Configuring an AD Domain
Overview
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is a directory service that can establish secure, scalable, and hierarchical directory structures on the network for unified identity authentication and authorization management. Through AD domains, administrators can easily manage users, computers, resources, and policies on the network in a unified manner.
This section describes how to configure an AD domain for an SMB SFS Turbo file system. After adding an SFS Turbo file system to an AD domain, you can authenticate user identities and manage permissions by file in the domain.

You need to submit a service ticket to apply for using this function.
Constraints
- Before adding the file system to an AD domain, ensure that no application is accessing the file system. Or, a request error may be reported.
- You can only configure Active Directory for SMB SFS Turbo file systems.
Joining a Domain
- Log in to the SFS Turbo console.
- In the SFS Turbo file system list, find the file system you want to add to a domain and click its name to go to its details page.
- Click the Active Directory Configuration tab.
- Click Join Domain.
Figure 1 Active Directory Configuration
- Enter the Active Directory configuration information.
Figure 2 Entering configuration information
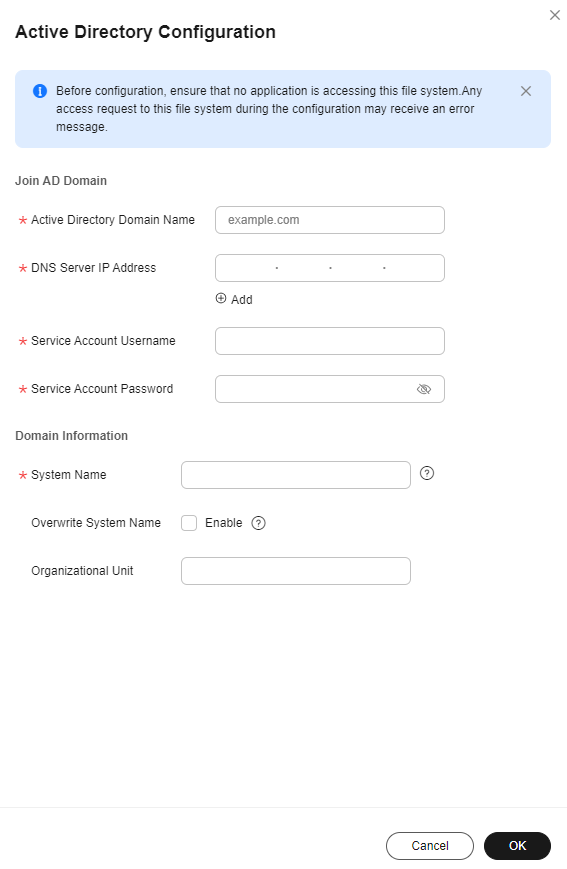
Table 1 Parameters required for joining an AD domain Parameter
Description
Active Directory Domain Name
The name of the AD domain, for example, example.com.
DNS Server IP Address
The IP address of the DNS server that resolves the domain name. You can click
 to add an alternative DNS server IP address. You can add a maximum of three IP addresses.
to add an alternative DNS server IP address. You can add a maximum of three IP addresses.Service Account Username
The administrator account of the AD domain server, for example, administrator.
Service Account Password
The password of the AD domain server administrator account.
System Name
The name of the file system in the AD domain. After the file system is added to the domain, clients can use this name to access the file system. This name is unique in the AD domain server. If a duplicate name is specified, the domain joining operation will fail.
Overwrite System Name
Once enabled, if there is a file system with the same name in the domain controller, the file system you specify will overwrite the one in the domain controller.
Organizational Unit
The unit of the AD domain server that the file system is added to. If not specified, the file system is added to the Computers unit, for example, cn=Computers,dc=example,dc=com.
- Wait a few seconds and you can see the Active Directory domain name, DNS server IP address, status, and system name.
Figure 3 Domain joined successfully

Leaving a Domain
- Log in to the SFS Turbo console.
- In the SFS Turbo file system list, find the file system you want to remove from a domain and click its name to go to its details page.
- Click the Active Directory Configuration tab.
- Locate the domain that the file system has joined and click Leave Domain in the Operation column.
Figure 4 Leave Domain button

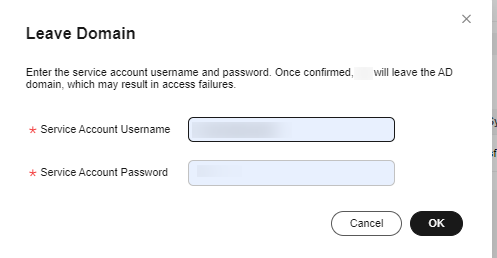
- Enter the username and password of the AD domain account, and click OK.
Figure 5 Page for entering the username and password to leave the domain
- Check that the AD domain disappears from the Active Directory Configuration page.
Figure 6 Domain left successfully
Related Operations
For an SMB file system, you can also click Edit in the Operation column to modify the information of the joined domain.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





