Using the ZSTD_JNI Compression Algorithm to Compress Hive ORC Tables
Scenario
ZSTD_JNI is a native implementation of the ZSTD compression algorithm. Compared with ZSTD, ZSTD_JNI has higher compression read/write efficiency and compression ratio, and allows you to specify the compression level as well as the compression mode for data columns in a specific format.
Currently, only ORC tables can be compressed using ZSTD_JNI. By contrast, ZSTD enables you to compress tables in the full storage format. Therefore, you are advised to use this feature only when you have high requirements on data compression.
Notes and Constraints
This section applies only to MRS 3.2.0 and later.
Creating a Hive Table in ZSTD_JNI Compression Format
- Log in to the node where the client is installed as the Hive client installation user.
- Run the following command to go to the client installation directory, for example, /opt/client:
cd /opt/client - Run the following command to configure environment variables:
source bigdata_env
- Check whether Kerberos authentication is enabled for the cluster.
- Run the following command to log in to the Hive client:
beeline
- Create a Hive table in ZSTD_JNI compression format.
- Set the orc.compress parameter to ZSTD_JNI when using ZSTD_JNI compression algorithm to create a Hive table:
create table tab_1(id string,name string) stored as orc TBLPROPERTIES("orc.compress"="ZSTD_JNI");
- The compression level of ZSTD_JNI ranges from 1 to 19. The larger the value, the higher the compression ratio, but the slower the compression speed. The smaller the value, the lower the compression ratio, but the faster the compression speed. The default value is 6. You can set the compression level through the orc.global.compress.level parameter when creating a table.
create table tab_1(id string,name string) stored as orc TBLPROPERTIES("orc.compress"="ZSTD_JNI", 'orc.global.compress.level'='3');
- This compression algorithm allows you to compress service data and columns in a specific data format. Currently, the following data formats are supported: JSON, Base64, timestamp, and UUID. You can achieve this function by setting the orc.column.compress parameter during table creation.
The following example code shows how to use ZSTD_JNI to compress data in the JSON, Base64, timestamp, and UUID formats, that is, data in column f2, f3, f4, and f5, respectively.
create table test_orc_zstd_jni(f1 int,f2 string,f3 string,f4 string,f5 string) stored as orc TBLPROPERTIES('orc.compress'='ZSTD_JNI', 'orc.column.compress'='[{"type":"cjson","columns":"f2"},{"type":"base64","columns":"f3"},{"type ":"gorilla","columns":{"format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS", "columns": "f4"}},{"type":"uuid","columns":"f5"}]');You can insert data in the corresponding format based on the site requirements to further compress the data.
- Set the orc.compress parameter to ZSTD_JNI when using ZSTD_JNI compression algorithm to create a Hive table:
- Run the following command to view the table information:
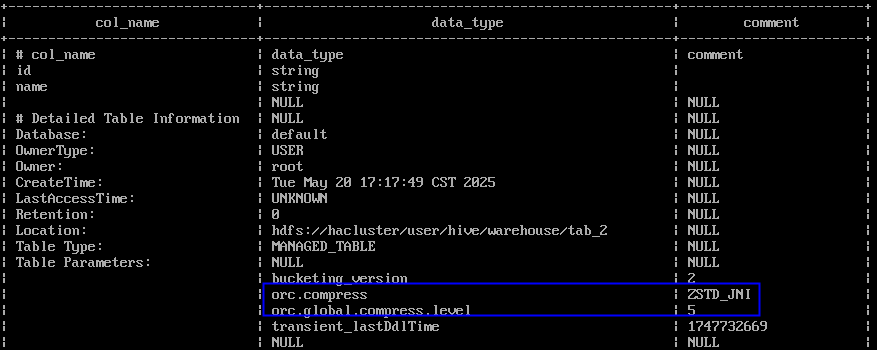
desc formatted tab_1;The command output displays the compression format information. In Figure 1, the Hive table is compressed in ZSTD_JNI format and its compression level is 5.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot