Context
For details about the MSP accounts of Huawei Qiankun, see MSP Account Types. The rights- and domain-based management principle of MSP accounts is similar to that of tenant accounts. MSP accounts can be managed in MSP workgroups at multiple levels.
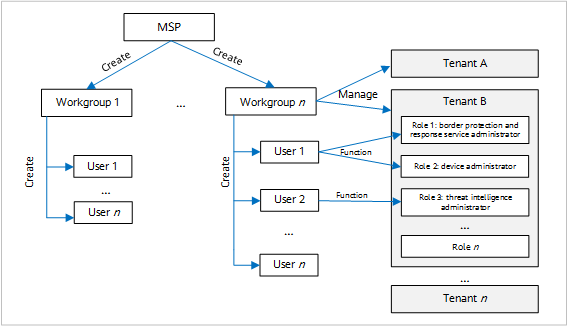
As shown in Figure 1, MSP workgroups are organized in an enterprise-like hierarchy. They can be divided based on the organization structure, and MSP users in each workgroup are assigned with specified permissions. This implements rights- and domain-based management.
Workgroup
Domain-based management is implemented on a per-workgroup basis.
The system provides a default workgroup, which is also called a root workgroup. The first registered MSP account is the root workgroup administrator, acting the role of a tenant administrator with all operation permissions. To ensure system security, the admin user can create multiple sub-accounts and assign different permissions to each sub-account based on the account role.
The sub-accounts and user roles created by an administrator are not isolated. As such, horizontal privilege escalation may occur, which brings security risks. For example, the default root administrator account, who has the highest permissions, creates accounts A and B, and assigns the accounts to subordinate departments or partners, respectively. If both accounts A and B have the account management and role management permissions, they can modify and delete accounts and roles of each other.
To prevent horizontal privilege escalation, you can configure workgroups to isolate accounts and user roles created by administrators. Workgroups are configured a hierarchical tree structure, that is, upper-level workgroups grant permissions to lower-level workgroups. Users in a workgroup can maintain accounts and user roles in their own workgroup and lower-level workgroups. Different accounts in parallel work groups have different authority, with data invisible to each other. To prevent horizontal privilege escalation, the default root administrator can assign workgroup administrator accounts, instead of sub-accounts, to subordinate departments or branches.

The administrator of the root workgroup can create lower-level workgroups based on the following rules:
- Each workgroup has an administrator. By default, the administrator of a workgroup can create users in the same workgroup. Common users (not the administrator) in a workgroup can create users in the workgroup only after being authorized.
- A maximum of five levels of workgroups are supported. By default, a workgroup is created, modified, or deleted by the administrator of the upper-level workgroup. Common users in the upper-level workgroup can create, modify, or delete lower-level workgroups only after being authorized.
User
A user refers to a person who uses the system. Information about a user includes a username, password, and permissions.
Users can be divided into the following types:
- Local: refers to a common user.
- Third-party: refers to a user who logs in to the console by invoking a northbound API. They are also known as northbound users.
- Remote: refers to a Huawei website user who needs to click Huawei Website Account when logging in to the Huawei Qiankun console.
Role
A role is a collection of user operation permissions. The operation permissions of an MSP depend on the roles assigned when the MSP or workgroup is created.
The Huawei Qiankun console supports two types of MSP roles: public roles and service roles.
To facilitate MSP operations, custom roles can be configured on the console. For details, see Table 1.
|
Role Type |
Role Name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Public role |
MSP administrator |
Has the read and write permissions for all MSP services and related configurations. |
|
MSP auditor |
Has the read permissions for all MSP services and related configurations. |
|
|
MSP open API operator |
Has permissions for open API services and related configurations. |
|
|
Service role
NOTE:
For more information, see related sections about the MSP permission control of each service. |
Common service role |
Has read and write permissions for some common services, such as the service ticket service, topic subscription service, and audit log service.
NOTE:
Ordinary MSP accounts (not MSP administrators or auditors) have operation permissions on specific services, such as service ticket management, subscription management, and log viewing, only after they are assigned the corresponding service roles. |
|
Custom role |
Custom role |
You can assign operation permissions to such a role based on your site requirements. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot