Pay-per-Use
Pay-per-use allows you to use resources before paying for them. It is recommended when you do not want to pay in advance or do not need the resources for long. This section describes the pay-per-use billing rules of exclusive ServiceComb engines.
Scenario
Pay-per-use is suitable for applications or services that cannot be interrupted when facing temporary or sudden traffic increases or unpredictable demands, such as e-commerce flash sales, testing, and scientific computing.
Billing Items
Select ServiceComb engine specifications based on the total number of microservice instances to be hosted. You will be billed for specifications you selected. The following items can be billed on a pay-per-use basis.
|
Billing Item |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Unit price of ServiceComb engine instance specifications (price per hour) |
You are billed for your selected engine instance specifications. ServiceComb engines support 100, 200, 500, or 2000 microservice instances. For details, see Pricing Details of Exclusive ServiceComb Engines. |
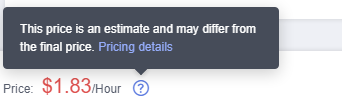
Example: When you purchase an exclusive ServiceComb engine that supports 100 microservice instances, fee details are at the bottom of the purchase page, as shown in Figure 1.

The prices are for reference only. Actual prices are subject to those in Pricing Details of Exclusive ServiceComb Engines.
Billing Cycle
In pay-per-use mode, exclusive ServiceComb engines are billed by second and settled by hour (UTC+08:00). After the settlement is complete, a new billing cycle starts. The billing starts when an engine is created, and stops when the engine is deleted.
For example, you purchased an exclusive ServiceComb engine at 08:05:00 and deleted it at 08:55:00. The billing cycle is from 08:00:00 to 09:00:00. You need to pay the fees generated from 08:05:00 to 08:55:00. There is a total of 3000s.
Billing Example
You purchased an exclusive pay-per-use ServiceComb engine (that supports 100 microservice instances) at 09:59:30 on April 18, 2023 and then deleted it at 10:45:46 on the same day.
- The first billing cycle is from 09:00:00 to 10:00:00. You need to pay the fees generated from 09:59:30 to 10:00:00. There is a total of 30s. The fee in this billing cycle is 1.83/3600 x 30 = $0.02 USD.
- The second billing cycle is from 10:00:00 to 11:00:00. You need to pay the fees generated from 10:00:00 to 10:45:46. There is a total of 2746s. The fee in this billing cycle is 1.83/3600 x 2746 = $1.40 USD.
You need to pay for each billing cycle. Table 2 lists the billing formula. The price of a resource listed in the product pricing details is per hour, so divide it by 3600 to obtain the price for each second.
|
Resource |
Billing Formula |
Unit Price |
|---|---|---|
|
Exclusive ServiceComb engines |
Unit price of instance specifications x Billing duration |
For details, see Pricing Details of Exclusive ServiceComb Engines. |

The prices are for reference only. Actual prices are subject to those in Pricing Details of Exclusive ServiceComb Engines.
Arrears Impact
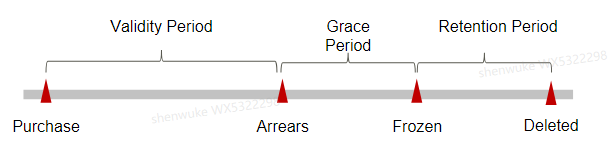
For the lifecycle of exclusive pay-per-use ServiceComb engines, see Figure 2. Once purchased, resources run within the billing cycle. This is their validity period. If your account is in arrears due to automatic fee deduction, your resources enter the grace period and then the retention period.
Arrears Alert
The system will deduct fees for pay-per-use resources at the end of each billing cycle. You will be notified by email, SMS, or internal messages when your account is in arrears.
Arrears Impact
Your account may be in arrears due to automatic fee deduction for exclusive ServiceComb engines. However, your resources will not be stopped immediately; instead, they enter the grace period. You will need to pay for the fees incurred during the grace period, which you can see on the Billing & Costs > Billing Center > Overview page of the Huawei Cloud console. Huawei Cloud will automatically deduct this amount when you top up.
If you do not pay the arrears within the grace period, your resources will enter the retention period and become frozen. You cannot perform any operations on the pay-per-use resources during this period.
If you do not pay the outstanding amount after the retention period expires, your engines will be deleted and their data cannot be recovered.
Both the grace and retention periods are 15 days.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot