Viewing a General-Purpose File System
You can search for a general-purpose file system by name, AZ, protocol type, mount point, or creation time, and then view the file system basic information.
Viewing details of general-purpose file systems depends on the VPC service. Ensure that the required role or policy has been configured.
The permissions of the SFS3 ReadOnlyAccess policy already include the permissions of VPC ReadOnlyAccess, which are required for querying general-purpose file system details. An IAM user assigned the SFS3 ReadOnlyAccess policy does not need to have the VPC ReadOnlyAccess policy assigned explicitly.
Procedure
- Log in to the SFS console.
- In the general-purpose file system list, view the file systems you have created. Table 1 describes the file system parameters.
Table 1 General-purpose file system parameters Parameter
Description
Name
Name of the general-purpose file system, for example, sfs-name-001
Availability Zone
Availability zone (AZ) where the file system resides
Protocol Type
File system protocol, which is NFS
Used Capacity
File system space already used for data storage
NOTE:This information is refreshed every hour.
Uploaded Files (Count)
Number of files that have been uploaded to the file system
NOTE:This information is refreshed every hour.
Standard Storage Used Capacity
Total standard storage used in the general-purpose file system
Uploaded Standard Files (Count)
Total number of files that use standard storage in the general-purpose file system
Warm Storage Used Capacity
Total infrequent access storage used in the general-purpose file system
Uploaded Warm Files (Count)
Total number of files that use infrequent access storage in the general-purpose file system
Mount Point
Address or location of the general-purpose file system. The format is <file-system-domain-name>:/<file-system-name>, for example, example.com:/sfs-name-001.
NOTE:- If the mount point is too long to display completely, you can adjust the column width.
- Hover over the mount point to view the full mount command.
Tag
Tag information of the general-purpose file system
Created
Time when the file system was created
Operation
The Configure Limits and Delete buttons are available.
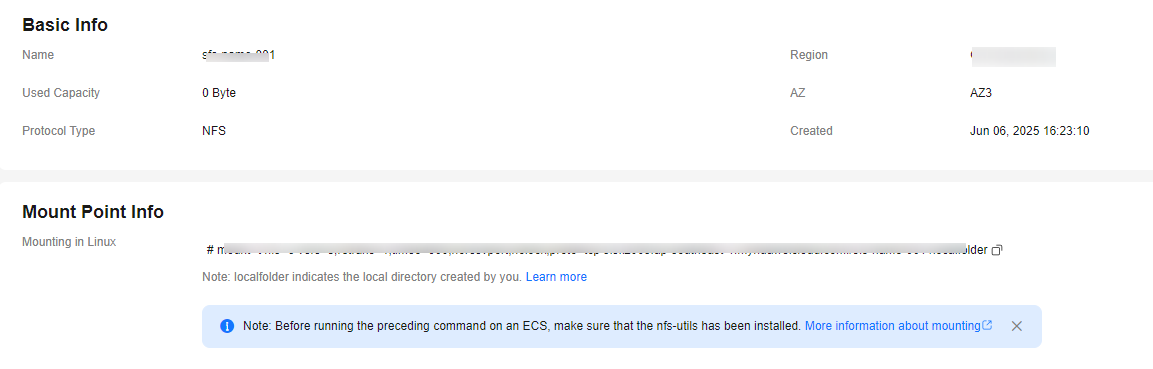
- Click the name of the general-purpose file system. On the Basic Information tab, view more information about the file system, as shown in Figure 1.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot