Periodic Stress Test on Lite Server Supernodes
Scenario
For Snt9b23 supernodes, you can perform periodic performance tests and fault diagnosis on Huawei Cloud AI servers to detect NPU faults in a timely manner and reduce impact on services.
|
Scenario |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Bandwidth test |
Test the bus bandwidth, memory bandwidth, and total time consumption. |
|
Compute test |
Construct a matrix multiplication A(m,k)*B(k,n) and execute it a certain number of times. Calculate the AI Core compute and the real-time power at full computational load of the entire PU or processor based on the computation workload and the time taken to execute the matrix multiplication. |
|
Power consumption test |
Detect the power consumption of the entire PU by running the single-operator model. |
|
Eye pattern test |
Test the network and query the current signal quality. |
|
Stream test |
One-click traffic testing and custom traffic testing are supported. |
|
Software and hardware version compatibility test |
The software and hardware compatibility tool obtains the hardware information, architecture, driver version, firmware version, and software version. |
|
Scenario |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Network diagnosis |
Diagnose the health status of the network and output the diagnosis result. |
|
Signal quality diagnosis |
Diagnose the signal quality and output the diagnosis result. |
|
On-chip memory diagnosis |
Diagnose the high bandwidth memory and output the diagnosis result. |
|
On-chip memory stress test |
Run a stress test on the high-bandwidth memory and output the diagnosis result. |
|
On-chip memory high-risk address stress test |
Run a stress test on the high-risk addresses of the high bandwidth memory and output the diagnosis result. |
|
AI Core diagnosis |
Diagnose the AI Core error and output the diagnosis result. |
|
AI FLOPs diagnosis |
Diagnose the chip compute and output the test result. |
|
Bandwidth diagnosis |
Diagnose the local bandwidth and output the diagnosis result. |
|
P2P stress test |
Check whether the HCCS communication link from the source device to the target device has hardware faults and output the test result. |
|
Power consumption stress test |
Perform the EDP/TDP power consumption stress test and output the diagnosis result. |
Constraints
- Only Snt9b23 supernodes are supported.
- Ascend DMI is used for stress test. Starting multiple processes on the same device to test performance data is not supported. If multi-process test is performed, the test result may be inaccurate or unpredictable.
- Performance test and fault diagnosis will affect training and inference services. Ensure that no service is running first.
- To ensure the correctness and accuracy of the test result, run each detection command separately.
- Ascend DMI can check only the NPUs that are properly installed. To ensure the accuracy of the test result, run the npu-smi info command first.
Performance Test 1: Bandwidth Test
Test the bus bandwidth, memory bandwidth, and total time consumption. Table 3 describes the parameters of the bandwidth test command.
ascend-dmi --bw -h
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-bw, --bw, --bandwidth] |
This parameter is used to test the bandwidth of the chip. -bw is supported, but --bw and --bandwidth are recommended. |
Yes |
|
[-t, --type] |
Specify the data flows to be tested. When the bandwidth test function is used, the tested data flows can be classified into the directions listed below. If this parameter is not specified, h2d, d2h, and d2d are returned by default. Bandwidth and total duration in the three directions.
|
No |
|
[-s, --size] |
Specify the data size to be transferred and the test result display mode. For supernodes, the maximum transmission value ranges from 1 byte to 4 GB in d2h, h2d, and p2p modes.
|
No |
|
[-et, --et, --execute-times] |
Specify the number of iterations, that is, the number of memory copy times. The value ranges from 1 to 1000. If this parameter is not specified, the default value 5 is used in step mode, and the default value 40 is used in fixed-length mode. |
No |
|
[-d, --device] |
Specify the ID of the device whose bandwidth needs to be tested. The device ID is the logical ID of the Huawei Cloud AI processor. If the device ID is not specified, the bandwidth information of device 0 is returned by default. |
No |
|
[-ds, --ds, --device-src] |
Specify the ID of the source device for a P2P test. This parameter must be specified together with the -dd, --dd, and --device-dst parameters. Otherwise, all Huawei Cloud AI NPU chips are tested. |
No |
|
[-dd, --dd, --device-dst] |
Specify the ID of the target device for a P2P test. This parameter must be specified together with the -ds, --ds, and --device-src parameters. Otherwise, all Huawei Cloud AI NPU chips are tested. |
No |
|
[-fmt, --fmt, --format] |
Specify the output format. The value can be normal or json. If not specified, the default value normal is used. |
No |
|
[-q, --quiet] |
If this parameter is specified, no foolproof message is displayed. By default, this operation is allowed. |
No |
The following uses data transmission from a device to the same device as an example to describe how to test the bandwidth and total duration.
ascend-dmi --bw -t d2d -d 0
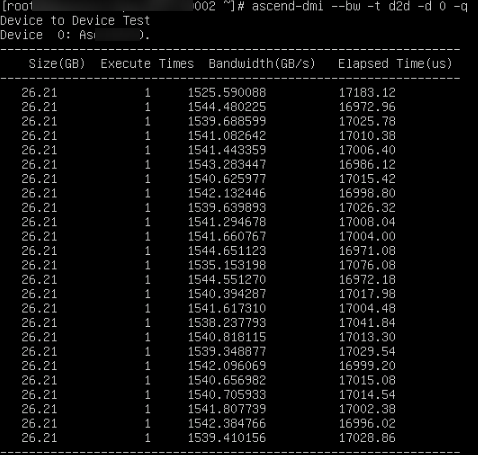
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Host to Device Test |
Data flow direction of the bandwidth. The possible outputs are as follows:
|
|
Device X: Ascend XXX |
X indicates the ID of the device to be tested, and XXX indicates the processor type. 0 indicates the source device, and 1 indicates the target device. |
|
ID |
0→1 indicates the unidirectional P2P bandwidth from device 0 to device 1. 0↔1 indicates the bidirectional P2P bandwidth between device 0 and device 1. |
|
Size(Bytes) |
Size of the data to be transferred, in bytes. |
|
Execute Times |
Number of iterations. |
|
Bandwidth(GB/s) |
Bandwidth of the chip. |
|
Elapsed Time(us) |
Total execution duration. |
Performance Test 2: Compute Test
Construct a matrix multiplication A(m,k)*B(k,n) and execute it a certain number of times. Calculate the AI Core compute and the real-time power at full computational load of the entire PU or processor based on the computation workload and the time taken to execute the matrix multiplication. For details about the parameters for compute test, see Table 5.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-f, --flops] |
This parameter is used to test the compute capability of the entire PU or chip. |
Yes |
|
[-t, --type] |
Specify the operator type. The value can be fp16, fp32, hf32, bf16, or int8. The default value is fp16. |
No |
|
[-d, --device] |
Specify the device ID. The entire PU where the device ID is located is tested. The device ID is the logical ID of the Huawei Cloud AI chip. If this parameter is not specified, the compute of device 0 is returned by default. |
No |
|
[-et, --et, --execute-times] |
Specify the number of times that the matrix multiplication is executed on a single AI Core of the chip.
|
No |
The following shows an example of running the int8 operator and 6 million executions of compute on device 7.
ascend-dmi -f -t int8 -d 7 -et 60 -q
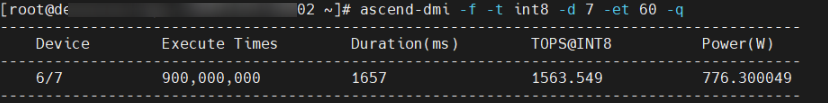
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Device |
Device ID. |
|
Execute Times |
Number of times that a single AI Core performs matrix multiplication multiplied by the number of AI Cores. |
|
Duration(ms) |
Time taken to perform matrix multiplication multiple times. |
|
TFLOPS@FP16 |
Compute obtained through compute test. FP16 is the specified operator run type. |
|
Power(W) |
Real-time power at full compute. |
Performance Test 3: Power Consumption Test
Detect the power consumption of the entire PU by running the single-operator model. For details about the parameters for power consumption test, see Table 7.
ascend-dmi -p -h
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-p, --power] |
This parameter is used to test the power consumption of the entire PU. |
Yes |
|
[-t, --type] |
Specify the operator type. The value can be fp16 or int8. The default value is fp16. |
No |
|
[-pt, --pt, --pressure-type] |
Specify the stress test type.
|
No |
|
[-dur, --dur, --duration] |
Specify the running time. If this parameter is not specified, the default value 600 is used. The unit is second. The value ranges from 60 to 604800. |
No |
|
[-it, --it, --interval-times] |
Specify the interval for refreshing the screen information. If this parameter is not specified, the default value 5 is used. The unit is second. The value ranges from 1 to 5. |
No |
|
[--skip-check] |
If this parameter is specified, the device health check is skipped. Otherwise, the device health status is checked by default. |
No |
|
[-pm, --pm, --print-mode] |
Specify the screen output mode. If this parameter is not specified, the default value refresh is used. Print modes:
|
No |
The following shows an example of executing for 60s at an interval of 5s in refresh mode.
ascend-dmi -p --dur 60 --it 5--pm refresh
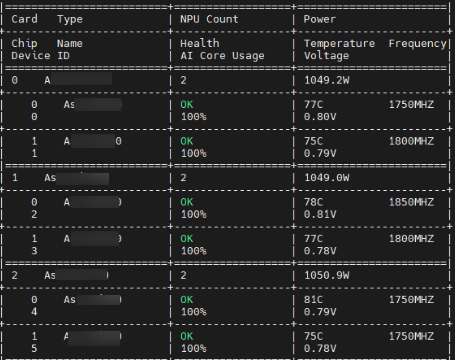

|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Type |
PU model |
|
PU |
PU ID |
|
Chip |
Processor No. |
|
Name |
Processor name |
|
Type |
Processor model |
|
Chip Name |
Chip name |
|
NPU Count |
Number of NPUs |
|
Power |
Actual power consumption of the entire PU or chip. |
|
Health |
Processor health status |
|
Temperature |
Current processor temperature |
|
Device ID |
Device logical ID of the processor |
|
AI Core Usage |
AI Core usage |
|
Voltage |
Current processor voltage |
|
Frequency |
Current processor frequency |
Performance Test 4: Eye Pattern Test
Test the network and query the current signal quality. This function is used to query the specific signal quality. To check whether the signal quality of the current port is normal, perform signalQuality diagnosis. If CDR loopback has been configured for an NPU, disable the loopback before performing the eye pattern test. For details about the parameters for eye pattern test, see Table 9.
ascend-dmi --sq -h
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-sq, --sq, --signal-quality] |
Query the signal quality of the PCIe, HCCS, and RoCE communication ports on the NPU. |
Yes |
|
[-d, --device] |
Specify the device ID to be queried. If multiple device IDs are specified, use commas (,) to separate them. If this parameter is not specified, all NPUs on the device are queried by default. |
No |
|
[-t --type] |
Specify the type of the communication port. Currently, HCCS and RoCE are supported. If multiple communication port types are specified, use commas (,) to separate them. If this parameter is not specified, the signal quality of the RoCE communication port is queried. |
No |
The following shows an example of querying the HCCS and RoCE signal quality of device 0 and device 1.
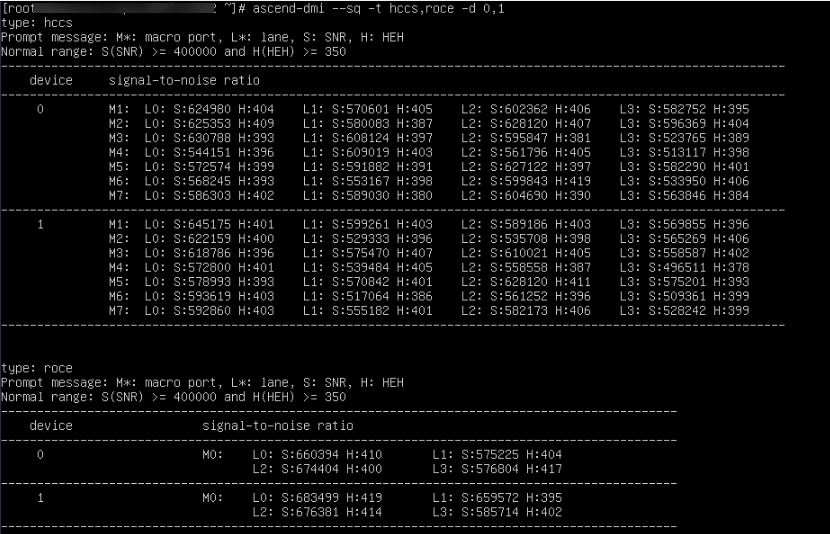
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
type |
Specify the type of the communication port. |
|
device |
Logical ID of an NPU. |
|
M* (macro port) |
Macro port, for example, M0 and M1 indicate macro ports 0 and 1, respectively. |
|
L* (LANE) |
Lane number of the HCCS link, for example, L0 and L1 indicate lane 0 and lane 1, respectively. |
|
S (SNR) |
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a lane. |
|
H (HEH) |
Half eye height of a lane. |
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
type |
Specify the type of the communication port. |
|
device |
Logical ID of the NPU. |
|
M* (macro port) |
Macro port, for example, M0 indicates macro port 0. |
|
S (SNR) |
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of a lane. |
|
H (HEH) |
Half eye height of a lane. |
|
L* (LANE) |
Lane number of the RoCE link, for example, L0 and L1 indicate lane 0 and lane 1, respectively. |
Performance Test 5: Stream Test
One-click traffic testing and custom traffic testing are supported.
|
Test Name |
Supported Traffic Mode |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
One-click traffic testing |
Stream test in a CDR loopback or fiber optic circulator (loopback device) |
Execute the one-click traffic test command. The Ascend DMI tool automatically sends and receives the streams of all lanes of the specified device. After a period of time, the streams are disabled and the results are queried. |
|
Custom traffic testing |
Stream test in a CDR loopback, fiber optic circulator (loopback device), and traffic test using direct connection between NPUs |
Custom traffic testing is to separate each step of one-click traffic testing. You can flexibly control the TX and RX directions and specify the lanes for traffic testing. |
There are three traffic testing modes:
- CDR loopback traffic test: A single device sends and receives traffic at the same time. This test can be used to check the signal quality from the physical SerDes port of the NPU to the CDR unit. Before starting traffic testing, ensure that the optical module is in position. Then, run the commands below to configure or disable CDR loopback.
Run the commands below to configure CDR loopback. In the commands, t uses values 3 and 0 in sequence and i indicates the NPU ID.
hccn_tool -i 0 -scdr -t 3
hccn_tool -i 0 -scdr -t 0
Run the commands below to disable CDR loopback. In the commands, t uses values 2 and 1 in sequence and i indicates the NPU ID.
hccn_tool -i 0 -scdr -t 2
hccn_tool -i 0 -scdr -t 1
- Traffic testing using a fiber optic circulator (loopback device) connected to an optical module: A single device sends and receives traffic at the same time. This method can be used to check the signal quality of the physical SerDes port of the NPU to the optical module. No loopback needs to be set.
- Traffic testing using direct connection between NPUs: After traffic is sent in the TX direction of the SerDes port on NPU A, data flows reach the SerDes port on NPU B through the tested link. NPU B compares the received data with the code pattern in the RX direction and collects statistics on bit errors. This method can be used to check the signal quality of the link between two NPUs (only custom traffic testing is supported).
For details about parameters for stream tests, see Table 13.
ascend-dmi --prbs-check -h
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-pc, --pc, --prbs-check] |
This parameter is used for PRBS stream tests. |
Yes |
|
[-d, --device] |
Specify the ID of the device for which the stream test is to be performed.
|
No |
|
[-dur, --dur, --duration] |
Specify the duration of the stream test.
|
No |
|
[--prbs-mode] |
Whether to switch the traffic testing status. EN: enabled DS: disabled
|
Yes |
|
[--generator-pattern] |
Specify the stream type of the TX end.
|
No |
|
[--generator-lanes] |
Specify the lane of the TX end.
|
No |
|
[--checker-pattern] |
Specify the stream type of the RX end.
|
No |
|
[--checker-lanes] |
Specify the lane of the RX end.
|
No |
|
[-show, --show, --show-diagnostic-info] |
Display the stream test result.
|
No |
|
[-clear, --clear, --clear-diagnostic-info] |
Clear the stream test result.
|
No |
The following is an example of one-click traffic testing:
ascend-dmi -pc -d 9 --pattern prbs15 -dur 5
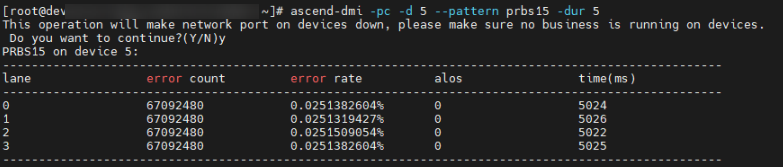
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
device |
Logical ID of the NPU. |
|
lane |
Lane ID of the RoCE link. |
|
error count |
Number of bit errors. The maximum value is 67092480, indicating full bit errors. |
|
error rate |
Bit error rate. If the bit error rate is less than 10-5, the signal quality is normal. |
|
alos |
The value 0 indicates normal, and the value 1 indicates that the input signal amplitude is too low. |
|
times |
Traffic testing duration. |
The following shows an example of custom traffic testing:
# Enable the stream test on Device8 and Device9. ascend-dmi -pc --clear --device 8,9 -q # On Device8 and Device9, the TX ends are lane 0 and lane 1, and the code pattern is PRBS20. The RX ends are lane 2 and lane 3, and the code pattern is PRBS23. ascend-dmi -pc --prbs-mode EN -q --device 8,9 --generator-pattern prbs20 --generator-lanes 0,1--checker-pattern prbs23 --checker-lanes 2,3 # Display the stream test results of Device8 and Device9. ascend-dmi -pc --show-diagnostic-info -d 8,9 -q # Disable traffic testing on Device8 and Device9. ascend-dmi -pc --prbs-mode DS -d 8,9 -q # Clear the traffic testing results on Device8 and Device9. ascend-dmi -pc --clear-diagnostic-info -d 8,9 -q
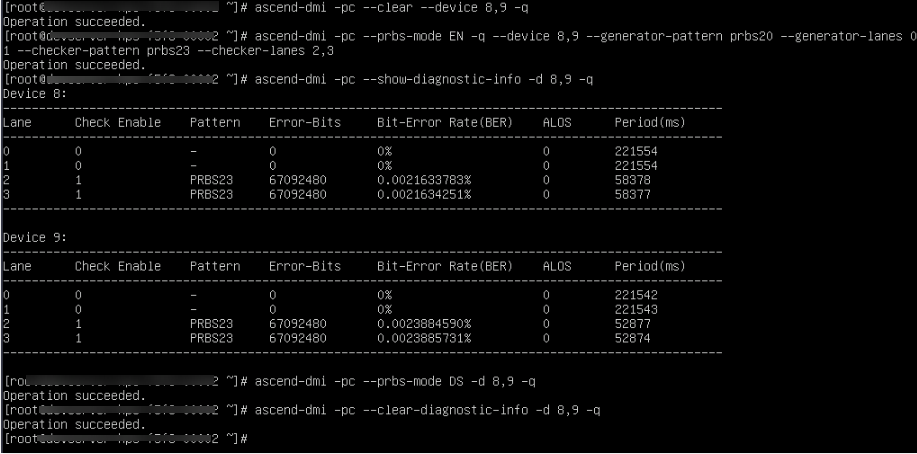
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Lane |
Lane ID of the RoCE link. |
|
Check Enable |
Check status of the RX end. The value 0 indicates disabled and 1 indicates enabled. |
|
Pattern |
Code pattern of check in the RX direction. |
|
Error-Bits |
Number of bit errors. The upper limit is 67092480 (full bit errors). |
|
Bit-Error Rate (BER) |
Bit error rate, which is the number of bit errors divided by the total number of transmitted bits multiplied by 100%. |
|
ALOS |
The value must be 0 for normal traffic testing. If the value is 1, the signal amplitude is too low. If no traffic is testing, this parameter is meaningless. |
|
Period |
Time when the traffic testing is controlled or the check result is read last time. |
Performance Test 6: Software and Hardware Version Compatibility Test
The software and hardware compatibility tool obtains the hardware information, architecture, driver version, firmware version, and software version. For details about the parameters for software and hardware compatibility tests, see Table 16.
ascend-dmi -c -h
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-c, --compatible] |
This parameter is used to check the software and hardware version compatibility.
|
Yes |
|
[-p, --path] |
You can specify the installation path of the CANN software package to be tested. If the installation path is not specified, the default installation path is used. Example command for specifying the installation path of the software package: ascend-dmi -c -p /home/xxx/Ascend |
No |
The following shows an example of the hardware and software version compatibility test:
ascend-dmi -c
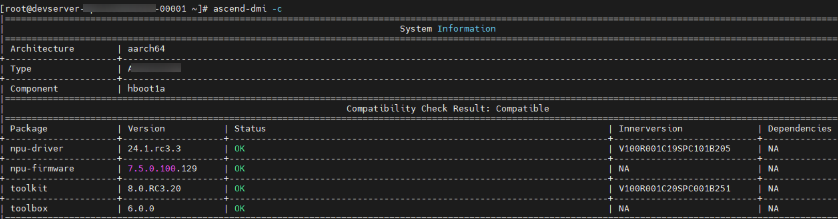
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
System Information |
System information |
|
Architecture |
Architecture |
|
Type |
PU or chip model |
|
Compatibility Check Result |
Compatibility check result |
|
Package |
Package name |
|
Version |
Version |
|
Status |
Status. Possible values are as follows:
|
|
Innerversion |
Internal version number |
|
Dependencies |
Dependencies |
Fault Diagnosis
View the parameters of the fault diagnosis command.
ascend-dmi --dg -h
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-dg, --dg, --diagnosis] |
This parameter is used to perform a fault diagnosis test on the entire PU. |
Yes |
|
[-i, --items] |
Specify the diagnosis check items.
|
No |
|
[-d, --device] |
Specify the ID of the device to be diagnosed. The device ID is the logical ID of the Huawei Cloud AI chip.
|
No |
|
[-r, --result] |
Specify the path for storing the stress test result and information collection result, for example, /test. The specified path must meet security requirements and cannot contain the wildcard (*).
|
No |
|
[-s, --stress] |
This parameter is used to perform stress tests. Currently, the following stress tests are supported: on-chip memory stress test, AI Core stress test, P2P stress test, and power consumption stress test.
|
No |
|
[-st, --st, --stress-time] |
Specify the time for the EDP and TDP stress tests.
|
No |
|
[-fmt, --fmt, --format] |
Specify the output format. The value can be normal or json.
|
No |
|
[-h, --help] |
View the parameters of the fault diagnosis command. |
No |
Fault Diagnosis 1: Network Diagnosis
Diagnose the health status of the network and output the diagnosis result.
# Example of diagnosing the network health status of Device0 ascend-dmi -dg -i network -d 0
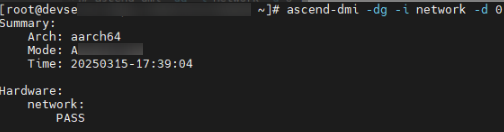
The parameters in the command output are as follows:
- PASS: The network is healthy.
- SKIP: The current product form does not support this check item.
- INFO: The network check result is informational.
- WARN: The network check result is an alarm.
- FAIL: The network check fails.
Fault Diagnosis 2: SignalQuality Diagnosis
Diagnose the signal quality and output the diagnosis result.
# Example of SignalQuality diagnosis ascend-dmi -dg -i signalQuality -q
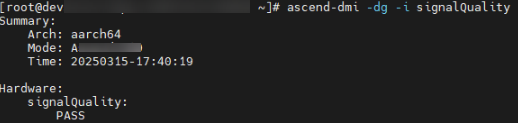
The parameters in the command output are as follows:
- PASS: The HCCS and RoCE communication ports on the NPU pass the test, and the signal quality is normal.
- SKIP: The current device does not support eye pattern diagnosis.
- IMPORTANT_WARN: Important warning. The signal quality of one or more of the HCCS and RoCE ports is abnormal. Contact Huawei engineers.
- FAIL: The eye pattern detection fails.
Fault Diagnosis 3: On-Chip Memory Diagnosis
Diagnose the high bandwidth memory and output the diagnosis result.
# Example of on-chip memory diagnosis ascend-dmi -dg -i hbm
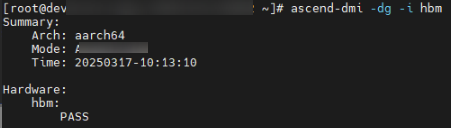
|
Output Status |
Description |
|---|---|
|
PASS |
The on-chip memory passes the check and is normal. |
|
SKIP |
The current hardware form does not support on-chip memory check. |
|
GENERAL_WARN |
There are isolated pages with historical multi-bit errors. The NPU chip triggering the alarm has a health management fault code of 0x80E18401. The NPU chip can still be used. |
|
IMPORTANT_WARN |
The number of isolated pages now differs from the previous count. Restart to reset the NPU chip. |
|
EMERGENCY_WARN |
|
|
FAIL |
The on-chip memory detection fails. Contact Huawei engineers. |
Fault Diagnosis 4: On-Chip Memory Stress Test
Run a stress test on the high-bandwidth memory and output the diagnosis result.
# Example ascend-dmi -dg -i hbm -s -st 60 -q
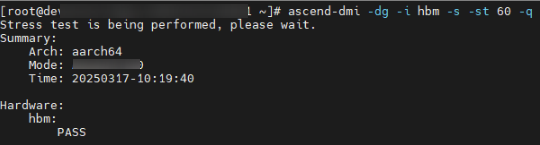
Output parameters:
- PASS: The on-chip memory stress test is passed.
- SKIP: The current device does not support the on-chip memory stress test.
- FAIL: The on-chip memory stress test fails because new multi-bit isolation pages are added. The software execution fails.
Fault Diagnosis 5: On-Chip Memory High-Risk Address Stress Test
Run a stress test on the high-risk addresses of the high bandwidth memory and output the diagnosis result.
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory |
|---|---|---|
|
[-s, --stress] |
This parameter is used to perform stress tests. Currently, the following stress tests are supported: on-chip memory stress test, AI Core stress test, P2P stress test, and power consumption stress test. |
Yes |
|
[-qs, --qs, --quick stress] |
Specify the range of fast stress test for high-bandwidth memory high-risk addresses.
|
Yes |
# Example of stress test on on-chip memory high-risk addresses ascend-dmi -dg -i hbm -s -qs 60-q
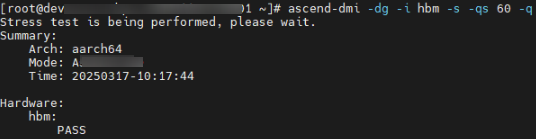
Output parameters:
- PASS: The high-bandwidth memory high-risk address fast stress test is passed. No isolation page is added.
- SKIP: The current device does not support the on-chip memory high-risk address stress test.
- FAIL: The high-bandwidth memory high-risk address fast stress test fails. New isolation pages are added.
Fault Diagnosis 6: AI Core Diagnosis
Diagnose the AI Core error and output the diagnosis result.
# Example of AI Core diagnosis ascend-dmi -dg -i aicore -q
Output parameters:
- PASS: The diagnosis result is normal.
- SKIP: The diagnosis is performed by a non-root user and AI Core diagnosis is not supported.
- EMERGENCY_WARN: emergency warning. Replace the hardware.
- FAIL: AI Core diagnosis fails. Contact Huawei engineers.
Fault Diagnosis 7: AI FLOPs Diagnosis
Diagnose the chip compute and output the test result.
# Example of AI FLOPs diagnosis ascend-dmi -dg -i aiflops -q
Output parameters:
- PASS: The compute test result is normal (greater than the reference value).
- WARN: The chip overheats during the compute test.
- FAIL: The compute test fails. The test result is smaller than the reference value.
Fault Diagnosis 8: Bandwidth Diagnosis
Diagnose the local bandwidth and output the diagnosis result.
# Example of performing bandwidth diagnosis on Device0 ascend-dmi --dg -i bandwidth -d 0
Output parameters:
- PASS: The bandwidth test result is normal.
- FAIL: The bandwidth test fails. The test result is smaller than the reference value. Contact Huawei engineers.
Fault Diagnosis 9: P2P Stress Test
Checks whether the HCCS communication link from the source device to the target device has hardware faults and outputs the test result.
# Example of P2P stress test ascend-dmi -dg -i bandwidth --type p2p -s
Output parameters:
- PASS: The stress test is passed, and the result is normal.
- SKIP: The current device does not support the P2P stress test.
- EMERGENCY_WARN: emergency warning. The stress test fails. Contact Huawei engineers to replace the hardware.
- FAIL: P2P stress test fails. Contact Huawei engineers.
Fault Diagnosis 10: Power Consumption Stress Test
Perform the EDP/TDP power consumption stress test and output the diagnosis result.
# Example of power consumption stress test ascend-dmi -dg -i edp -s -st 60 -q ascend-dmi -dg -i tdp -s -st 60 -q
Output parameters:
- PASS: The power consumption stress test result is normal.
- SKIP: The current device does not support the power consumption stress test.
- IMPORTANT_WARN: A chip alarm is generated during the stress test. Handle the alarm based on the description. If the fault persists, contact Huawei engineers.
- FAIL: The power consumption stress test fails. Contact Huawei engineers.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





