Edge Gateway Overview
What Is an Edge Gateway?
An edge gateway can connect subnets in the same VPC but from both HomeZones and central AZs.
Edge gateways are supported in the AF-Johannesburg region.
Edge gateways are free of charge, but if there is a change, you will be notified in advance.
Application Scenarios
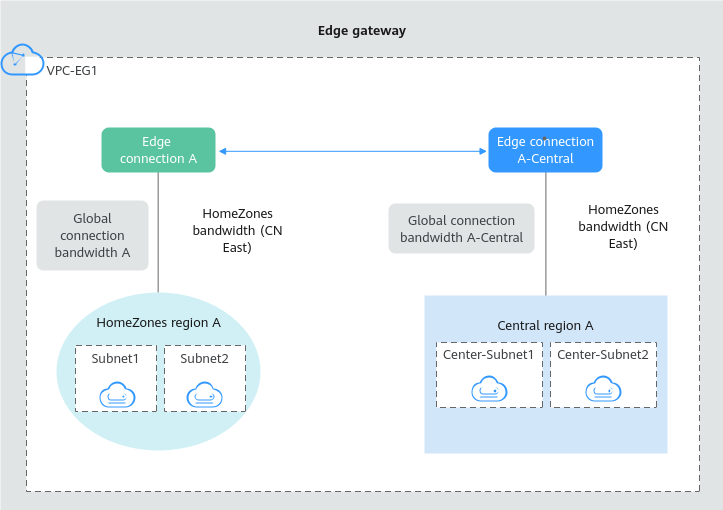
|
Edge Gateway |
AZ |
Region |
Edge Connection |
Global Connection Bandwidth-HomeZones (CN East) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Edge gateway |
|
HomeZones region A |
Edge connection A |
Global connection bandwidth A |
|
Central region A |
Edge connection A-Central |
Global connection bandwidth A-Central |
|
Scenario |
Required Resource |
Description |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
|
In VPC-EG1, connect subnets in HomeZones and central AZs. |
|
In VPC-EG1, Subnet1 and Subnet2 in the HomeZones AZ and Center-Subnet1 and Center-Subnet2 in the central AZ need to communicate with each other.
|
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





