Billing Examples
Scenario 1
On May 15, 2025, CAE hosted a microservice application and provided services for users.
- Specifications: one 4 vCPU | 8 GiB component and two 1 vCPU | 2 GiB components.
- Running: The application started at 10:00:00 and stopped at 15:00:00 every day. During peak hours (11:00:00-12:30:00), the 4 vCPU | 8 GiB component expanded to five instances, and the 1 vCPU | 2 GiB components expanded to three instances. During off-peak hours, each component required two instances to process services. 2.56 GB of traffic data was used in total.
- Off-peak hours: 210 min/day x 15 days = 3,150 min
- Peak hours: 90 min/day x 15 days = 1,350 min
- Traffic: 2.56 GB/day x 15 days = 38.4 GB
- The prices in the figure are for reference only. The actual calculation is subject to the prices in CAE Pricing Details.
- In this example, the vCPU and memory specifications did not exceed the minimum specifications. So they were billed based on the minimum specifications (8 vCPU | 32 GiB) using the premium unit price.
Figure 1 Total price for a pay-per-use CAE instance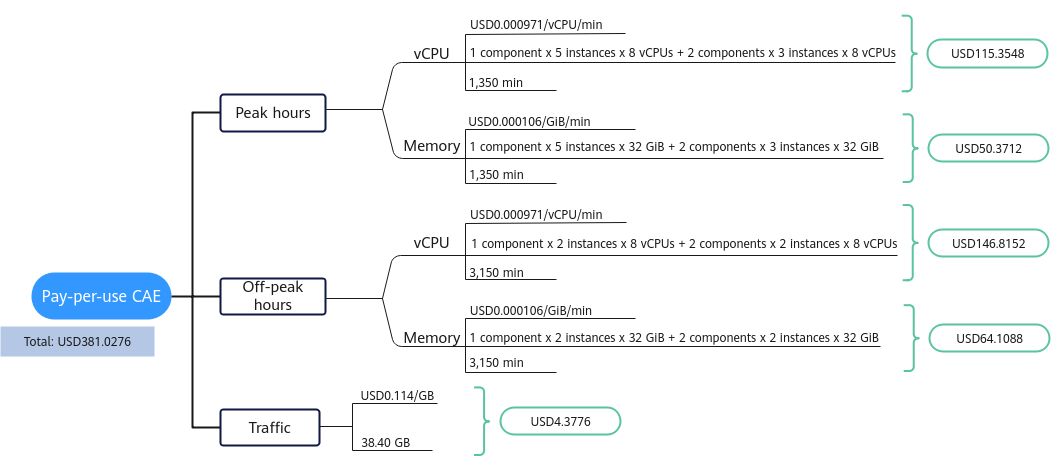
Scenario 2
CAE hosted many applications, and used 15,000 core-hours of vCPUs, 30,000 GiB-hours of memory, and 1 TB of traffic data in a month.
Billing Analysis
- Unit prices in this example are used for reference only, and the calculated prices are estimated fees. As unit prices may change from time to time, the calculated prices may differ from actual prices. For details, see the data released on the Huawei Cloud official website.
- In this example, the vCPU and memory specifications (15,000 vCPU | 30,000 GiB) exceed the minimum specifications. You were billed for:
- Specifications at or below the minimum specifications (8 vCPU | 32 GiB). This portion is billed based on the premium unit price.
- Specifications in excess of the minimum specifications. This portion (14,992 vCPU | 29,968 GiB) is billed based on the general unit price.
|
Billing Mode |
Formula |
Billing Cycle |
Price |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Pay-per-use |
vCPU: Instance specification unit price x Instance specifications x Usage duration |
Monthly |
CPU: 0.05826 (USD/core-hour) x 8 (core-hour) + 0.080898 (USD/core-hour) x 14992 (core-hour) = USD1213.288896/month |
|
Memory: Instance specification unit price x Instance specifications x Usage duration |
Memory: 0.00636 (USD/GiB-hour) x 32 (GiB-hour) + 0.00885 (USD/GiB-hour) x 29968 (GiB-hour) = USD265.42032/month |
||
|
Traffic: Traffic unit price x Traffic volume |
Traffic: $116.736 USD/TB x 1 TB = $116.736 USD/month |
||
|
Total |
USD1595.445216/month |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





