What Can I Do If a BCS Instance Is in the Abnormal State?
Symptom
The BCS instance is in the Abnormal state.
Fault Locating
Check item 1: Check whether the cluster, storage, and server resources on which the blockchain depends are normal.
Check item 2: Check whether the ECS specifications can meet the requirements.
Solution
- Check item 1: Check whether the cluster, storage, and server resources on which the blockchain depends are normal.
- Check the CCE cluster status.
- Log in to the CCE console, click Clusters, and check the status of the abnormal blockchain's cluster.
If the cluster status is abnormal, locate the fault by following the CCE instructions: How Do I Rectify the Fault When the Cluster Status Is Unavailable?
- Log in to the CCE console, click Nodes, and check the status of the abnormal blockchain's nodes.
If the node status is abnormal, locate the fault by following the CCE instructions: What Should I Do If a Cluster Is Available But Some Nodes Are Unavailable?
- Log in to the CCE console, click Clusters, and check the status of the abnormal blockchain's cluster.
- Check the ECS status.
Log in to the ECS console and check the status of the ECS where the abnormal blockchain is deployed. ECS names usually take the following format: Name of the target blockchain's cluster-A random number.
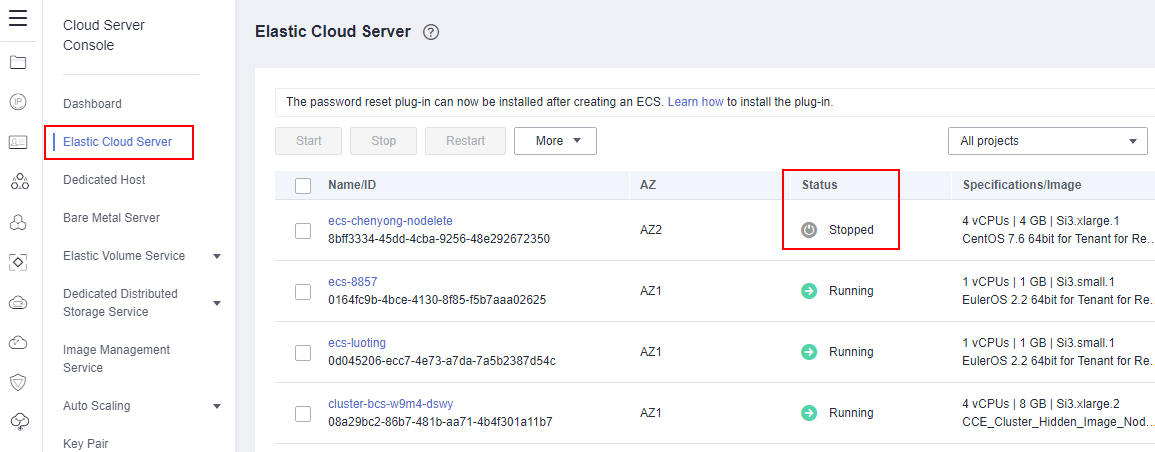
If the ECS is in the Stopped state, start the ECS, wait for about 5 minutes, and check its status again.
- Check the storage status.
- Log in to the BCS console, go to the Instance Management page, and click the abnormal instance to view its volume type.
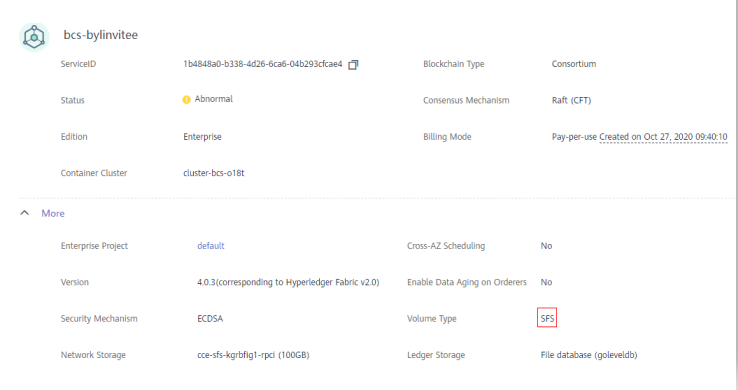
- Log in to the CCE console, click Clusters, and select a target cluster. On the cluster details page, click Storage. On the PersistentVolumeClaims (PVCs) tab page, check the storage status.
- If the SFS Turbo volume is in the Lost state, the state of the BCS instance will be displayed as Abnormal.
Solution:
Check whether the SFS Turbo file system exists or whether it is frozen, or contact the SFS technical support.
- Log in to the BCS console, go to the Instance Management page, and click the abnormal instance to view its volume type.
- Check the CCE cluster status.
- Check item 2: Check whether the ECS specifications can meet the requirements.
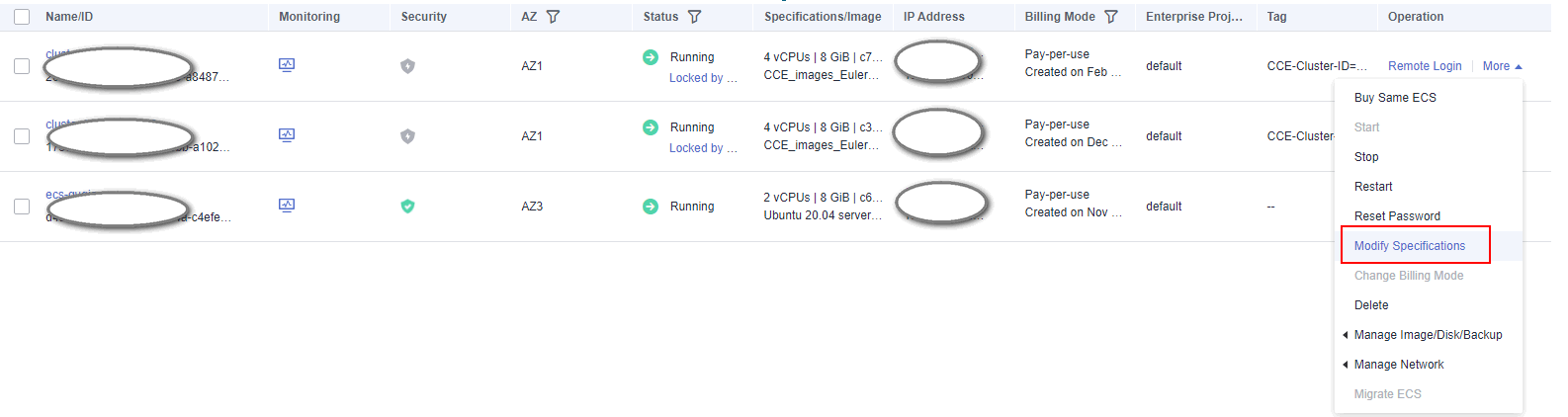
- Log in to the ECS where the BCS instance is deployed.
Log in to the ECS console, locate the target ECS, and click Remote Login in the Operation column. ECS names usually take the following format: Name of the target blockchain's cluster-A random number.

- Run the top command to check whether the resource usage of any application is too high.
Figure 1 top command details
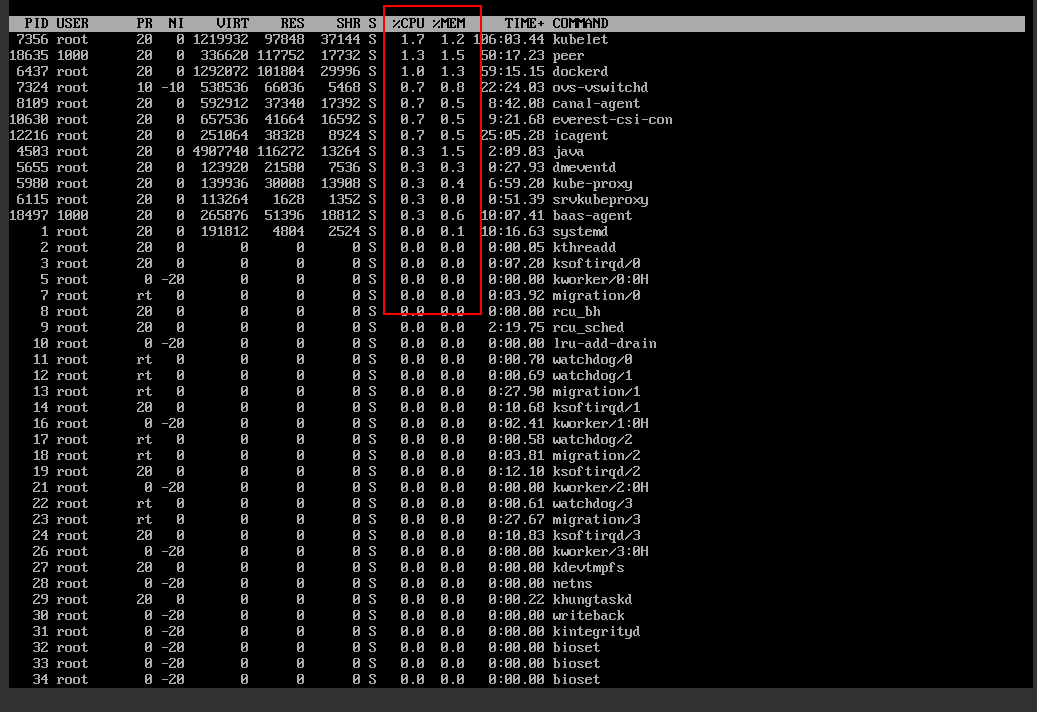
- If the CPU or memory usage of the peer, orderer, and baas-agent containers exceeds 60% and continues to increase as the transaction quantity increases, the current ECS specifications cannot meet the transaction requirements. In this case, you need to expand the ECS specifications.
- If there are resources taking up 100% or even higher CPU or memory usage, contact technical support to remove unnecessary resources.
- Log in to the ECS where the BCS instance is deployed.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot