Codec for Strings and Variable-Length Strings
Scenarios
A smoke detector provides the following functions:
- Reporting smoke alarms (fire severity) and temperature simultaneously, or reporting the temperature separately.
- Reporting description. The data type of description can be string (string type) or varstring (variable-length string type).
 NOTE:
NOTE:
This scenario describes how to develop a codec for data in strings and data in variable-length strings. The data reporting and command delivery codecs are developed in the same way. Therefore, data reporting is used as an example and command delivery is not described.
Defining the Profile File
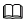
Define the profile file in the development space of the smoke sensor.
Developing a Codec
This section describes only the procedure for developing the codec for reporting the description (other_info). For details on how to develop the codec for reporting the smoke alarms (level) and temperature (temperature), see Codec for Multiple Data Reporting Messages.
- In the development space of the smoke sensor, click Codec Development.

- Configure a data reporting message to report the fire severity and temperature. For details, see 2.
- Configure a data reporting message to report only the temperature. For details, see 3.
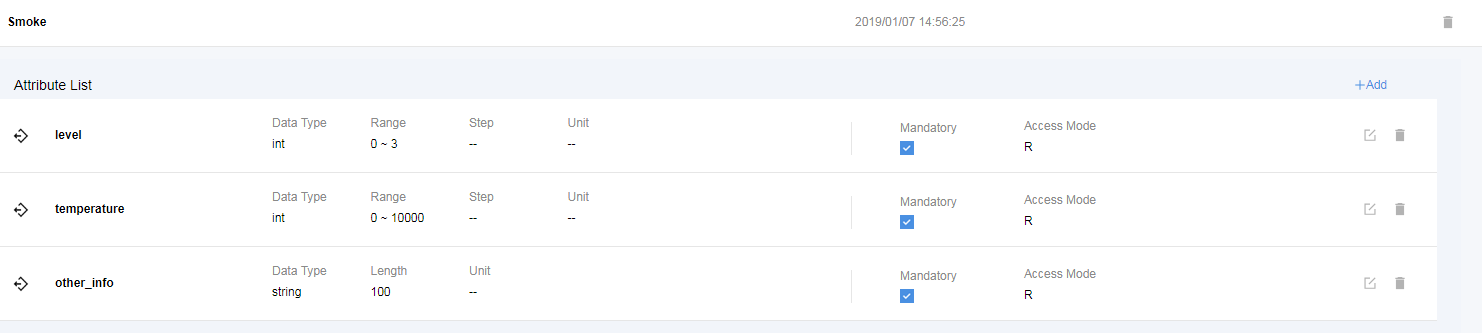
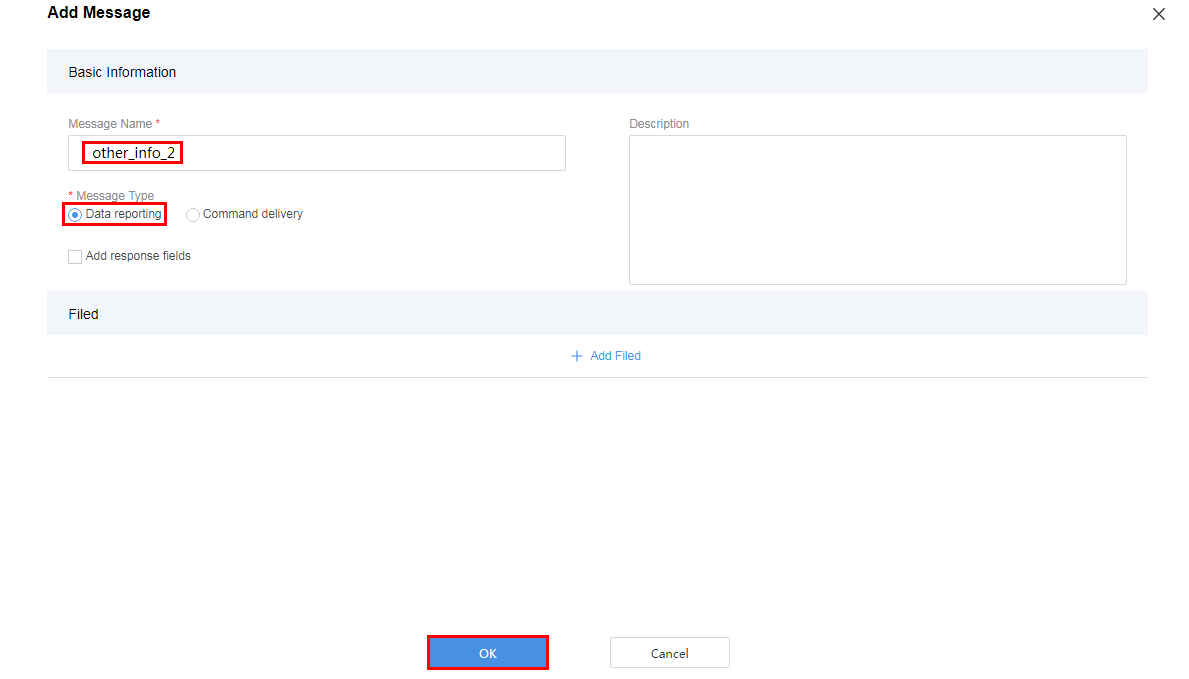
- Configure a data reporting message to report the description of the string type.
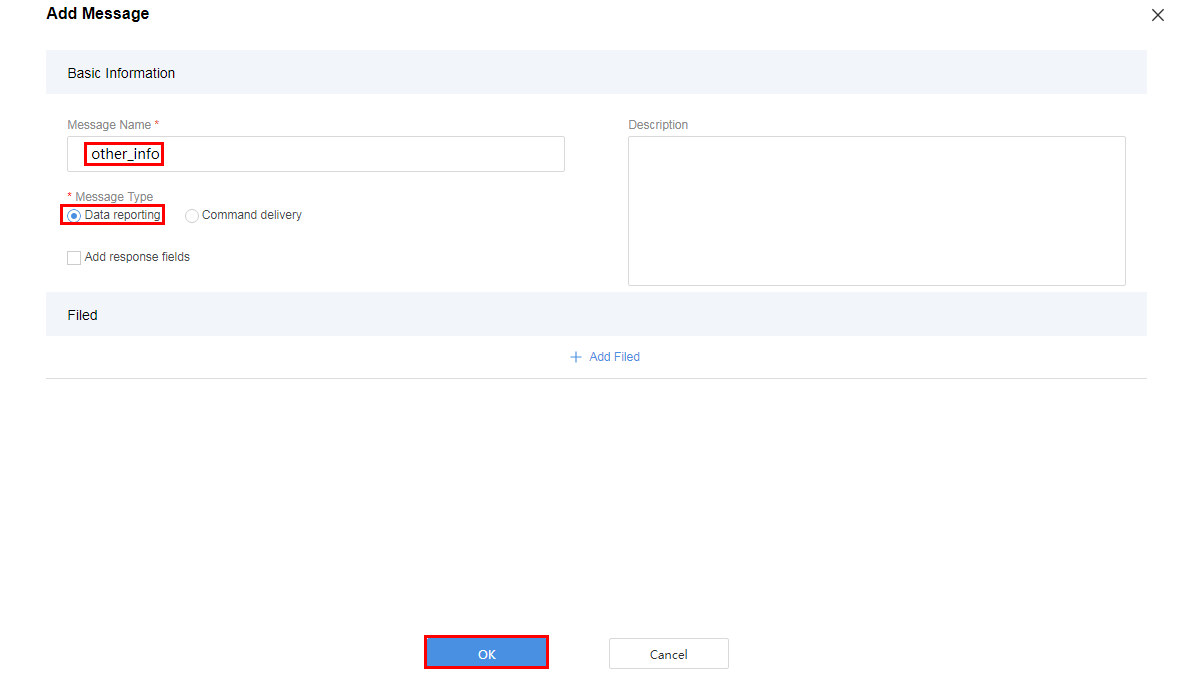
Add the messageId field to indicate the message type. In this scenario, the value 0x0 is used to identify the message that reports the fire severity and temperature, 0x1 is used to identify the message that reports only the temperature, and 0x2 is used to identify the message that reports the description (of the string type).
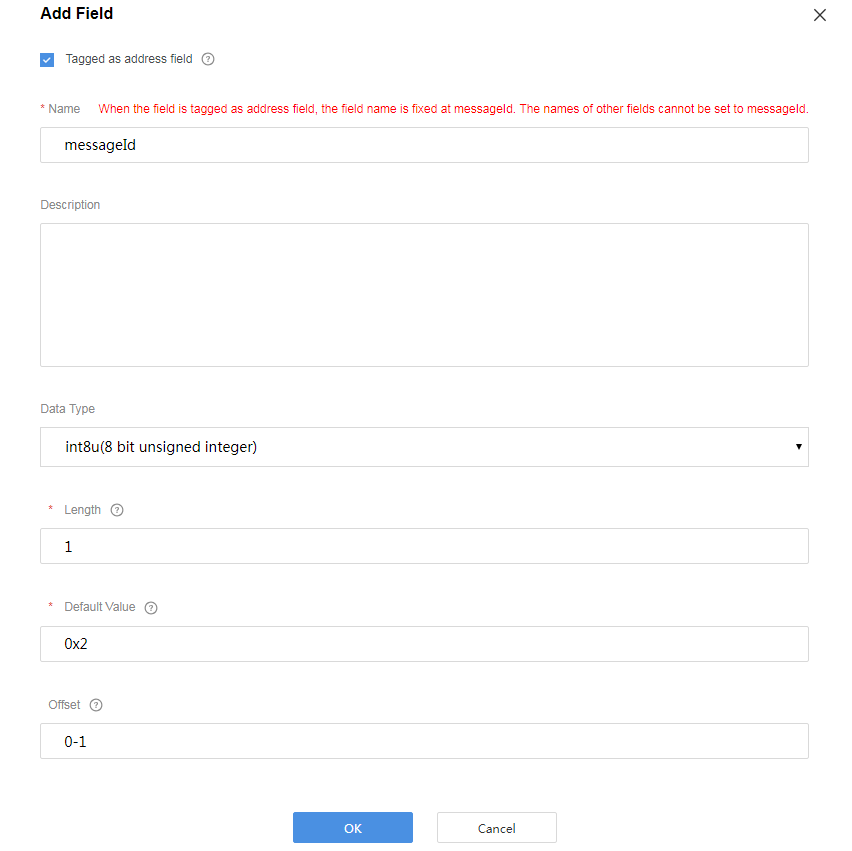
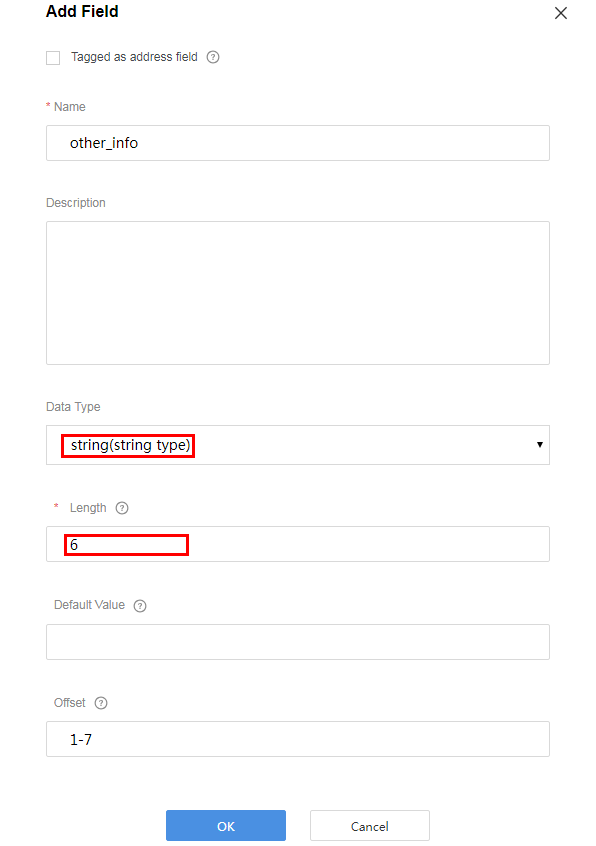
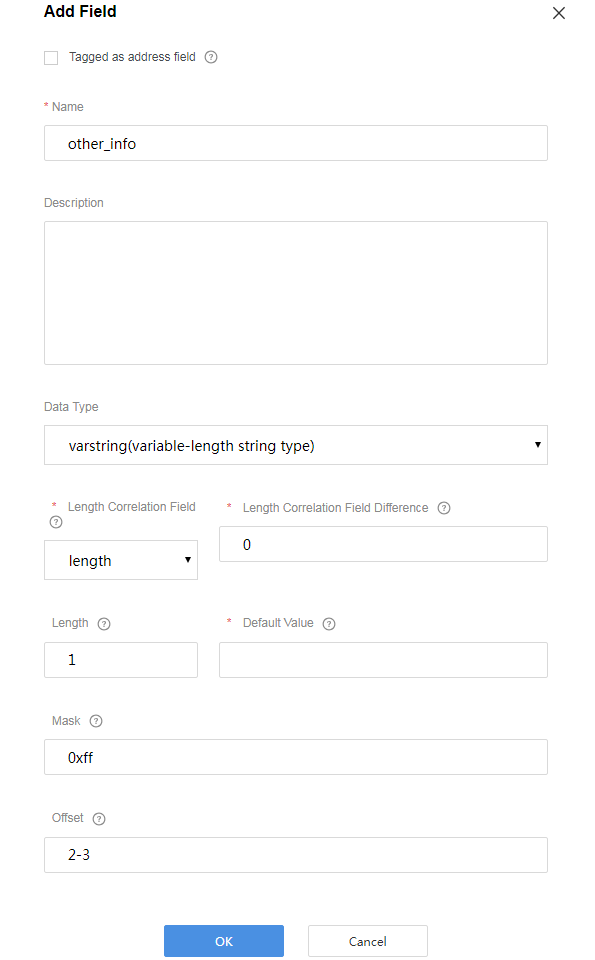
Add the other_info field to indicate the description of the string type. In this scenario, set Length to 6.
- Configure a data reporting message to report the description of the variable-length string type.
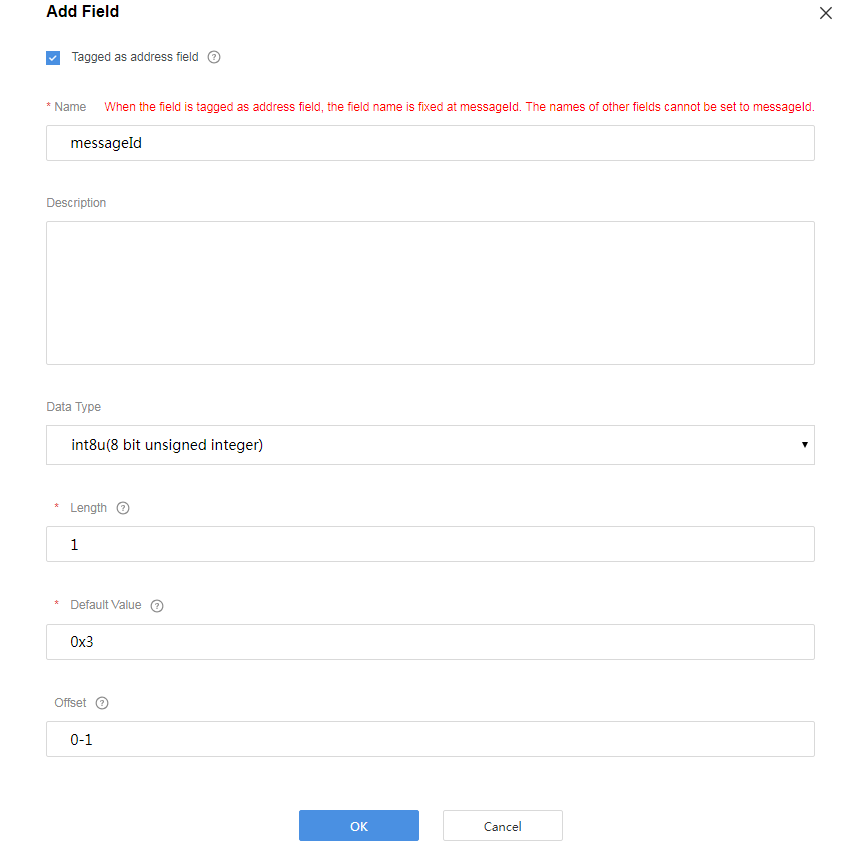
Add the messageId field to indicate the message type. In this scenario, the value 0x0 is used to identify the message that reports the fire severity and temperature, 0x1 is used to identify the message that reports only the temperature, and 0x3 is used to identify the message that reports the description (of the variable-length string type).
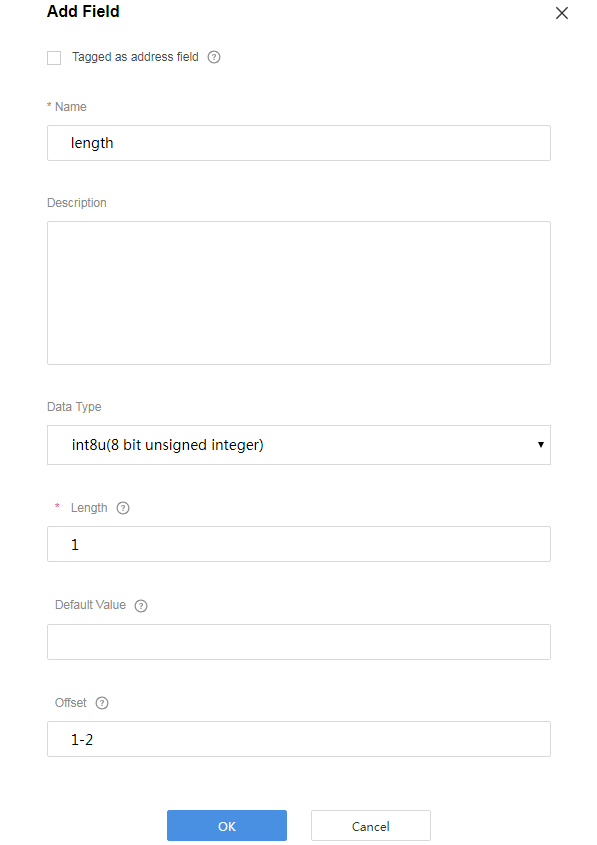
Add the length field to indicate the length of a string. Data Type is configured based on the length of the variable-length string. If the string contains 255 or fewer characters, set this parameter to int8u.
Add the other_info field to indicate the description of the variable-length string type. Set Length Correlation Field to length. The values of Length Correlation Field Difference and Length are automatically filled.
- Drag the property fields in Device Model on the right to set up a mapping with the fields in the data reporting messages.
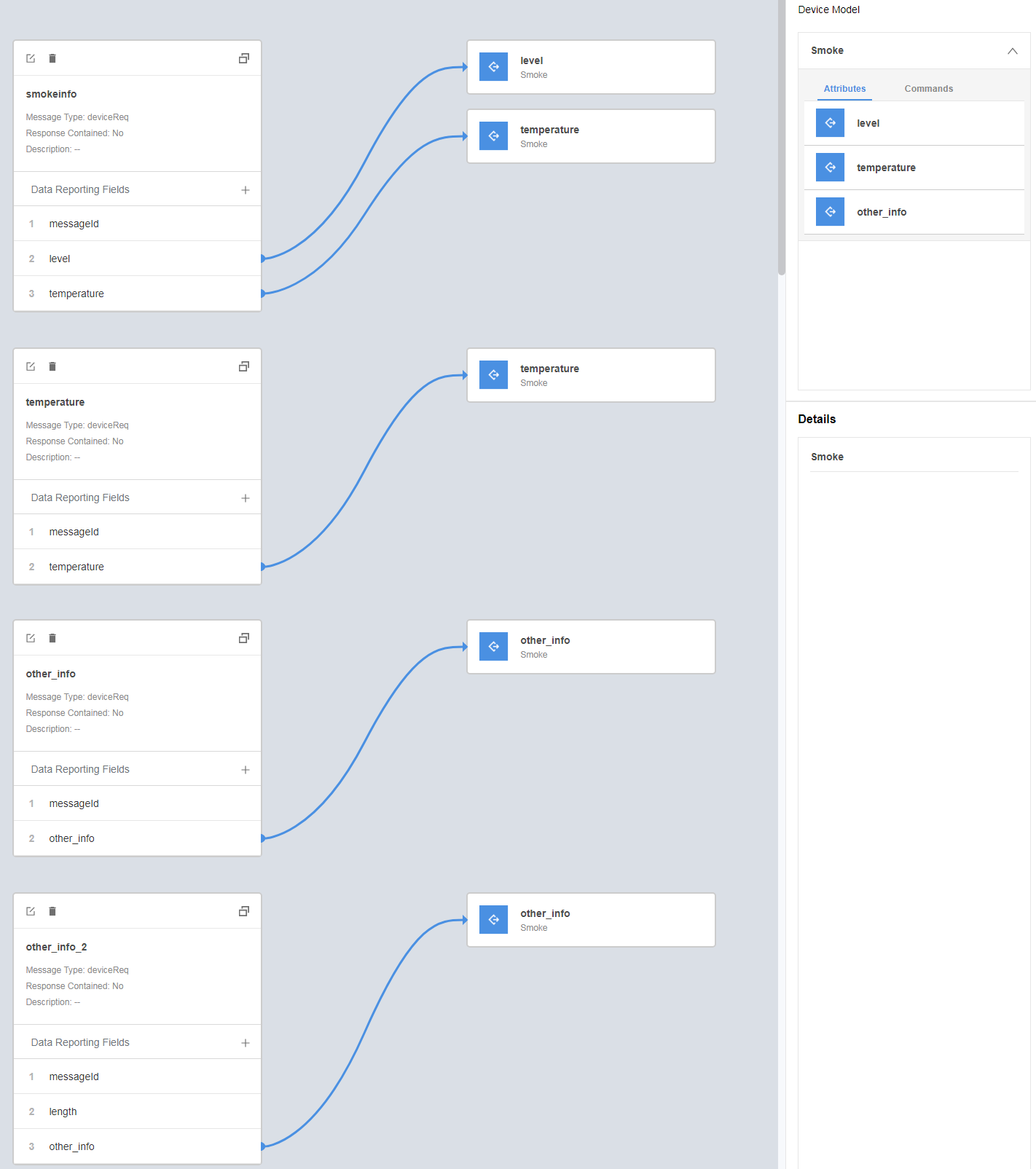
- Click Save and then Deploy to deploy the codec on the IoT platform.

Testing the Codec
- In the development space of the smoke sensor, click Online Testing and add a virtual device to test the codec.
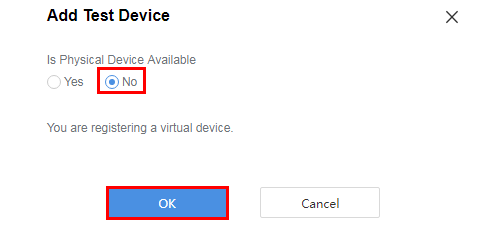
Select No for Is Physical Device Available and click OK.
- Use the device simulator to report the description of the string type.
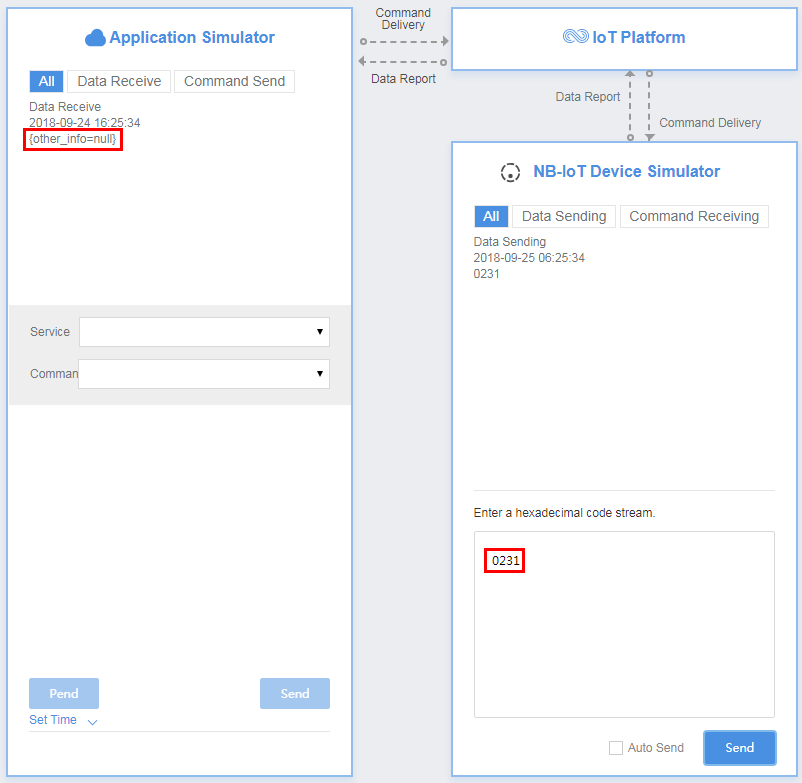
For example, a hexadecimal code stream (0231) is reported. 02 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the string type. 31 indicates the description and its length is one byte.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=null}) in Application Simulator. The length of the description is less than six bytes. Therefore, the codec cannot parse the description.
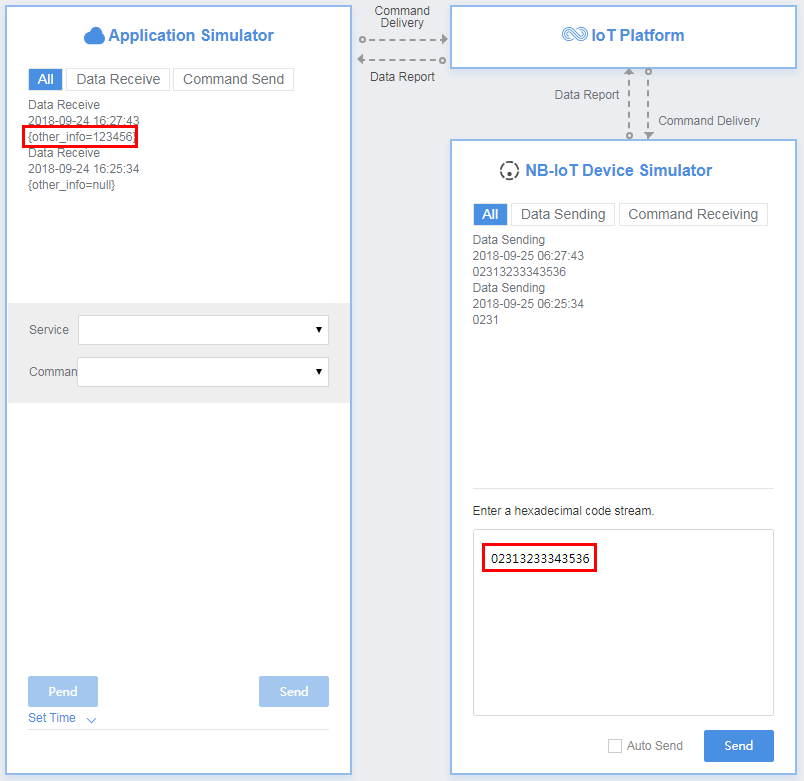
In the second hexadecimal code stream example (02313233343536), 02 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the string type. 313233343536 indicates the description and its length is six bytes.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=123456}) in Application Simulator. The length of the description is six bytes. The description is parsed successfully by the codec.
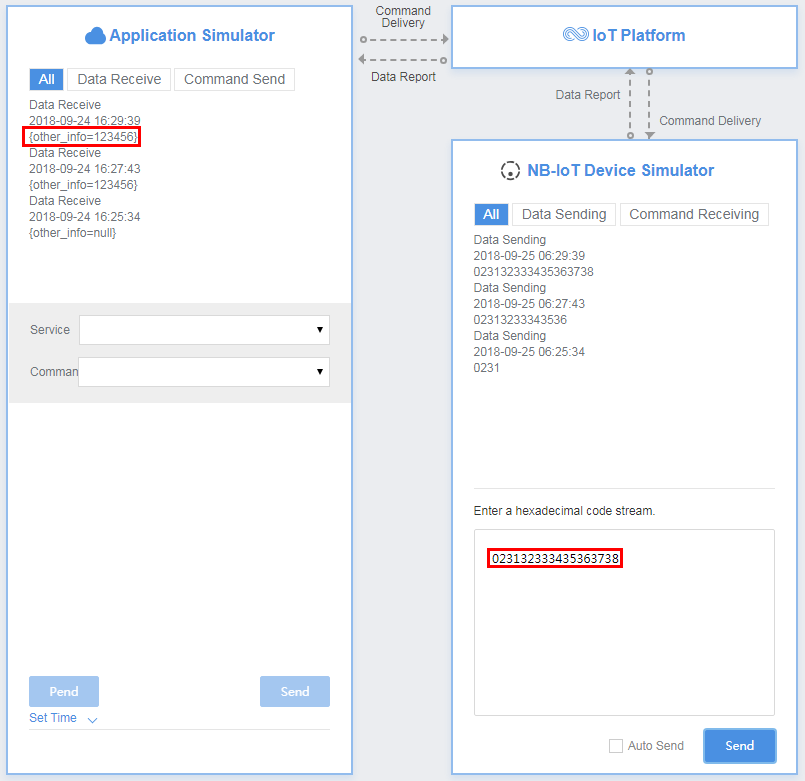
In the third hexadecimal code stream example (023132333435363738), 02 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the string type. 3132333435363738 indicates the description and its length is eight bytes.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=123456}) in Application Simulator. The length of the description exceeds six bytes. Therefore, the first six bytes are intercepted and parsed by the codec.
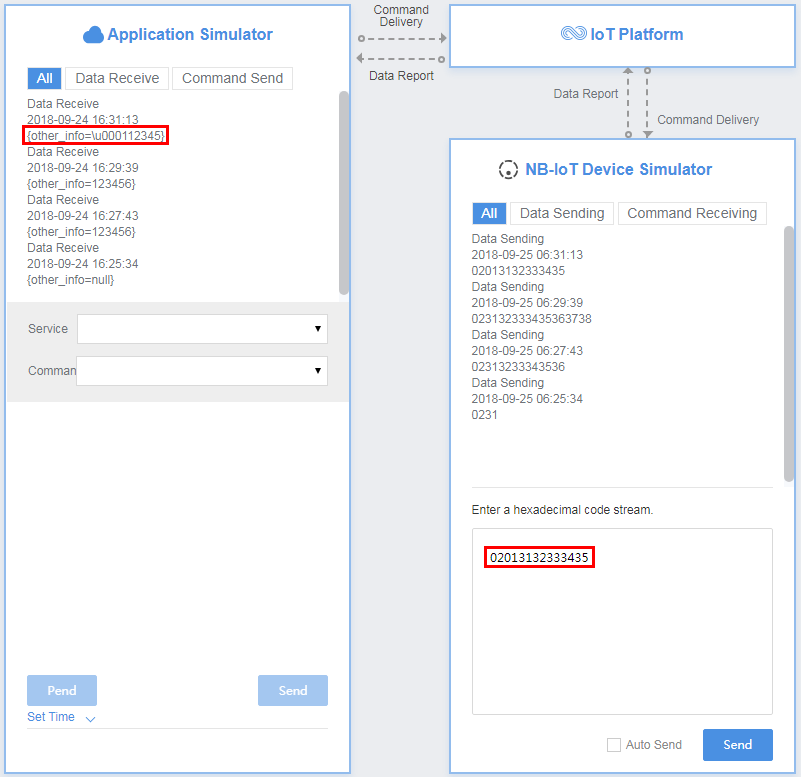
In the fourth hexadecimal code stream example (02013132333435), 02 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the string type. 013132333435 indicates the description and its length is six bytes.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=\u000112345}) in Application Simulator. In the ASCII code table, 01 indicates start of headline which cannot be represented by specific characters. Therefore, 01 is parsed to \u0001.
- Use the device simulator to report the description of the variable-length string type.
For example, a hexadecimal code stream (030141) is reported. In this code stream, 03 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the variable-length string type. 01 indicates the length of the description (one byte) and its length is one byte. 41 indicates the description and its length is one byte.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=A}) in Application Simulator. A corresponds to 41 in the ASCII code table.
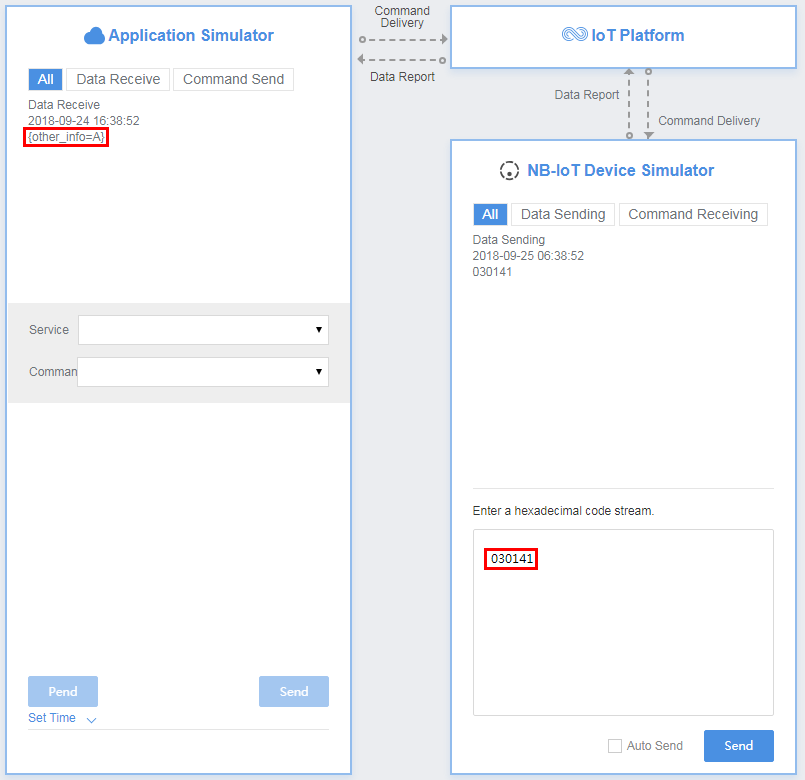
In the second hexadecimal code stream example (03024142), 03 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the variable-length string type. 02 indicates the length of the description (two bytes) and its length is one byte. 4142 indicates the description and its length is two bytes.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=AB}) in Application Simulator. A corresponds to 41 and B corresponds to 42 in the ASCII code table.
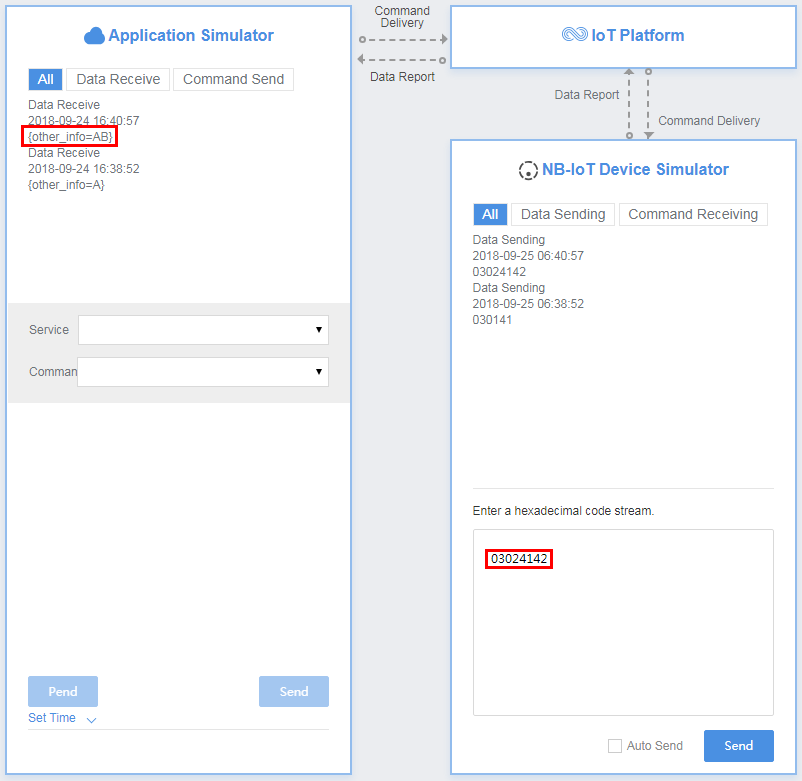
In the third hexadecimal code stream example (030341424344), 03 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the variable-length string type. The second 03 indicates the length of the description (three bytes) and its length is one byte. 41424344 indicates the description and its length is four bytes.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=ABC}) in Application Simulator. The length of the description exceeds three bytes. Therefore, the first three bytes are intercepted and parsed. In the ASCII code table, A corresponds to 41, B to 42, and C to 43.
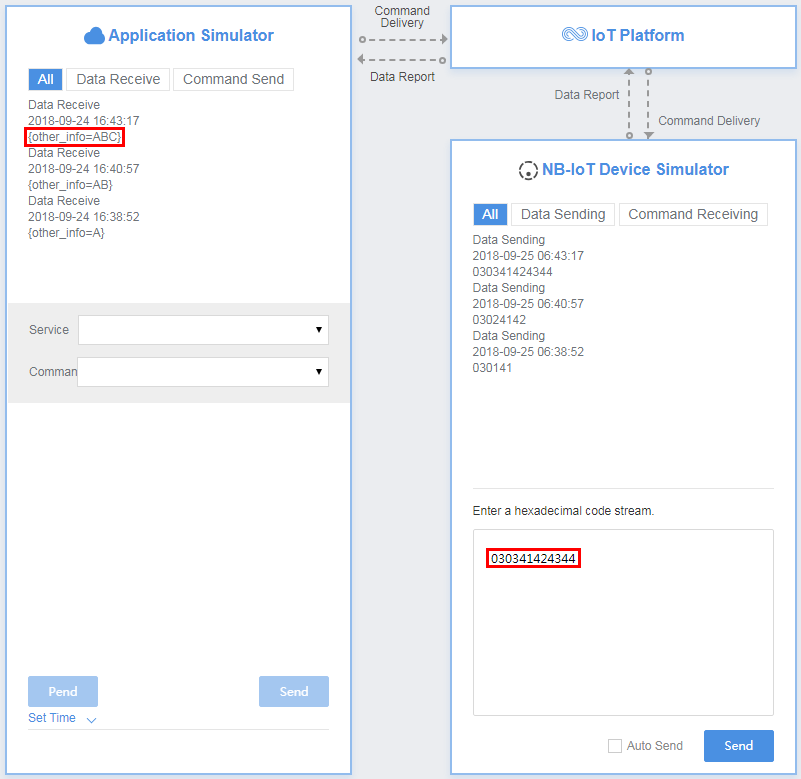
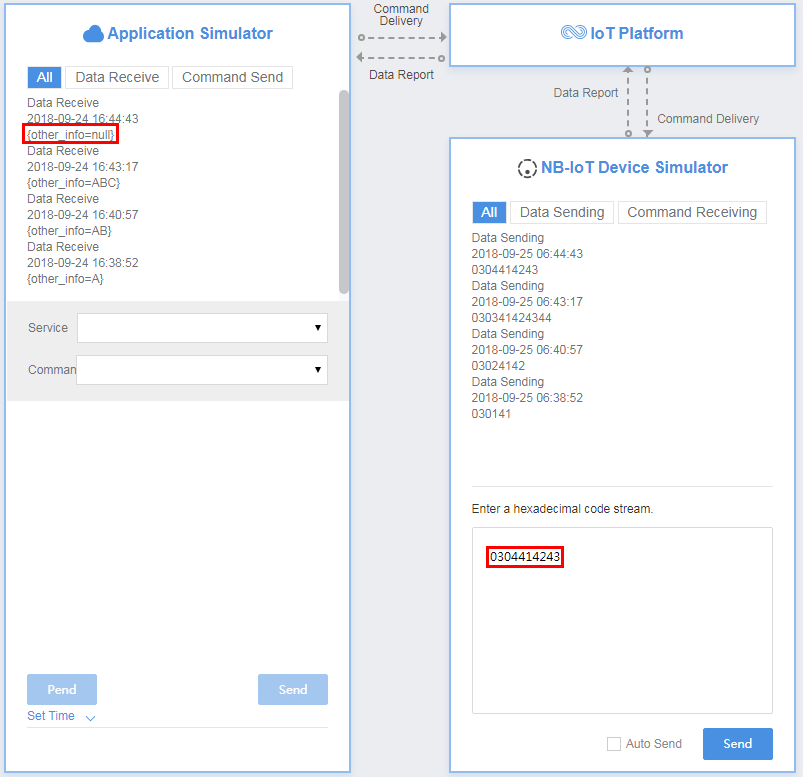
In the fourth hexadecimal code stream example (0304414243), 03 indicates the messageId field and specifies that this message reports the description of the variable-length string type. 04 indicates the string length (four bytes) and its length is one byte. 414243 indicates the description and its length is four bytes.
View the data reporting result ({other_info=null}) in Application Simulator. The length of the description is less than four bytes. The codec fails to parse the description.
Summary
- When data is a string or a variable-length string, the codec processes the data based on the ASCII code. When data is reported, the hexadecimal code stream is decoded to a string. For example, 21 is parsed to an exclamation mark (!), 31 to 1, and 41 to A. When a command is delivered, the string is encoded into a hexadecimal code stream. For example, an exclamation mark (!) is encoded into 21, 1 into 31, and A into 41.
- When the data type of a field is varstring(variable-length string type), the field must be associated with the length field. The data type of the length field must be int.
- For variable-length strings, the codecs for command delivery and data reporting are developed in the same way.
- Online developed codecs encode and decode strings and variable-length strings using the ASCII hexadecimal standard table. During decoding (data reporting), if the parsing results cannot be represented by specific characters such as start of headline, start of text, and end of text, the \u+2 byte code stream values are used to indicate the results. For example, 01 is parsed to \u0001 and 02 to \u0002. If the parsing results can be represented by specific characters, specific characters are used.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





