Creating a Custom Query
Scenarios
You can use the query statements preset by Config or customize query statements based on resource configuration attributes to query specific cloud resource configurations.
This section includes the following content:
Creating a Custom Query
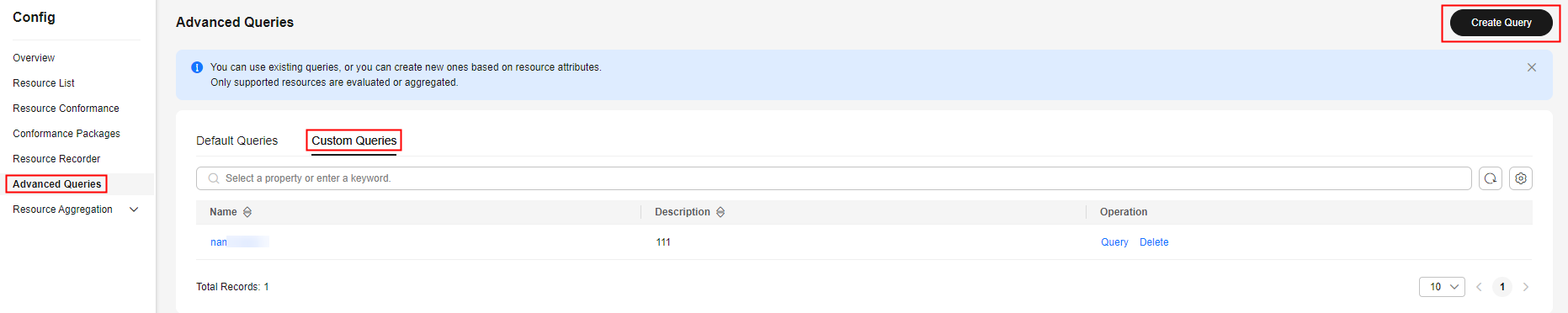
- Log in to the Config console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Advanced Queries.
- Choose the Custom Queries tab and click Create Query in the upper right corner.
Figure 1 Creating a query
- In the Query Editor, enter the query statements.
On the left of the page, the Schema information is displayed. Schema information shows detailed resource attributes that are specified by the properties parameter in the statement. For details about the configuration example of the query statement, see Configuration Examples of Advanced Queries.
- Click Save Query and enter the query name and description.
A query name can contain only digits, letters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-). It cannot exceed 64 characters.
- Click OK.
Figure 2 Saving a query

There is a limit to how many custom queries you can create. If you exceed this limit, you will receive a notification: "The maximum number of custom queries has been reached." Although the query cannot be saved, you can still run the query and export the results.
- Click Run and then view the query results. Up to 4,000 query results can be displayed and exported.
- Click Export above the list and select the format of the file to be exported (CSV or JSON).
- Click Execution Records to view details about when the query was executed and the query statements.
You can perform the following operations:
- Run: running the query
- Copy: copying the query statements
- Save: saving the query as a new query
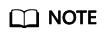
After you close the browser window or log out, the execution records of advanced queries will be cleared.
Figure 3 Execution records
Using a Predefined Query
You can modify the name, description, and statement of a default query or a custom query and save it as a new query. The following procedure uses a default query as an example.
- Choose Advanced Queries > Default Queries.
All default queries are displayed in a list.
- Click Query in the Operation column for the target query.
Alternatively, click the query name and then click Query in the lower right corner of the query overview page.
Figure 4 Running a default query
- In the Query Editor, modify the query.
For details, see Configuration Examples of Advanced Queries.
- Click Save As and enter the query name and description.
- In the dialog box that is displayed, click OK.
After a new query is created, the new query becomes a custom query and will be displayed in the custom query list.
On the Execution Records page, you can also save an existing query as a new query. For details, see Step 10.
Figure 5 Saving as a new query
Configuration Examples of Advanced Queries
Advanced queries use ResourceQL, a subset of SQL SELECT syntax, to query resource configuration data. You do not need to call specific APIs for the query or use multiple APIs to download full data and manually analyze the data. ResourceQL can only query data from the resources table.
|
Parameter |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
id |
String |
Specifies the resource ID. |
|
name |
String |
Specifies the resource name. |
|
provider |
String |
Specifies the cloud service name. |
|
type |
String |
Specifies the resource type. |
|
region_id |
String |
Specifies the region ID. |
|
project_id |
String |
Specifies the project ID. |
|
ep_id |
String |
Specifies the enterprise project ID. |
|
checksum |
String |
Specifies the resource checksum. |
|
created |
Date |
Specifies the time when the resource was created. |
|
updated |
Date |
Specifies the time when the resource was updated. |
|
provisioning_state |
String |
Specifies the result of an operation on resources. |
|
tag |
Array(Map<String,String>) |
Specifies the resource tag. |
|
properties |
Map<String,Object> |
Specifies the resource attribute details. |
Example quires are as follows:
- Example 1: List ECSs in the Stopped state.
SELECT name FROM resources WHERE provider = 'ecs' AND type = 'cloudservers' AND properties.status = 'SHUTOFF'
- Example 2: List EVS disks with certain specifications.
SELECT * FROM resources WHERE provider = 'evs' AND type = 'volumes' AND properties.size = 100
- Example 3: List OBS buckets queried by fuzzy search.
SELECT * FROM resources WHERE provider = 'obs' AND type = 'buckets' AND name LIKE '%figure%'
- Example 4: List ECSs and the EVS disks attached to each ECS.
SELECT ECS_EVS.id AS ecs_id, EVS.id AS evs_id FROM ( SELECT id, evs_id FROM ( SELECT id, transform(properties.ExtVolumesAttached, x -> x.id) AS evs_list FROM resources WHERE provider = 'ecs' AND type = 'cloudservers' ) ECS CROSS JOIN UNNEST(evs_list) AS t (evs_id) ) ECS_EVS, ( SELECT id FROM resources WHERE provider = 'evs' AND type = 'volumes' ) EVS WHERE ECS_EVS.evs_id = EVS.id - Example 5: List ECSs and the EIPs bound to each ECS.
SELECT ECS.id AS ECS_id, publicIpAddress AS ip_address FROM ( SELECT id, transform(properties.addresses, x -> x.addr) AS ip_list FROM resources WHERE provider = 'ecs' AND type = 'cloudservers' ) ECS, ( SELECT name, properties.publicIpAddress FROM resources WHERE provider = 'vpc' AND type = 'publicips' AND properties.type = 'EIP' AND properties.status = 'ACTIVE' ) EIP WHERE CONTAINS (ECS.ip_list, EIP.name) - Example 6: List resources with a quantity greater than 100 in each region.
WITH counts AS ( SELECT region_id, provider, type, count(*) AS number FROM resources GROUP BY region_id, provider, type ) SELECT * FROM counts WHERE number > 100For details about query statements, see ResourceQL Syntax.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





