Edge-Cloud Message Overview
IEF provides the function of routing messages exchanged between the edge and cloud. Based on configured routes, IEF forwards messages to the corresponding endpoint. In this way, messages can be forwarded based on specified paths, enhancing flexibility in data routing control and improves data security.
- Message endpoint: a party that sends or receives a message. It can be an end device or a cloud service.
- Message route: a message forwarding path.
Message Endpoints
IEF provides the following default message endpoints:
- SystemEventBus: MQTT broker on an edge node, which can communicate with other endpoints on behalf of the edge node. It can function as a source endpoint to send data to the cloud, or as a destination endpoint to receive messages from the cloud. MQTT topics on the edge node are used as endpoint resources of the MQTT broker.
- SystemREST: a REST gateway interface in the cloud. It can function as a source endpoint to send REST requests to the edge. REST request paths are used as endpoint resources of SystemREST.
You can also create the following message endpoints:
- Service Bus: an endpoint deployed on an edge node to process transaction requests. It can function as a destination endpoint to process file upload requests. REST request paths are used as endpoint resources of Service Bus.
- DIS: data injection service. It can function as a destination endpoint to receive data forwarded by IEF. DIS streams created in DIS are used as endpoint resources.
- API Gateway: API gateway service. It can function as a destination endpoint to receive data forwarded by IEF. API URLs created in API Gateway are used as endpoint resources.
Routes
Currently, IEF supports the following message forwarding paths:
- SystemREST -> Service Bus: The REST gateway interface in the cloud is called to obtain file services on edge nodes.
- SystemREST -> SystemEventBus: The REST gateway interface in the cloud is called to send messages to SystemEventBus (MQTT broker) on edge nodes.
- SystemEventBus -> DIS/API Gateway: You can publish end device data to a custom topic in the MQTT broker of an edge node. IEF forwards the device data to a DIS stream or an API Gateway address. Then, you can extract the data for processing and analysis. You must customize an MQTT topic when creating the route. For details about custom topics, see Custom Topics.
To use the message routing function, create endpoints and then create routes.
Creating an Endpoint
- Log in to the IEF console, and click Switch Instance on the Dashboard page to select a platinum service instance.
- In the navigation pane, choose Edge-Cloud Messages > Endpoints.
- Click Create Endpoint in the upper right corner, and set the endpoint parameters.
Figure 1 Creating an endpoint
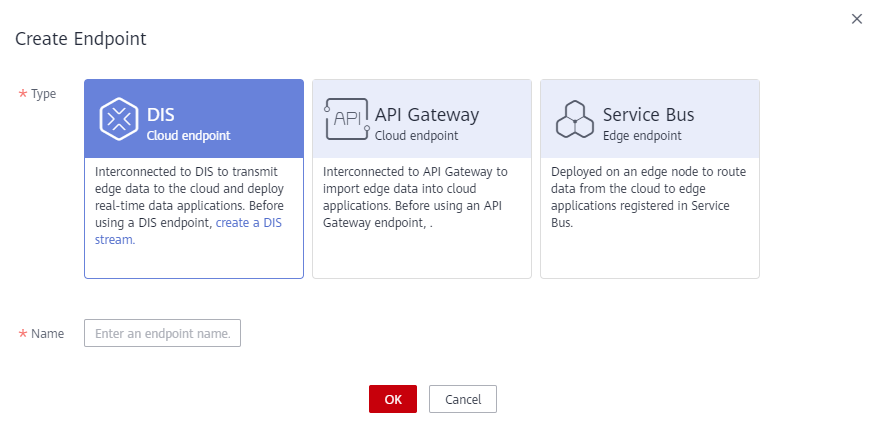
- Type: Select an endpoint type. DIS, API Gateway, and Service Bus are supported.
- Name: Enter an endpoint name.
- Service Port: Available only for endpoints of the Service Bus type. Ranges from 1 to 65535.
- Click OK. The endpoint is successfully created and the endpoint list page is displayed.
Creating a Route
- Log in to the IEF console, and click Switch Instance on the Dashboard page to select a platinum service instance.
- In the navigation pane, choose Edge-Cloud Messages > Routes.
- Click Create Route in the upper right corner.
- Set the route parameters.
- Name: Enter a route name.

Message routes and system subscriptions are of the same resource type. Their names cannot conflict with each other.
- Source Endpoint: Select a source endpoint, for example, SystemREST or SystemEventBus.
- Source Endpoint Resource: Select a source endpoint resource.
- When SystemREST is selected:
Enter the REST path, for example, /abc/ab.
- When SystemEventBus is selected:
Custom topic: Select a node and enter a topic.
Device data upload channel: Select a node and select the MQTT devices bound to the node.
You can only select MQTT devices.
- When SystemREST is selected:
- Destination Endpoint: Select a destination endpoint, for example, SystemEventBus.
- Destination Endpoint Resource: Select a destination endpoint resource.
- Name: Enter a route name.
- Click Create. The route is successfully created and the route list page is displayed.
IEF forwards messages sent to the specified resource of the source endpoint to the specified resource of the destination endpoint based on the route.
Disabling or Enabling a Route
- To disable a route, click Disable in the row where the route resides.
After the route is disabled, IEF will not forward messages destined for the specified resource of the source endpoint.
- To enable a route, click Enable in the row where the route resides.
After the route is enabled, IEF will forward messages destined for the specified resource of the source endpoint.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





