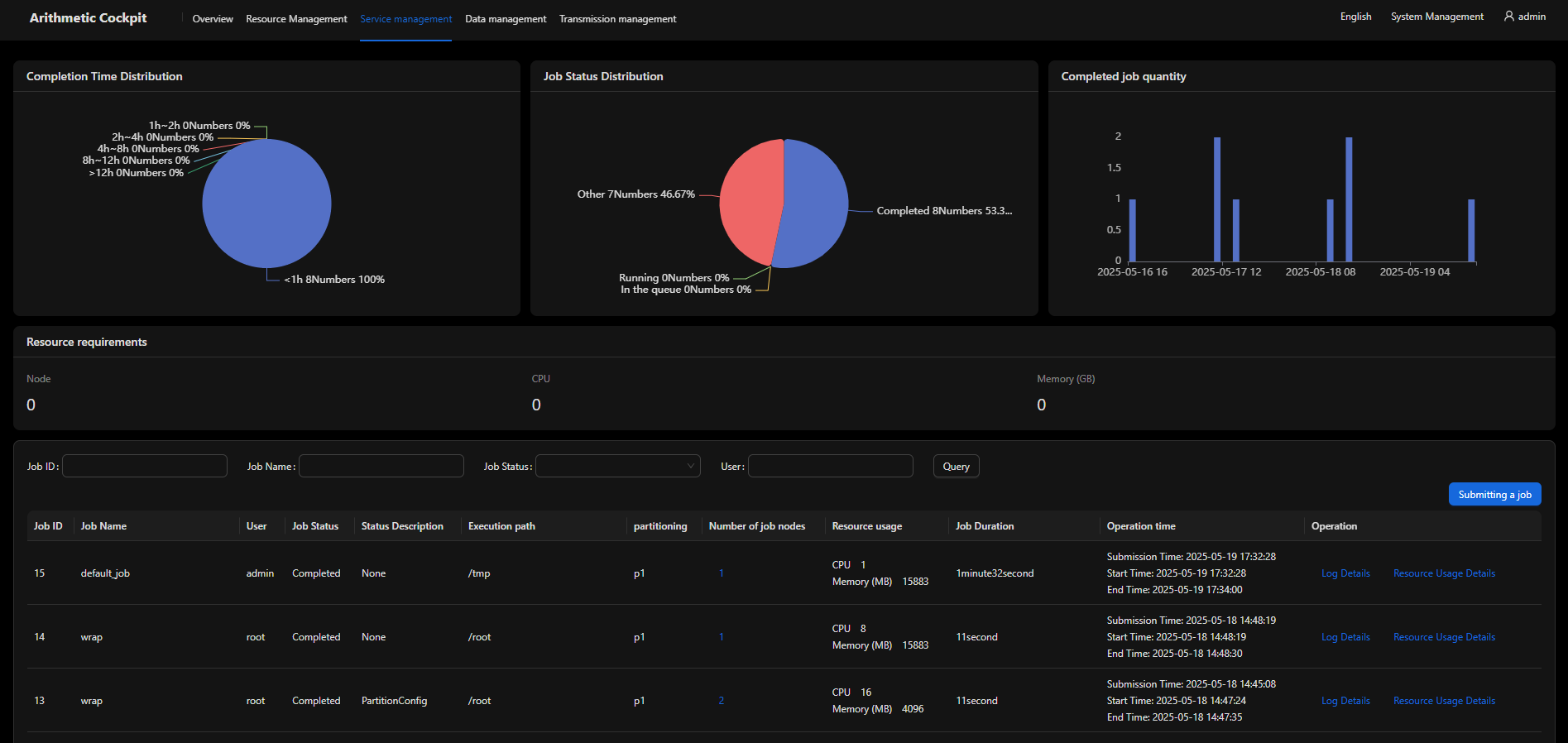
Dynamic Scheduling
Dynamic scheduling optimizes job execution by adapting to real-time cluster conditions, ensuring efficient resource utilization while maintaining fair access for all users.
Dynamic Resource Scheduling
Function 1: Scaling up when loads stack up and scaling down when nodes are idle
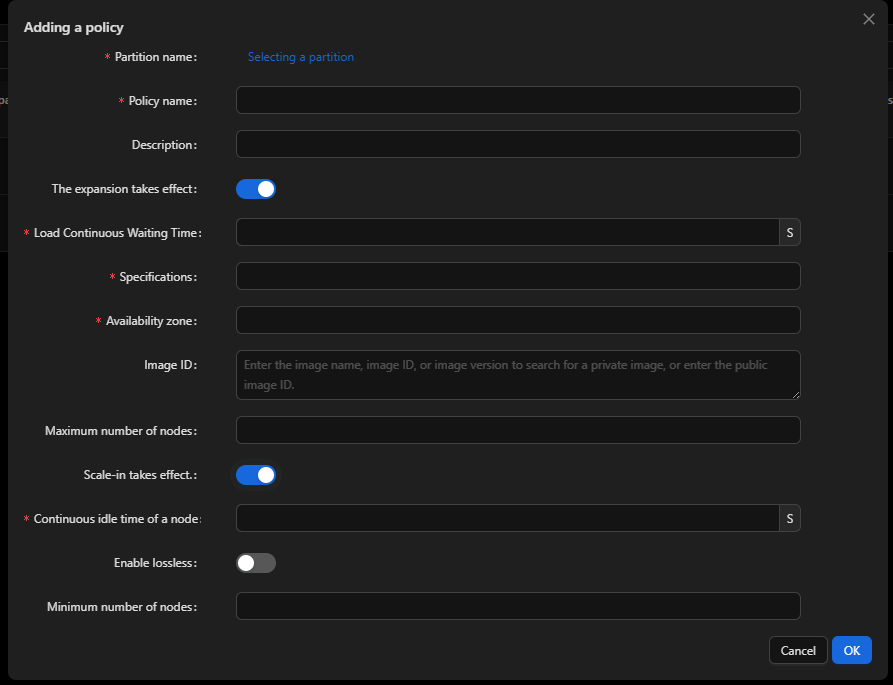
- If no node is available, new sites are automatically added at the preset time.
- Resources are automatically released when a node remains idle for the preset time (300 seconds).
Function 2: Setting stable nodes

No nodes are deleted even when they are idle.
Function 3: Provisioning hybrid resources elastically
You can create compute nodes of different specifications in a partition.
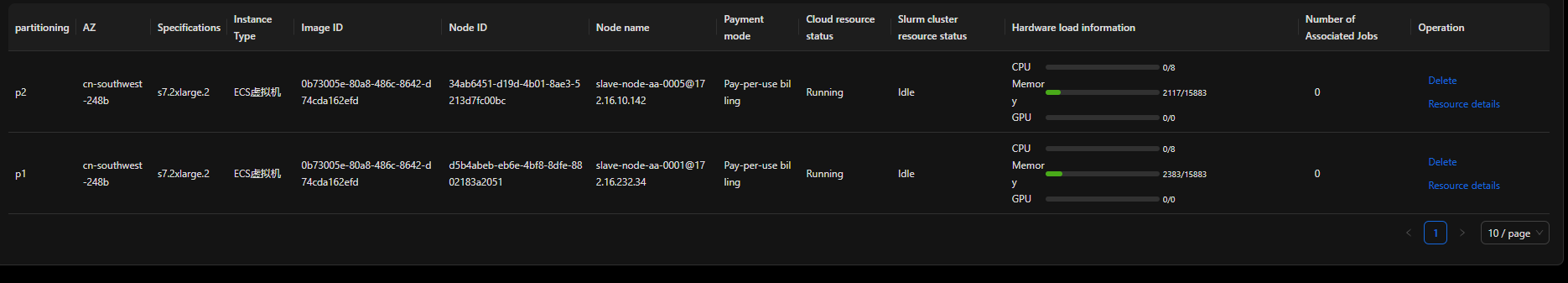
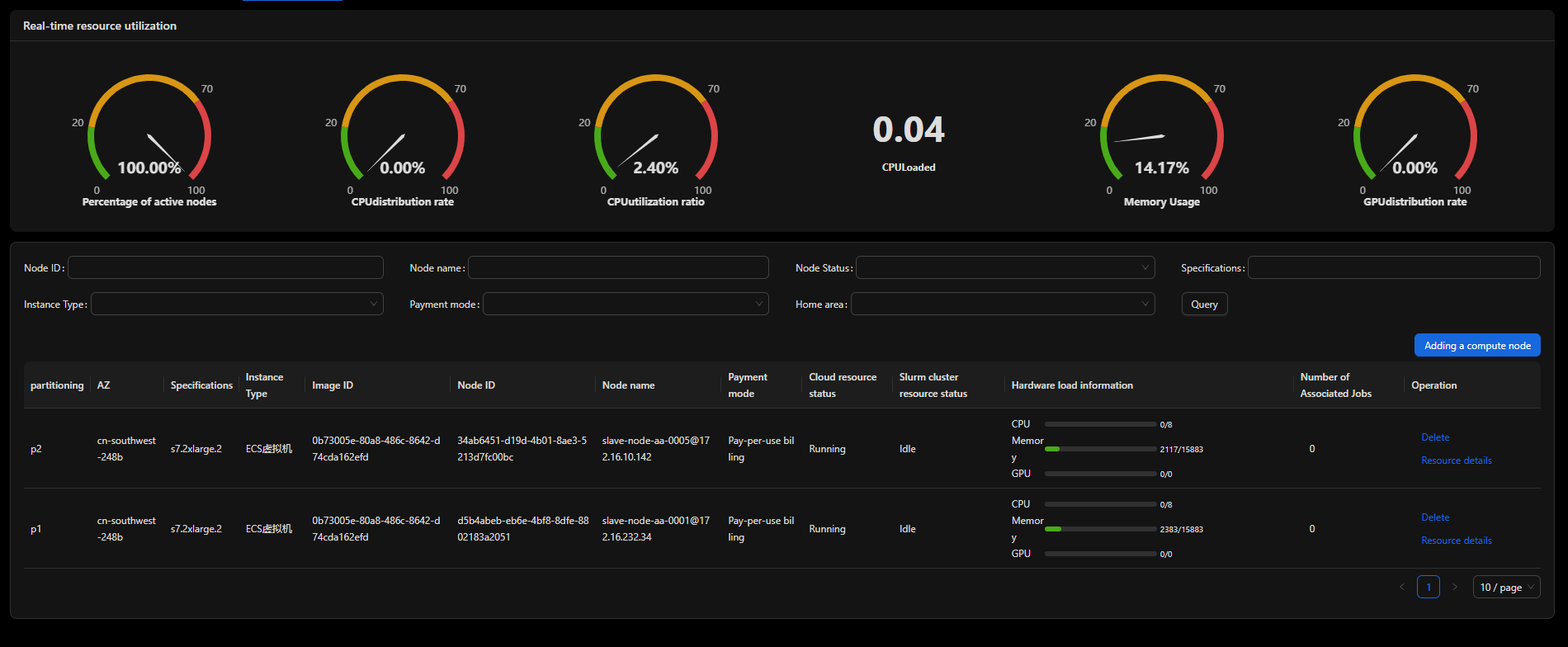
Checking resource scheduling
Check the partitions where the compute nodes are located.
Dynamic Job Scheduling
Job Scheduling Policies
- Backfill scheduling
- Principles: Low-priority small jobs are executed when resources are idle without delaying high-priority jobs.
- Dynamic performance of the HPC Management and Scheduling Plug-in:
- Calculates the earliest start time (EST) of each job in real time.
- Scans queues to schedule jobs for idle resources to process.
- Key dependency: You need to specify the accurate start time (in the --time parameter). Otherwise, the backfilling efficiency decreases.
- Example:
sbatch -p [partition] --time=00:30:00 job.sh # Accurately specify the job start time to facilitate backfilling.
- Preemption
- Principles: When a high-priority job is submitted, Slurm can terminate or suspend low-priority jobs to release resources for use by this high-priority job.
- Preemption mechanisms
Type
Action
Application Scenarios
Requeue
When a job is preempted, it is returned to the queue to be scheduled again later.
Long jobs that can be interrupted
Suspend
A job is paused, allowing higher-priority jobs to run first. Once resources become available, the suspended job resumes.
Running of short-term high-priority jobs
Cancel
The job is terminated completely and does not get rescheduled.
Emergency tasks (exercise caution when setting this value)
- Configuration methods:
Enable the preemption policy in the QoS or partition.
# Create a QoS preemption. sacctmgr add qos low_prio Preempt=high_prio # Allow jobs running under the low_prio QoS to be preempted by jobs associated with the high_prio QoS.
- Dynamic adjustment of the priority
- Fair-share: The priority weights are dynamically calculated based on historical resource usages of users or user groups (for example, CPU hours used in the last 30 days).
sshare -l # Check the fair-share values of users. (A smaller fair-share value means a higher scheduling priority.)
- Real-time feedback mechanism:
- When a user uses more resources than allowed, the user's job priority automatically decreases. Otherwise, the user's job priority increases.
- The weight is calculated using the following formula: Priority = f(Age, FairShare, QoS, Partition,...). The priority is recalculated every several seconds.
- Fair-share: The priority weights are dynamically calculated based on historical resource usages of users or user groups (for example, CPU hours used in the last 30 days).
Dynamical scheduling optimization policies
- On the administrator side
- Enable backfill scheduling:
# Enable backfill scheduling in the slurm.conf file.
SchedulerType=sched/backfill # Use the backfill scheduler. SchedulerParameters=bf_max_job_test=100 # Set the maximum number of jobs that can be scanned during each scheduling.
- Configure the preemption policy.
# Define global preemption rules in slurm.conf. PreemptType=preempt/partition_prio # Preempt by partition priority. PreemptMode=SUSPEND # Suspend jobs, instead of terminating them.
- Set dynamic priority weights.
PriorityType=priority/multifactor # Enable multi-factor priority calculation. PriorityWeightFairshare=1000 # Specify the weight of fair-share usage. PriorityWeightAge=100 # Specify the weight of the job age.
- Enable backfill scheduling:
- On the user side
- Accurately specify resource requirements.
sbatch -p [partition] --ntasks=4 --mem=8G --time=1:00:00 job.sh # Avoid requesting excessive resources.
- Use QoS to improve priority.
sbatch --qos=urgent job.sh # Submit the job to a high-priority QoS queue.
- Accurately specify resource requirements.
Job scheduling monitoring
- Check the backfill scheduling.
scontrol show config | grep Backfill # Check the backfill scheduler status. sdiag -f | grep "Backfill cycle" # Check the backfill scheduling cycles.
- Analyze preemption events.
sacct -X -j <job_id> -o JobID,PreemptedBy # Check the jobs whose resources are preempted by other jobs.
- Track the priority in real time.
sprio -w -j <job_id> # Displays a detailed breakdown of the priority factors influencing a specific job's scheduling.
Typical Scenarios and Solutions
Scenario 1: Small jobs are queued for a long time.
- Problem: Small jobs experience delays when large jobs occupy resources.
- Solution: Enable backfill scheduling with the --time parameter correctly specified.
sbatch --time=00:10:00 small_job.sh # Specify the running time to help backfill.
Scenario 2: An urgent job needs to be executed immediately.
- Problem: High-priority jobs need to preempt resources for running immediately.
- Solution: Add a QoS with preemption enabled.
# Administrator configuration sacctmgr add qos urgent Priority=1000 Preempt=low_prio # Submitted by users sbatch --qos=urgent critical_job.sh
Scenario 3: Uneven resource usages
- Problem: Some nodes are idle, but jobs are still queuing.
- Solution: Check whether the partition configuration is too strict or adjust the node sharing policy (for example, enable OverSubscribe).
Limitations of Dynamic Scheduling
- Time estimation deviation: If the user underestimates the job running time, backfilling will fail. If the user overestimates the job running time, resources will be wasted.
- Preemption cost: Frequent job suspension or restart may increase the system overhead (for example, when the checkpoint mechanism is disabled).
- Configuration complexity: Dynamic scheduling parameters need to be finely adjusted (such as weight allocation and backfilling depth). Improper configuration may reduce the overall efficiency.
Summary
You can set automatic scaling policies to schedule resources to maximize resource utilization. Dynamic job scheduling implements efficient resource utilization through backfilling, preemption, and real-time priority adjustment. You should properly specify the resource requirements and time limits. The administrator needs to optimize scheduling policy parameters (such as the weights and preemption rules).
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot