Related Concepts
Composite Application
A composite application integrates multiple business flows into a sophisticated automation solution, enabling end-to-end service process automation across systems and services to meet diverse requirements.
For example, you can connect business flows, such as data collection, processing, storage, and notification, to create a complete data processing pipeline. Composite applications offer flexibility and scalability, allowing you to adjust or extend workflows as service needs evolve. They also support data sharing and collaboration between workflows, enhancing operational efficiency.
A composite application can contain multiple service flows. You can edit, start, stop, and debug these flows.
Business Flow
A business flow is a sequence of automated tasks executed in a predefined order to complete a specific service process. It orchestrates tasks like data reading, processing, storage, and notification to implement complex service logic, supporting features such as conditional branching, loops, and error handling. By automating these processes, business flows reduce manual effort and enhance efficiency.
Key elements of a business flow include triggers, connectors, and processors.
Trigger
A trigger is a condition or event that starts a flow. It monitors specific external events or time points and automatically initiates the flow when the condition is met. Triggers can be event-driven, such as a file upload to OBS or a database update, or time-driven, like a task scheduled for early morning daily.
Serving as the flow's starting point, triggers ensure processes run automatically at the right time. Their flexible configuration allows flows to adapt to various service scenarios for efficient, automated responses.

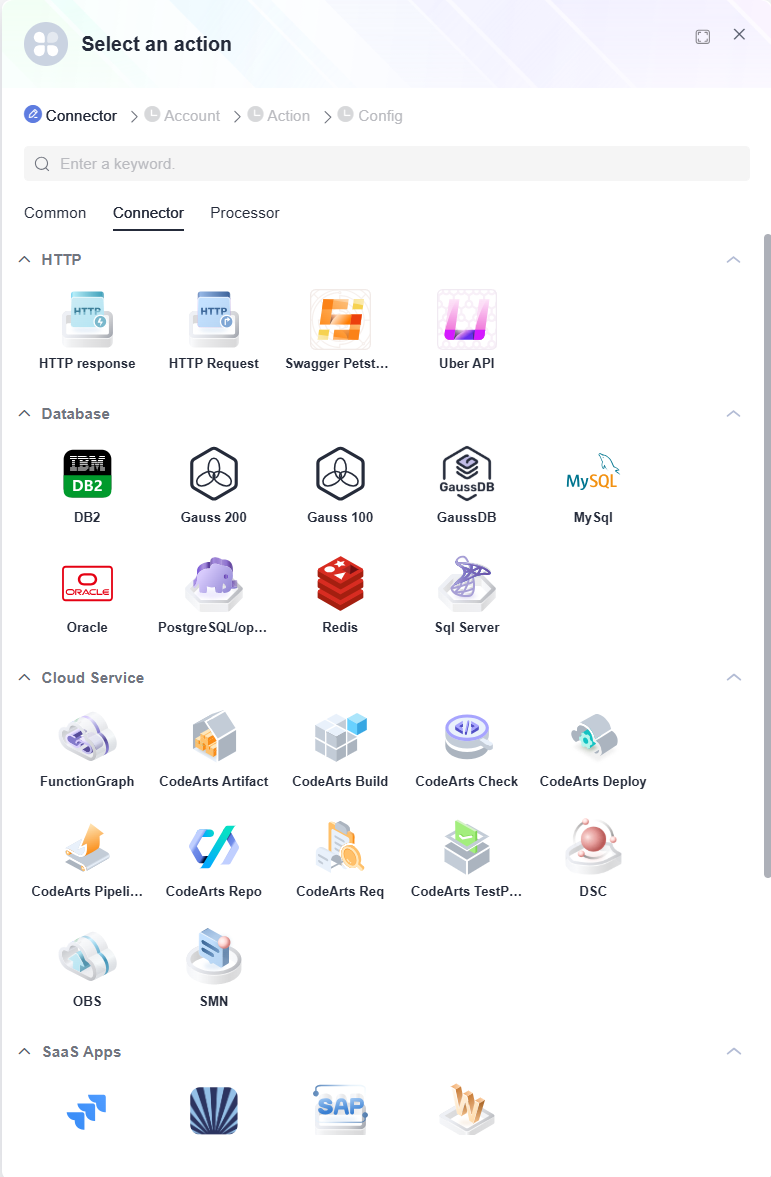
Connector
A connector links to external services or systems, encapsulating communication details to simplify integration. It supports various services, including cloud platforms, messaging systems, databases, HTTP, and third-party tools like email and WeChat. Connectors provide predefined API calls, authentication, and data format conversion, enabling flows to easily read/write external data, call APIs, or send notifications.
For example, use a database connector to access Huawei Cloud RDS or an email connector to send notifications. Connectors reduce integration complexity and enhance flow scalability and versatility.
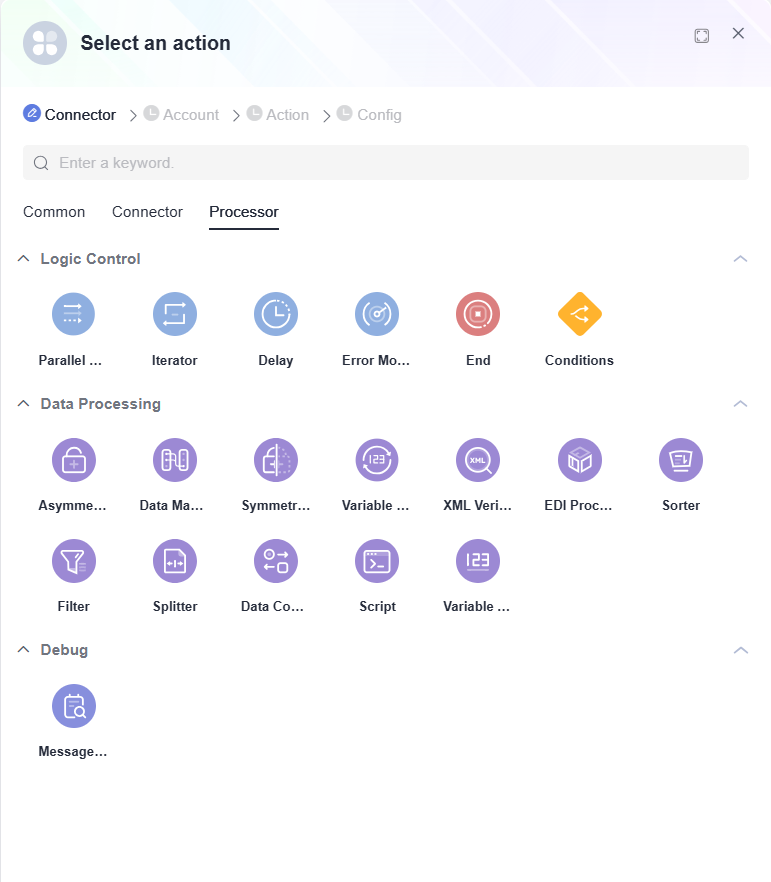
Processor
A processor is a core component that operates on and transforms data within a flow. It receives input from a trigger, connector, or previous processor, processes it according to predefined logic, and passes the result to the next component.
Processors are categorized into logical control, data processing, and fault detection types to handle diverse data processing needs.
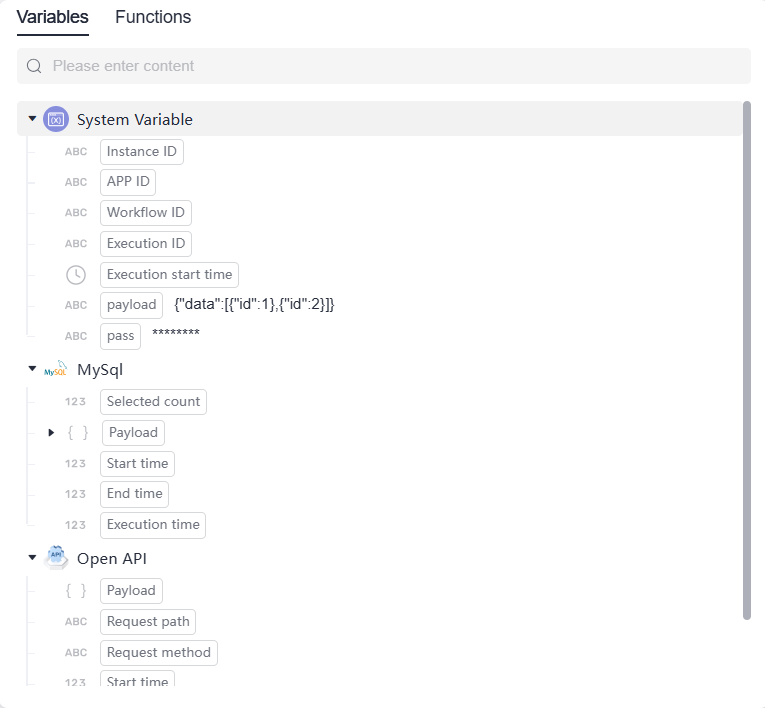
Variable
A variable is a container for temporary data within a flow, used to store and transfer information during execution. It can originate from triggers, connectors, processors, or system variables defined in composite applications.
Variables may hold basic data types (string, number, Boolean) or objects (arrays, JSON). Using variables enables data sharing between processors and connectors to support complex service logic.
Function
A function is a logical expression used to calculate, convert, and manipulate data within a flow. It supports various built-in operations, including math, string handling, date processing, and encryption, to address complex data needs.
Functions enable dynamic calculations, output formatting, and type conversions in processors and connectors.

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





