Despliegue híbrido de trabajos en línea y fuera de línea
Trabajos en línea y fuera de línea
Los trabajos se pueden clasificar en trabajos en línea y trabajos fuera de línea en función de si los servicios están siempre en línea.
- Online job: Estos trabajos se ejecutan durante mucho tiempo, con aumentos de tráfico regulares, solicitudes de recursos de marea y altos requisitos en SLA, como servicios de publicidad y comercio electrónico.
- Offline jobs: Estos trabajos se ejecutan durante poco tiempo, tienen altos requisitos de cómputo y pueden tolerar una alta latencia, como la IA y los servicios de big data.
Sobresuscripción de recursos y despliegue híbrido
Muchos servicios ven aumentos en el tráfico. Para garantizar el rendimiento y la estabilidad, a menudo se solicitan recursos al máximo necesario. Sin embargo, las oleadas pueden disminuir muy pronto y los recursos, si no se liberan, se desperdician en horas no pico. Especialmente para trabajos en línea que solicitan una gran cantidad de recursos para garantizar el SLA, la utilización de recursos puede ser tan baja como sea posible.
La sobresuscripción de recursos es el proceso de hacer uso de los recursos solicitados inactivos. Los recursos sobresuscritos son adecuados para desplegar trabajos sin conexión, que se centran en el rendimiento, pero tienen bajos requisitos de SLA y pueden tolerar ciertos fallos.
El despliegue híbrido de trabajos en línea y sin conexión en un clúster pueden utilizar mejor los recursos del clúster.
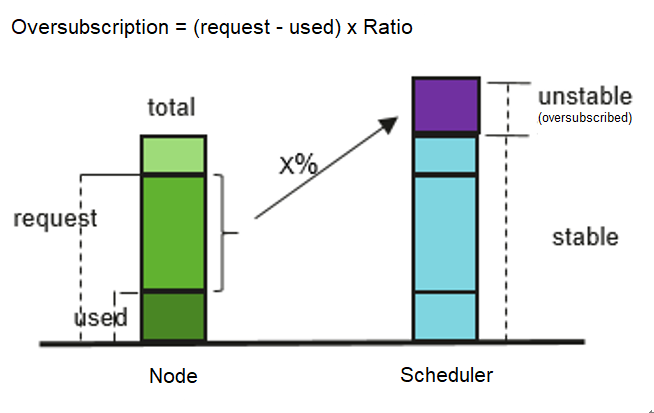
Sobresuscripción para despliegue híbrido
Se admite el despliegue híbrido, y los recursos de CPU y memoria se pueden sobresuscribir. Las características clave son las siguientes:
- Los trabajos sin conexión se ejecutan preferentemente en los nodos sobresuscritos.
Si existen los nodos sobresuscritos y no sobresuscritos, el primero puntuará más alto que el último y los trabajos fuera de línea se programan preferentemente para los nodos sobresuscritos.
- Los trabajos en línea solo pueden usar recursos que no estén sobresuscritos si se programan para un nodo sobresuscrito.
Los trabajos sin conexión pueden utilizar recursos tanto sobresuscritos como no sobresuscritos de un nodo sobresuscrito.
- En el mismo período de programación, los trabajos en línea tienen prioridad sobre los trabajos sin conexión.
Si existen trabajos en línea y sin conexión, los trabajos en línea se programan primero. Cuando el uso de recursos de nodo excede el límite superior y las solicitudes de nodo superan el 100%, se desalojarán los trabajos sin conexión.
- El aislamiento de CPU/memoria es proporcionado por los núcleos.
Aislamiento de CPU: Los trabajos en línea pueden adelantarse rápidamente a los recursos de CPU de los trabajos sin conexión y suprimir el uso de CPU de los trabajos sin conexión.
Aislamiento de memoria: cuando se agotan los recursos de memoria del sistema y se activa OOM Kill, el núcleo desaloja primero los trabajos sin conexión.
- Reglas de admisión de trabajos sin conexión de kubelet:
Después de programar el pod en un nodo, kubelet inicia el pod solo cuando los recursos del nodo pueden cumplir con la solicitud de pod (predicateAdmitHandler.Admit). kubelet inicia el pod cuando se cumplen las dos condiciones siguientes:
- La solicitud total de pods que se iniciarán y los trabajos en ejecución en línea < nodos asignables
- La solicitud total de pods que se iniciarán y el trabajo en ejecución online/offline < nodos asignables+nodos sobresuscritos
- Sobresuscripción de recursos y despliegue híbrido:
Si solo se utiliza el despliegue híbrido, debe configurar la etiqueta volcano.sh/colocation=true para el nodo y eliminar la etiqueta de nodo volcano.sh/oversubscription o establecer su valor en false.
Si la etiqueta volcano.sh/colocation=true está configurada para un nodo, el despliegue híbrido está habilitado. Si la etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscription=true está configurada, la sobresuscripción de recursos está habilitada. En la siguiente tabla se enumeran las combinaciones de funciones disponibles después de activar el despliegue híbrido o la sobresuscripción de recursos.Despliegue híbrido activado (volcano.sh/colocation=true)
Sobresuscripción de recursos activada(volcano.sh/oversubscription=true)
¿Usar recursos sobresuscritos?
Condiciones para desalojar los pod fuera de línea
No
No
No
No hay
Sí
No
No
El uso de recursos de nodo excede el umbral alto.
No
Sí
Sí
El uso de recursos de nodo excede el umbral alto, y la solicitud de nodo excede el 100%.
Sí
Sí
Sí
El uso de recursos de nodo excede el umbral alto.
Notas y restricciones
- Versión del clúster
- v1.19: v1.19.16-r4 o posterior
- v1.21: v1.21.7-r0 o posterior
- v1.23: v1.23.5-r0 o posterior
- v1.25 o posterior
- Tipo de clúster: CCE o CCE Turbo
- Sistema operativo del nodo: EulerOS 2.9 (kernel-4.18.0-147.5.1.6.h729.6.eulerosv2r9.x86_64) o Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0
- Tipo de nodo: ECS
- La versión adicional del volcán: 1.7.0 o posterior
- Antes de activar el complemento de sobresuscripción del volcán, asegúrese de que el complemento de sobresuscripción no esté activado.
- La modificación de la etiqueta de un nodo sobresuscrito no afecta a los pods en ejecución.
- Los pods en ejecución no se pueden convertir entre servicios en línea y sin conexión. Para convertir los servicios, necesita reconstruir los pods.
- Si la etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscription=true está configurada para un nodo del clúster, la configuración oversubscription debe agregarse al complemento volcán. De lo contrario, la planificación de los nodos sobrevendidos será anormal. Asegúrese de que ha configurado correctamente las etiquetas porque el planificador no comprueba las configuraciones de complementos y nodos. Para obtener más información sobre las etiquetas, consulte Configuración de etiquetas de sobresuscripción para la programación.
- Para deshabilitar la sobresuscripción, realice las siguientes operaciones:
- Quite la etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscription del nodo sobresuscrito.
- Establezca over-subscription-resource a false.
- Modifique el mapa de configuración del planificador del volcán llamado volcano-scheduler-configmap y quite el complemento de sobresuscripción.
- Si cpu-manager-policy se establece en enlace de núcleo estático en un nodo, no asigne la clase QoS de Guaranteed a los pods sin conexión. Si se requiere la unión del núcleo, cambie los pods a los en línea. De lo contrario, los pods sin conexión pueden ocupar la CPU de los pods en línea, causando errores de inicio de pods en línea, y los pods sin conexión no se pueden iniciar aunque se programan correctamente.
- Si cpu-manager-policy se establece como enlace de núcleo estático en un nodo, no enlaza núcleos a todos los pods en línea. De lo contrario, los pods en línea ocupan todos los recursos de CPU o memoria, dejando un pequeño número de recursos sobresuscritos.
Configuración de etiquetas de sobresuscripción para la programación
Si la etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscription=true está configurada para un nodo del clúster, la configuración oversubscription debe agregarse al complemento volcán. De lo contrario, la planificación de los nodos sobrevendidos será anormal. Para obtener más información sobre la configuración relacionada, consulte Tabla 1.
Uso del despliegue híbrido
- Configurar el complemento de volcano.
- Utilice kubectl para conectarse al clúster.
- Instale el complemento de volcado y agregue el complemento oversubscription a volcano-scheduler-configmap. Asegúrese de que la configuración del complemento no contenga el complemento overcommit. Si - name: overcommit existe, elimine esta configuración.
# kubectl edit cm volcano-scheduler-configmap -n kube-system apiVersion: v1 data: volcano-scheduler.conf: | actions: "enqueue, allocate, backfill" tiers: - plugins: - name: gang - name: priority - name: conformance - name: oversubscription - plugins: - name: drf - name: predicates - name: nodeorder - name: binpack - plugins: - name: cce-gpu-topology-predicate - name: cce-gpu-topology-priority - name: cce-gpu
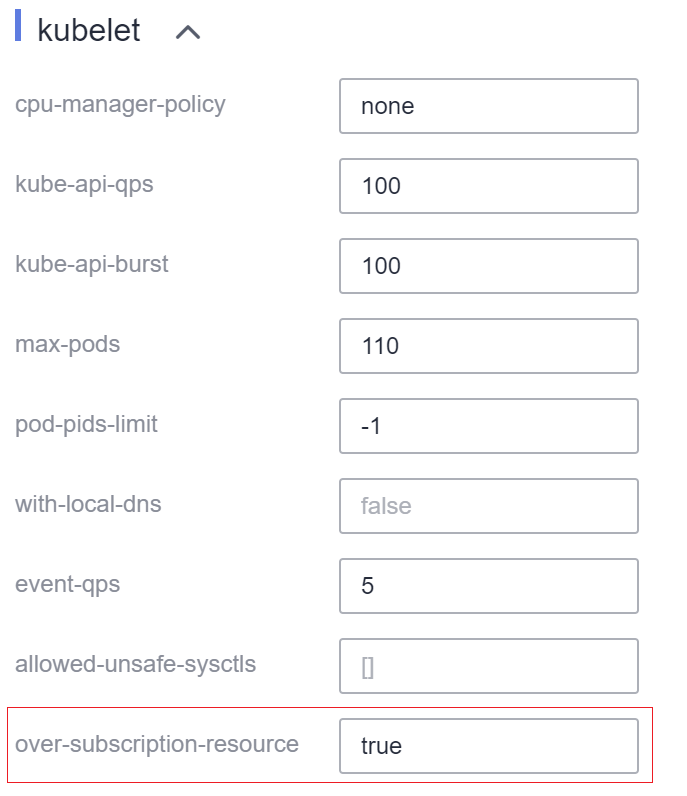
- Habilite la función de sobresuscripción de nodo.
Una etiqueta se puede configurar para usar recursos sobresuscritos solo después de que la función sobresuscripción esté habilitada para un nodo. Los nodos relacionados solo se pueden crear en un grupo de nodos. Para habilitar la función de sobresuscripción, realice los siguientes pasos:
- Cree un grupo de nodos.
- Elija More > Manage en la columna Operation del grupo de nodos creado.
- En la ventana Manage Component que se muestra, establezca over-subscription-resource en kubelet en true y haga clic en OK.
- Establezca la etiqueta de sobresuscripción del nodo.
La etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscription debe configurarse para un nodo sobresuscrito. Si esta etiqueta se establece para un nodo y el valor es true, el nodo es un nodo sobresuscrito. De lo contrario, el nodo no es un nodo sobresuscrito.
kubectl label node 192.168.0.0 volcano.sh/oversubscription=true
Un nodo con sobresuscripción también admite los umbrales de sobresuscripción, como se indica en Tabla 2. Por ejemplo:
kubectl annotate node 192.168.0.0 volcano.sh/evicting-cpu-high-watermark=70
Consultar la información del nodo
# kubectl describe node 192.168.0.0 Name: 192.168.0.0 Roles: <none> Labels: ... volcano.sh/oversubscription=true Annotations: ... volcano.sh/evicting-cpu-high-watermark: 70Tabla 2 Anotaciones de sobresuscripción de nodos Nombre
Descripción
volcano.sh/evicting-cpu-high-watermark
Cuando el uso de CPU de un nodo excede el valor especificado, se activa el desalojo de trabajo sin conexión y el nodo se vuelve impredecible.
El valor predeterminado es 80, que indica que el desalojo de trabajos sin conexión se activa cuando el uso de CPU de un nodo supera el 80%.
volcano.sh/evicting-cpu-low-watermark
Después de activar el desalojo, la programación comienza de nuevo cuando el uso de CPU de un nodo es menor que el valor especificado.
El valor predeterminado es 30, que indica que la programación comienza de nuevo cuando el uso de CPU de un nodo es inferior al 30%.
volcano.sh/evicting-memory-high-watermark
Cuando el uso de memoria de un nodo excede el valor especificado, se activa el desalojo del trabajo sin conexión y el nodo se vuelve impredecible.
El valor predeterminado es 60, que indica que el desalojo del trabajo sin conexión se activa cuando el uso de memoria de un nodo supera el 60%.
volcano.sh/evicting-memory-low-watermark
Después de activar el desalojo, la programación comienza de nuevo cuando el uso de memoria de un nodo es menor que el valor especificado.
El valor por defecto es el 30 que indica que la programación comienza de nuevo cuando el uso de memoria de un nodo es inferior al 30%.
volcano.sh/oversubscription-types
Tipo de recurso sobresuscrito. Las opciones son las siguientes:
- CPU (CPU con sobresuscripción)
- memoria (memoria sobresuscrita)
- cpu,memoria (sobresuscritas CPU y memoria)
El valor predeterminado es cpu,memory.
- Despliegue los trabajos en línea y fuera de línea.
La etiqueta volcano.sh/qos-level debe agregarse a la anotación para distinguir los trabajos sin conexión. El valor es un entero que oscila entre -7 y 7. Si el valor es menor que 0, el trabajo es un trabajo sin conexión. Si el valor es mayor o igual que 0, el trabajo es un trabajo de alta prioridad, es decir, un trabajo en línea. No es necesario establecer esta etiqueta para los trabajos en línea. Para los trabajos en línea y fuera de línea, establezca schedulerName en volcano para habilitar el programador Volcano.
Las prioridades de los trabajos online/online y offline/offline no se diferencian, y la validez del valor no se verifica. Si el valor de volcano.sh/qos-level de un trabajo sin conexión no es un entero negativo que oscila entre -7 y 0, el trabajo se procesa como un trabajo en línea.
Para un trabajo fuera de línea:
kind: Deployment apiVersion: apps/v1 spec: replicas: 4 template: metadata: annotations: metrics.alpha.kubernetes.io/custom-endpoints: '[{"api":"","path":"","port":"","names":""}]' volcano.sh/qos-level: "-1" # Offline job label spec: schedulerName: volcano # The Volcano scheduler is used. ...Para un trabajo en línea:
kind: Deployment apiVersion: apps/v1 spec: replicas: 4 template: metadata: annotations: metrics.alpha.kubernetes.io/custom-endpoints: '[{"api":"","path":"","port":"","names":""}]' spec: schedulerName: volcano # The Volcano scheduler is used. ... - Ejecute el siguiente comando para comprobar el número de recursos sobresuscritos y el uso de recursos:
kubectl describe el nodo <nodeIP>
# kubectl describe node 192.168.0.0 Name: 192.168.0.0 Roles: <none> Labels: ... volcano.sh/oversubscription=true Annotations: ... volcano.sh/oversubscription-cpu: 2335 volcano.sh/oversubscription-memory: 341753856 Allocatable: cpu: 3920m memory: 6263988Ki Allocated resources: (Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.) Resource Requests Limits -------- -------- ------ cpu 4950m (126%) 4950m (126%) memory 1712Mi (27%) 1712Mi (27%)
Ejemplo de despliegue híbrido
A continuación se utiliza un ejemplo para describir cómo desplegar trabajos en línea y sin conexión en modo híbrido.
- Suponga que un clúster tiene dos nodos: un nodo sobresuscrito y un nodo no sobresuscrito.
# kubectl get node NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION 192.168.0.173 Ready <none> 4h58m v1.19.16-r2-CCE22.5.1 192.168.0.3 Ready <none> 148m v1.19.16-r2-CCE22.5.1
- 192.168.0.173 es un nodo sobresuscrito (con la etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscirption=true).
- 192.168.0.3 es un nodo no sobresuscrito (sin la etiqueta volcano.sh/oversubscirption=true).
# kubectl describe node 192.168.0.173 Name: 192.168.0.173 Roles: <none> Labels: beta.kubernetes.io/arch=amd64 ... volcano.sh/oversubscription=true - Enviar solicitudes de creación de trabajos sin conexión. Si los recursos son suficientes, todos los trabajos sin conexión se programarán en el nodo sobresuscrito.
La plantilla de trabajo sin conexión es la siguiente:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: offline namespace: default spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: offline template: metadata: labels: app: offline annotations: volcano.sh/qos-level: "-1" # Offline job label spec: schedulerName: volcano # The Volcano scheduler is used. containers: - name: container-1 image: nginx:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: requests: cpu: 500m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: "1" memory: 512Mi imagePullSecrets: - name: default-secretLos trabajos sin conexión se programan en el nodo sobresuscrito.# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE offline-69cdd49bf4-pmjp8 1/1 Running 0 5s 192.168.10.178 192.168.0.173 offline-69cdd49bf4-z8kxh 1/1 Running 0 5s 192.168.10.131 192.168.0.173
- Envíe solicitudes de creación de empleo en línea. Si los recursos son suficientes, los trabajos en línea se programarán para el nodo no sobresuscrito.
La plantilla de trabajo en línea es la siguiente:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: online namespace: default spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: online template: metadata: labels: app: online spec: schedulerName: volcano # The Volcano scheduler is used. containers: - name: container-1 image: resource_consumer:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: requests: cpu: 1400m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: "2" memory: 512Mi imagePullSecrets: - name: default-secretLos trabajos en línea se programan para el nodo no sobresuscrito.# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE online-ffb46f656-4mwr6 1/1 Running 0 5s 192.168.10.146 192.168.0.3 online-ffb46f656-dqdv2 1/1 Running 0 5s 192.168.10.67 192.168.0.3
- Mejore el uso de recursos del nodo sobresuscrito y observe si se activa el desalojo de trabajos sin conexión.
Despliegue trabajos en línea en el nodo sobresuscrito (192.168.0.173).
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: online namespace: default spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: online template: metadata: labels: app: online spec: affinity: # Submit an online job to an oversubscribed node. nodeAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - 192.168.0.173 schedulerName: volcano # The Volcano scheduler is used. containers: - name: container-1 image: resource_consumer:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent resources: requests: cpu: 700m memory: 512Mi limits: cpu: 700m memory: 512Mi imagePullSecrets: - name: default-secretEnvíe los trabajos en línea o sin conexión al nodo sobresuscrito (192.168.0.173) al mismo tiempo.# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE offline-69cdd49bf4-pmjp8 1/1 Running 0 13m 192.168.10.178 192.168.0.173 offline-69cdd49bf4-z8kxh 1/1 Running 0 13m 192.168.10.131 192.168.0.173 online-6f44bb68bd-b8z9p 1/1 Running 0 3m4s 192.168.10.18 192.168.0.173 online-6f44bb68bd-g6xk8 1/1 Running 0 3m12s 192.168.10.69 192.168.0.173
Observe el nodo sobresuscrito (192.168.0.173). Puede encontrar que existen recursos sobresuscritos y que la tasa de asignación de CPU supera el 100%.# kubectl describe node 192.168.0.173 Name: 192.168.0.173 Roles: <none> Labels: … volcano.sh/oversubscription=true Annotations: … volcano.sh/oversubscription-cpu: 2343 volcano.sh/oversubscription-memory: 3073653200 … Allocated resources: (Total limits may be over 100 percent, i.e., overcommitted.) Resource Requests Limits -------- -------- ------ cpu 4750m (121%) 7350m (187%) memory 3760Mi (61%) 4660Mi (76%) …Aumente el uso de la CPU de los trabajos en línea en el nodo. Se activa el desalojo de trabajo sin conexión.# kubectl get pod -o wide NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE offline-69cdd49bf4-bwdm7 1/1 Running 0 11m 192.168.10.208 192.168.0.3 offline-69cdd49bf4-pmjp8 0/1 Evicted 0 26m <none> 192.168.0.173 offline-69cdd49bf4-qpdss 1/1 Running 0 11m 192.168.10.174 192.168.0.3 offline-69cdd49bf4-z8kxh 0/1 Evicted 0 26m <none> 192.168.0.173 online-6f44bb68bd-b8z9p 1/1 Running 0 24m 192.168.10.18 192.168.0.173 online-6f44bb68bd-g6xk8 1/1 Running 0 24m 192.168.10.69 192.168.0.173
Sugerencias sobre el manejo
- Después de reiniciar el kubelet del nodo sobresuscrito, la vista de recursos del planificador del volcano no se sincroniza con la de kubelet. Como resultado, OutOfCPU se produce en algunos trabajos programados recientemente, lo cual es normal. Después de un período de tiempo, el programador de Volcano puede programar correctamente trabajos en línea y fuera de línea.
- Después de enviar trabajos en línea y fuera de línea, no se recomienda cambiar dinámicamente el tipo de trabajo (agregando o eliminando anotación _volcano.sh/qos-level: "-1" ) porque el núcleo actual no admite el cambio de un trabajo fuera de línea a un trabajo en línea.
- CCE recopila el uso de recursos (CPU/memoria) de todos los pods que se ejecutan en un nodo basado en la información de estado en el sistema cgroups. El uso de recursos puede ser diferente del uso de recursos monitorizado, por ejemplo, las estadísticas de recursos mostradas ejecutando el commando top.
- Puede agregar recursos sobresuscritos (como CPU y memoria) en cualquier momento.
Puede reducir los tipos de recursos sobresuscritos solo cuando la tasa de asignación de recursos no exceda del 100%.






