Known Issues
This section describes known issues of public images. Private images also have these issues.
SCSI Disk Capacity Remains Unchanged After Being Expanded (Specific to an ECS Created from a Windows Server 2016 Standard/Database Image)
Symptom:
A C7, C9, aC6, aC7, aC8, or aM8 ECS was created from a Windows Server 2016 Standard/Database image and then a SCSI disk was attached to the ECS. After the disk capacity was expanded, the disk size remained unchanged when you logged in to the ECS and checked it.
Involved images:
Windows Server 2016 Standard/Datacenter
Solutions:
- On your local computer, click Start. Enter Computer Management in the search box and open it.
- Click Disk Management. Then, choose Action > Rescan Disks.

Network Disconnection Caused by a Windows Server DHCP Lease Longer Than 99 Days
Symptom:
If the DHCP lease is longer than 99 days, instance IP addresses cannot be automatically renewed. As a result, the instance network will be disconnected when the lease comes to an end.
Involved images:
Public and private images of Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server 2019
Solutions:
- Change the DHCP lease of the subnet where the instance is located to one day or unlimited.
- Run the following command to make the change take effect:
The following command will temporarily disconnect you from the network. Do it during off-peak hours.
ipconfig /renew
Data Is Lost During Disk Reset Due to the Incompatibility Between Server Manager of Windows Server 2012 R2 and VMTools
Symptom:
A Windows Server 2012 R2 cloud server is configured with two data disks. When Windows Server Manager resets the second data disk, the first data disk is reset. As a result, the data of the first data disk is lost.
Involved images:
Windows Server 2012 R2 public image before 2019-02-19
Solutions:
Upgrade VMTools of involved cloud servers to 2.5.0.156 or later.
SCTP Traffic Unreachable to the PEP Network Segment 198.19.32.0/19 Due to Restrictions in Linux Kernel 5.4.0 to 5.13.0
Symptom:
In Linux kernel versions 5.4.0 to 5.13.0, a kernel-level restriction prevents SCTP traffic from successfully reaching the network segment 198.19.32.0/19 of Public Endpoint (PEP).
Involved images:
Linux public images with kernel versions from 5.4.0 to 5.13.0
Solutions:
Use the latest version of Huawei Cloud EulerOS or upgrade the original image kernel to 5.14.0 or later.
OS Panics and Restarts Are Triggered in Rocky Linux 9 or AlmaLinux 9 by Capacity Expansion of VBD EVS Disks on aC8, C7t, C7e, C7h, and C9 ECSs
Symptom:
A bug exists in kernel versions from 5.14.0-362.13.1.el9_3 to 5.14.0-427.42.1.el9_4. OS panics and restarts may occur in Rocky Linux 9 and AlmaLinux 9 when the capacities of VBD EVS disks are expanded on aC8, C7t, C7e, C7h, and C9 ECSs.
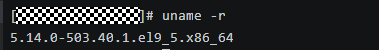
Run uname -r to check the kernel version.
Involved images:
|
Image |
|---|
|
Rocky Linux 9.0 public images released from April 27, 2024 to July 11, 2025 |
|
Rocky Linux 9.2 public images released from January 7, 2025 to June 11, 2025 |
|
AlmaLinux 9.0 public images released from April 27, 2024 to July 11, 2025 |
Solutions:
This issue has been resolved in kernel version 5.14.0-503.11.1.el9_5. You are advised to upgrade the kernel to 5.14.0-503.11.1.el9_5 or later. The command for upgrading the kernel is as follows:
yum update kernel
Restart the OS after the kernel is upgraded.
Occasional System Errors Triggered By Adding or Deleting NICs
Symptom:
After an ECS is started, adding or deleting a NIC or other equivalent actions may:
- Trigger a kernel panic, and the OS automatically restarts.
- Trigger frequent software interrupts, and the network may fail to receive or send packets.
Involved images:
CentOS 7 public and private images
Solutions:
Upgrade the kernel to 3.10.0-1160.25.1.e17.x86_64 of CentOS 7.
Kernels Are Occasionally Disconnected from the TCP Network
Symptom:
This issue is caused by the kernel vulnerability CVE-2019-11477 (TCP SACK). When the socket buffer is low, the network may be disconnected.
The involved images are listed in the following table.
|
Image Type |
Kernel Version |
|---|---|
|
CentOS 7 public images from 2019-06-26 to 2019-09-29 |
3.10.0-957.21.3.e17.x86_64 |
|
Ubuntu 16 and Ubuntu 18 public images from 2019-06-26 to 2019-10-15 |
Ubuntu 16.04: 4.4.0-151-generic Ubuntu 18.04: 4.15.0-52-generic |
|
Debian 9.0 public images from 2019-06-26 to 2019-10-15 |
4.9.0-9-amd64 |
|
Fedora 29 and openSUSE 15.0 public images from 2019-06-27 to 2019-10-15 |
Fedora 29: 5.1.11-200.fc29.x86_64 openSUSE 15.0: 4.12.14-1p150.12.64-default |
Solutions:
Upgrade the kernel to the latest version. Run the following commands to upgrade the kernel of each image type:
- CentOS/Fedora: yum update kernel
- Ubuntu: apt-get update && apt-get install linux-image-generic
- openSUSE: zypper refresh && zypper install kernel-default
- Debian: apt-get update && apt search linux-image && apt-get install linux-image-xxx
You can run the apt search linux-image command to query for the latest kernel version. The apt-get install linux-image-xxx command is used to upgrade a kernel to the latest version.
OS Parameter Settings Do Not Take Effect
Symptom:
After net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets is configured in the /etc/sysctl.conf file, the check result of sysctl -a indicates that the configuration does not take effect. The configurations in /etc/sysctl.d/huawei.conf and /etc/security/limits.d/huawei-nofile.conf have been built in public images and these configurations have higher priorities than those in /etc/sysctl.conf. As a result, the configurations in /etc/sysctl.conf do not take effect.
The involved parameters are listed in the following table.
|
Parameter |
Configuration File |
|---|---|
|
vm.swappiness net.core.somaxconn net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog |
/etc/sysctl.d/huawei.conf |
|
* soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535 |
/etc/security/limits.d/huawei-nofile.conf |
Involved images:
- CentOS 7 public images from 2018-09-25 to 2019-09-29
- CentOS 6 public images from 2018-09-25 to 2019-10-10
- Ubuntu, openSUSE 15.0, Debian, and Fedora 29 public images from 2018-09-28 to 2019-10-15
Solutions:
- Delete the built-in configuration files.
rm -rf /etc/sysctl.d/huawei.conf
rm -rf /etc/security/limits.d/huawei-nofile.conf
- Modify the kernel parameter configuration files (limits.conf and sysctl.conf).
cat >>/etc/security/limits.conf <<EOF
root soft nofile 65535
root hard nofile 65535
* soft nofile 65535
* hard nofile 65535
EOF
cat >>/etc/sysctl.conf <<EOF
vm.swappiness=0
net.core.somaxconn=1024
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets=5000
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog=1024
EOF
1822 NIC-based Offloading Is Incompatible with the Linux 3.16.x Kernel
Symptom:
ECSs that use hardware offloading provided by Huawei-developed 25GE intelligent high-speed NICs may be incompatible with Linux 3.16.47 to 3.16.x, which may cause occasional network disconnections of ECSs. ECSs that have this issue include but are not limited to C3ne, M3ne, C6, M6, G5, P2v, G5r, P2vs, P2s, Pi2, FP1cn1, Ai1, e3.26xlarge.14, e3.52xlarge.14, e3.52xlarge.20, KC1, and KM1.
Involved images:
Debian 8.2.0 64bit and Debian 8.8.0 public images
Solutions:
Remove Debian 8 public images from flavors. Migrate services of ECSs using this offloading function to S3 and C3 ECSs as soon as possible.
Service Interruptions Caused By Lingering CLOSE_WAIT Connections
Symptom:
Some services are interrupted because a socket in a TCP connection created by the one-click password reset plug-in process stays in the CLOSE_WAIT state.
Involved images:
- CentOS and EulerOS public images issued before June 5, 2019
- Ubuntu and Debian public images issued before June 3, 2019
Solutions:
Update the one-click password reset plug-ins for the ECSs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





