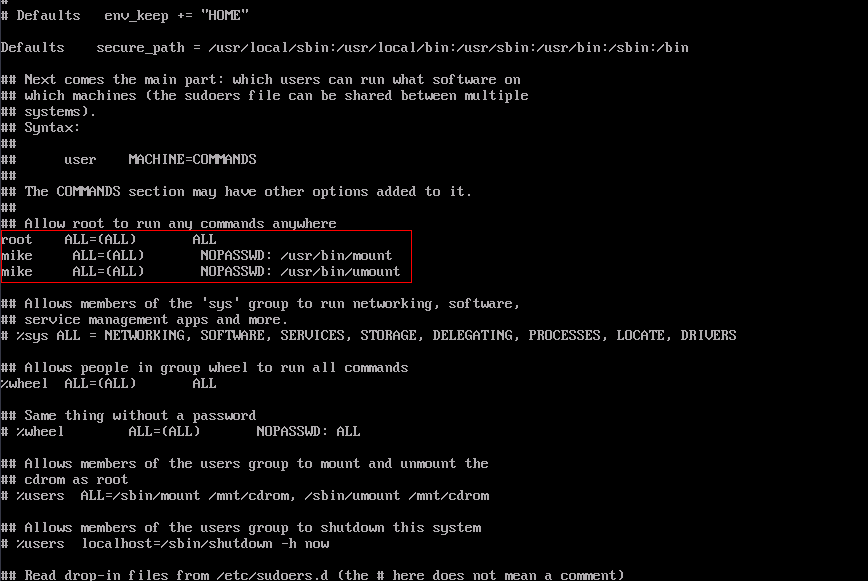
- Add a user under root. In this example, user mike is added.
Figure 2 Adding a user
- Press Esc, enter :wq, and press Enter to save and exit.
- Run chmod 440 /etc/sudoers to make the sudoers file read-only.
- Log in to the ECS as user mike.
- Mount the file system. For details about the mount parameters, see Table 1.
sudo mount -t nfs -o vers=3,timeo=600,noresvport,nolock <Shared path> <Local path>
Table 1 Parameters required for mounting file systems Parameter
Description
<Shared path>
The format is <File system IP address>:/, for example, 192.168.0.0:/.
NOTE:Variable x is a digit or letter.
If the shared path is too long to display completely, you can adjust the column width.
<Local path>
A local directory on the ECS used to mount the file system, for example, /local_path.
- View the mounted file system.
mount -l
If the command output contains the following information, the file system has been mounted:example.com:/share-xxx on /local_path type nfs (rw,vers=3,timeo=600,nolock,addr=)
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





