Using ELB to Redirect HTTP Requests to an HTTPS Listener for Higher Service Security
Scenarios
HTTPS is an extension of HTTP. HTTPS encrypts data between a web server and a browser. You can use ELB to redirect HTTP requests to an HTTPS listener to improve your service security.

- If the listener protocol is HTTP, only the GET or HEAD method can be used for redirection. If you create a redirect for an HTTP listener, the client browser will change POST or other methods to GET. If you want to use other methods rather than GET and HEAD, add an HTTPS listener.
- HTTP requests are forwarded to the HTTPS listener as HTTPS requests, which are then routed to backend servers over HTTP.
- If HTTP requests are redirected to an HTTPS listener, no certificate can be deployed on the backend servers associated with the HTTPS listener. If certificates are deployed, HTTPS requests will not take effect.
Prerequisites
- You have created a dedicated load balancer. For details, see Creating a Dedicated Load Balancer.
- You have created two ECSs (ECS_client and ECS_server) that are running in the same VPC as the dedicated load balancer. ECS_client sends HTTPS requests, while ECS_server processes requests. For details, see Purchasing an ECS.
- You have gotten a server certificate ready for adding an HTTPS listener. For details, see Adding a Server Certificate.
Procedure

Step 1: Add an HTTPS Listener
- Go to the load balancer list page.
- On the displayed page, locate the target load balancer and click its name.
- On the Listeners tab, click Add Listener. Configure the parameters based on Table 1.
Figure 2 Adding an HTTPS listener
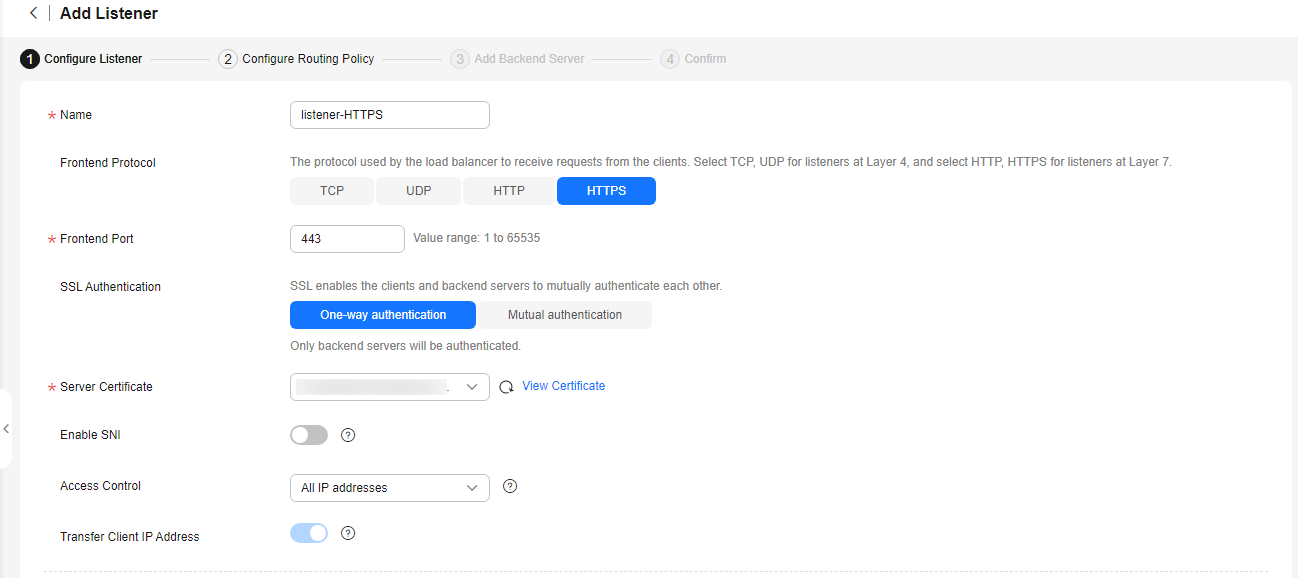
Table 1 Parameters for configuring an HTTPS listener Parameter
Example Value
Description
Frontend Protocol
HTTPS
Specifies the protocol that will be used by the load balancer to receive requests from clients.
Listening Port
443
Specifies the port that will be used by the load balancer to receive requests from clients.
Name (Optional)
listener-HTTPS
Specifies the listener name.
Transfer Client IP Address
Enabled by default
Specifies whether to transmit IP addresses of the clients to backend servers.
Advanced Forwarding
Enabled
Specifies whether to enable advanced forwarding. You can configure advanced forwarding policies to forward requests to different backend server groups based on a wide range of forwarding rules and actions.
Access Control
All IP addresses
Specifies how access to the listener is controlled. Access from specific IP addresses can be controlled using a whitelist or blacklist.
SSL Authentication
One-way authentication
Specifies how you want the clients and backend servers to be authenticated. In this practice, One-way authentication is selected.
Server Certificate
The existing server certificate
Specifies the certificate that will be used by the backend server for SSL handshake negotiation to authenticate clients and ensure encrypted transmission.
SNI
Not enabled
Specifies whether to enable SNI when HTTPS is used as the frontend protocol. SNI can be used when a server uses multiple domain names and certificates.
- Retain the default values for parameters under More (Optional) and click Next: Configure Request Routing Policy.
- Select Create new for Backend Server Group, retain the default values for other parameters, and click Next: Add Backend Server.
- Add ECS_server to the backend server group you have created, enable Health Check, and retain the default values for the health check.
- Click Next: Confirm and then click Submit.
Step 2: Add an HTTP Listener and Enable Redirect to Another Listener
You can enable redirection when adding an HTTP listener and select an HTTPS listener to which requests are redirected. Alternatively, you can add a forwarding policy for an HTTP listener to redirect requests to an HTTPS listener.
- Go to the load balancer list page.
- On the Load Balancers page, locate the target load balancer and click its name.
- On the Listeners tab, click Add Listener. Configure the parameters based on Table 2.
Figure 3 Adding an HTTP listener
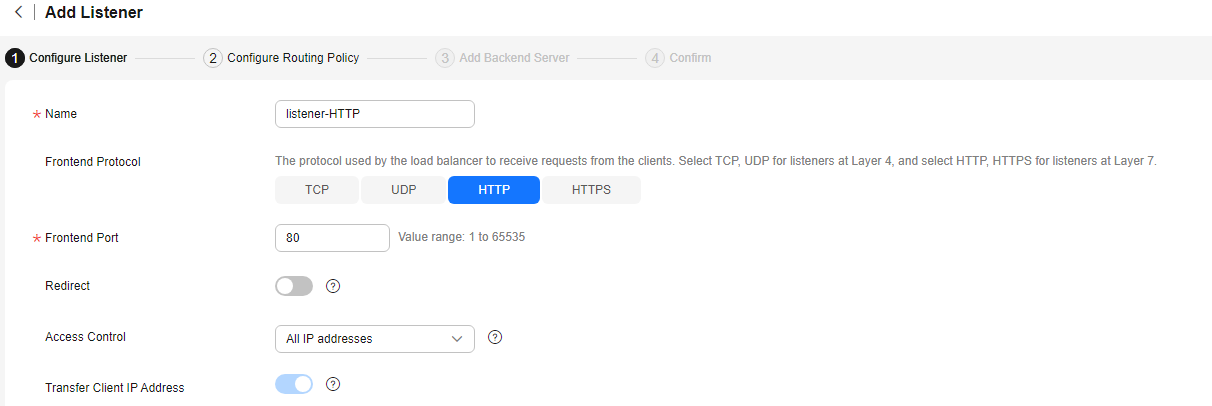
Table 2 Parameters for configuring an HTTP listener Parameter
Example Value
Description
Frontend Protocol
HTTP
Specifies the protocol that will be used by the load balancer to receive requests from clients.
Listening Port
80
Specifies the port that will be used by the load balancer to receive requests from clients.
Name (Optional)
listener-HTTP
Specifies the listener name.
Redirect to another listener
Select it and choose the HTTPS listener created in Step 1: Add an HTTPS Listener.
Specifies whether to enable redirection. You can use this function to redirect the requests from an HTTP listener to an HTTPS listener to ensure security.
Transfer Client IP Address
Enabled by default
Specifies whether to transmit IP addresses of the clients to backend servers.
Advanced Forwarding
Enabled
Specifies whether to enable advanced forwarding. You can configure advanced forwarding policies to forward requests to different backend server groups.
Access Control
All IP addresses
Specifies how access to the listener is controlled. Access from specific IP addresses can be controlled using a whitelist or blacklist.
- Retain the default values for parameters under More (Optional) and click Next: Confirm.
- Click Submit.
- After the redirection is added, the configurations for the HTTP listener will not be applied, but access control configured for that listener will still be applied.
- After the redirection is added for an HTTP listener, the backend server will return 301 Moved Permanently to the clients.
Step 3: Verify the Redirection to HTTPS
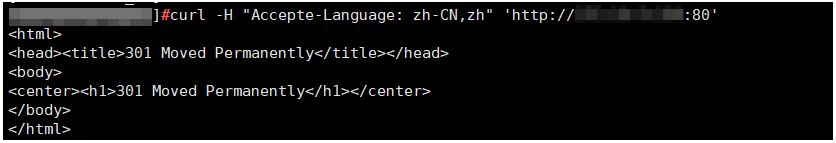
Remotely log in to ECS_client and run curl -H "Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh" "http://ELB-private-IP-address:80 to check whether HTTP requests are redirected.
If 301 Moved Permanently is returned, as shown in the below figure, HTTP requests are directed to an HTTPS listener.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





