Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring
Introduction
The Cluster Native Cluster Monitoring add-on (kube-prometheus-stack) uses Prometheus-operator and Prometheus to provide easy-to-use, end-to-end Kubernetes cluster monitoring.
This add-on allows the monitoring data to be interconnected with Monitoring Center so that you can view monitoring data and configure alarms in Monitoring Center.
Open source community: https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus
Permissions
The node-exporter component of the Cluster Native Cluster Monitoring add-on needs to read the Docker info data from the /var/run/docker.sock directory on the host for monitoring the Docker disk space.
The following permission is required for running node-exporter:
- cap_dac_override: reads the Docker info data.
Installing the Add-on
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Add-ons. Locate Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring on the right and click Install.
- On the Install Add-on page, select a version.
- Configure the parameters.
- Interconnecting with AOM: Prometheus data will be reported to AOM. If this option is enabled, you need to select an AOM instance. Basic metrics are free of charge. Custom metrics are billed based on the standard pricing of AOM. For details, see Product Pricing Details. To interconnect with AOM, you must have certain permissions. Only Huawei Cloud accounts, HUAWEI IDs, and IAM users in the admin user group can perform this operation.
- User-defined indicator HPA: Application metrics are automatically collected in the form of service discovery. After this function is enabled, you need to add related configurations to the target application. For details, see Creating an HPA Policy Using Custom Metrics.
- Click Install.
After the add-on is installed, you may need to perform the following operations:
- To use this add-on to provide system resource metrics (such as CPU and memory usage) for workload auto scaling, enable the Metric API. For details, see Providing Resource Metrics Through the Metrics API. After the configuration, you can use Prometheus to collect system resource metrics.
Components
All Kubernetes resources created during kube-prometheus-stack add-on installation are created in the namespace named monitoring.
Component |
Description |
Resource Type |
|---|---|---|
prometheusOperator (workload name: prometheus-operator) |
Deploys and manages the Prometheus Server based on CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs), and monitors and processes the events related to these CRDs. It is the control center of the entire system. |
Deployment |
prometheus (workload name: prometheus-lightweight) |
A Prometheus Server cluster deployed by the operator based on the Prometheus CRDs that can be regarded as StatefulSets. |
StatefulSet |
kubeStateMetrics (workload name: kube-state-metrics) |
Converts the Prometheus metric data into a format that can be identified by Kubernetes APIs.
NOTE:
If the components run in multiple pods, only one pod provides metrics. |
Deployment |
nodeExporter (workload name: node-exporter) |
Deployed on each node to collect node monitoring data. |
Pod |
adapter (workload name: custom-metrics-apiserver) |
Aggregates custom metrics to the native Kubernetes API server. |
Deployment |
Providing Resource Metrics Through the Metrics API
Resource metrics of containers and nodes, such as CPU and memory usage, can be obtained through the Kubernetes Metrics API. Resource metrics can be directly accessed, for example, by using the kubectl top command, or used by HPA or CustomedHPA policies for auto scaling.
The add-on can provide the Kubernetes Metrics API that is disabled by default. To enable the API, create the following APIService object:
apiVersion: apiregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: APIService
metadata:
labels:
app: custom-metrics-apiserver
release: cceaddon-prometheus
name: v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io
spec:
group: metrics.k8s.io
groupPriorityMinimum: 100
insecureSkipTLSVerify: true
service:
name: custom-metrics-apiserver
namespace: monitoring
port: 443
version: v1beta1
versionPriority: 100
You can save the object as a file, name it metrics-apiservice.yaml, and run the following command:
kubectl create -f metrics-apiservice.yaml
Run the kubectl top pod -n monitoring command. If the following information is displayed, the Metrics API can be accessed:
# kubectl top pod -n monitoring NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes) ...... custom-metrics-apiserver-d4f556ff9-l2j2m 38m 44Mi ......

To uninstall the add-on, run the following kubectl command and delete the APIService object. Otherwise, the metrics-server add-on cannot be installed due to residual APIService resources.
kubectl delete APIService v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io
Creating an HPA Policy Using Custom Metrics
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose ConfigMaps and Secrets. Click Create from YAML.
You can add multiple collection rules by adding multiple configurations under the rules field. For details, see Metrics Discovery and Presentation Configuration. The following is an example of a custom collection rule:
kind: ConfigMap apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: user-adapter-config namespace: monitoring data: config.yaml: |- rules: - seriesQuery: 'container_network_receive_bytes_total{namespace!="",pod!=""}' # Original metrics required for scale-out (metrics from kubelet) seriesFilters: [] resources: overrides: namespace: resource: namespace pod: resource: pod name: matches: container_(.*)_total as: "pod_${1}_per_second" # Metric alias metricsQuery: sum(rate(<<.Series>>{<<.LabelMatchers>>}[30s])) by (<<.GroupBy>>) # Metric change rate of all containers for a workload within 30s
In the preceding example, the aggregation time is 30s. If this time is set to a value less than 15s (a collection period), the metrics may be inaccurate.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Add-ons. In the right pane, locate the Cloud Native Cluster Monitoring add-on, click Edit in the Operation column, and enable the custom metric HPA.
Click Install.

You need to create collection rules described in 2 and then enable the custom metric HPA to trigger add-on redeployment for custom metric collection to take effect.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Workloads. Locate the workload for which you want to create an HPA policy and choose More > Auto Scaling. In the Custom Policy area, you can select the preceding parameters to create an auto scaling policy.

After a workload is created, create an HPA policy unless all pods for that workload are ready and the metrics of the first collection period are collected.
Figure 1 Creating an HPA policy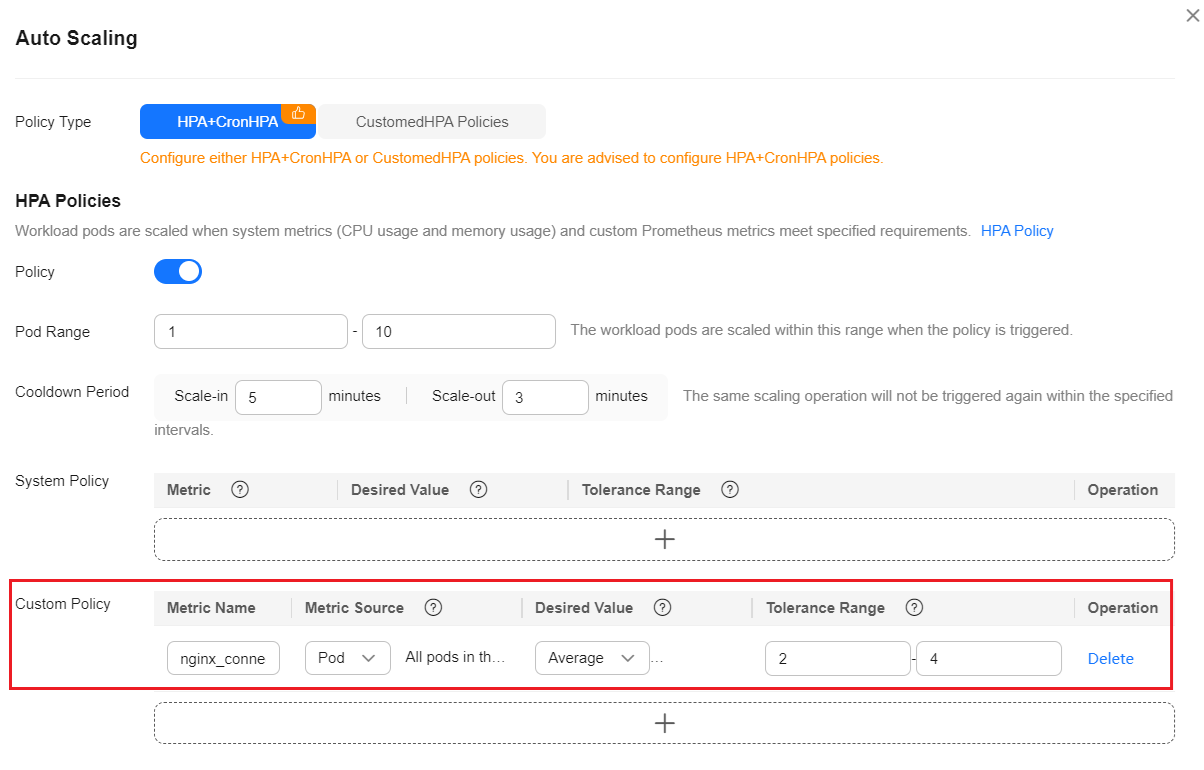
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot








