Configuring Policies
Scenario
After HSS is enabled, you can configure HSS policies based on your service requirements.
Constraints
- The professional, enterprise, premium, WTP, or container edition is enabled.
- For the default policy groups, you are advised to retain their default configurations.
- Modifications on a policy take effect only in the group it belongs to.
Accessing the Policies Page
- Log in to the HSS console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region or project.
in the upper left corner and select a region or project.
- In the navigation tree on the left, choose Security Operations > Policies. On the displayed page, Policy group parameters describes the fields.
Figure 1 Policy management

Table 1 Policy group parameters Parameter
Description
Policy Group
Name of a policy group The preset policy group names are as follows:
- tenant_linux_advanced_default_policy_group: preset policy of the Linux professional edition, which can only be viewed but cannot be copied or deleted.
- tenant_windows_advanced_default_policy_group: preset policy of the Windows professional edition, which can only be viewed but cannot be copied or deleted.
- tenant_linux_container_default_policy_group: preset Linux policy of the container edition. You can copy this policy group and create a new one based on it.
- tenant_linux_enterprise_default_policy_group is the default Linux policy of the enterprise edition. This policy group can only be viewed, and cannot be copied or deleted.
- tenant_windows_enterprise_default_policy_group: preset Windows policy of the enterprise edition. This policy group can only be viewed, and cannot be copied or deleted.
- tenant_linux_premium_default_policy_group: preset Linux policy of the premium edition. You can create a policy group by copying this default group and modify the copy.
- tenant_windows_premium_default_policy_group: preset Windows policy of the premium edition. You can create a policy group by copying this default group and modify the copy.
- wtp_ServerName is a WTP edition policy group. It is generated by default when WTP is enabled for a server.
Description
Detailed description of a policy group.
Supported Version
HSS edition supported by a policy group.
Supported OS
OS supported by a policy group.
Associated Servers
To view details about the servers associated with a policy group, click the number in the Servers column of the group.
- (Optional) If you have enabled the enterprise project function, select an enterprise project from the Enterprise Project drop-down list in the upper part of the page to view its data.
- If All projects is selected, the policy change will apply to the servers under all enterprise projects.
- If a specific enterprise project is selected, the policy change will only apply to the servers under this project.
- Click the name of a policy group to access the policy detail list.
Figure 2 Policies

- In the row of the policy, click Enable or Disable in the Operation column.
After a policy is disabled, HSS does not check for security issues based on the policy.
- Click the name of a policy to modify it. The following sections describe the policies.
Asset Discovery
- Click Asset Discovery.
- On the displayed page, modify the settings as required. For more information, see Table 2.
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Scan Time
Fixed time for automatic assets scan. The scan time can be customized for middleware, web frameworks, kernel modules, web applications, websites, web services, and databases.
Offset time is the automatic adjust ahead of or behind the specified scan time.
- Accounts: Linux accounts are automatically checked every hour, and Windows accounts are checked in real time.
- Open ports are automatically checked every 30 seconds.
- Processes are automatically checked every hour.
- Installed software is automatically checked once a day.
- Auto-started items are automatically checked every hour.
- Middleware/Web framework: You can select the scan date and time together.
- Kernel modules: You can set the scan date and time as required.
- Web applications/Websites/Web services/Databases: You can select the scan date and time together.
Scanned Web Directories
Specifies a web directory to be scanned.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Weak Password Detection
The baseline check has been upgraded. After your agent is upgraded to Linux 3.2.19 or Windows 4.0.28, you can go to the baseline check page and configure the scheduled check policy of the new baseline check. For details, see Configuring a Baseline Check Policy. If the agent has not been upgraded, you can perform the following operations to view the scheduled policy of the old baseline check. The policy cannot be modified.
Weak passwords are not attributed to a certain type of vulnerabilities, but they bring no fewer security risks than any type of vulnerabilities. Data and programs will become insecure if their passwords are cracked.
- Click Weak Password Detection.
- In the Policy Settings area, view the policy settings. For more information, see Table 3.
Table 3 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Scan Time
Time when scans are performed. It can be accurate to the minute.
Random Deviation Time (Seconds)
Random deviation time of the weak password based on Scan Time. The value range is 0 to 7,200s.
Scan Days
Days in a week when weak passwords are scanned. You can select one or multiple days.
User-defined Weak Passwords
You can add a password that may have been leaked to this weak password text box to prevent server accounts from using the password.
Enter only one weak password per line. Up to 300 weak passwords can be added.
Password Complexity Policy Check
A password complexity policy refers to the password rules and standards set on a server. If you enable Password Complexity Policy Check, HSS will check the password complexity policy when you manually perform a baseline check.
Configuration Check
The baseline check has been upgraded. After your agent is upgraded to Linux 3.2.19 or Windows 4.0.28, you can go to the baseline check page and configure the scheduled check policy of the new baseline check. For details, see Configuring a Baseline Check Policy. If the agent has not been upgraded, you can perform the following operations to view the scheduled policy of the old baseline check. The policy cannot be modified.
- Click Configuration Check.
- On the Configure Check, view policy settings.
Table 4 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Scan Time
Time when scans are performed. It can be accurate to the minute.
Random Deviation Time (Seconds)
Random deviation time of the system detection. The value ranges from 0 to 7,200, in seconds.
Scan Days
Day in a week when a scan is performed. You can select any days from Monday to Sunday.
System Default Baseline Library
The scan baseline has been configured in the system. You only need to select the baseline you want to scan. All parameters are in their default values and cannot be modified.
Web Shell Detection
If User-defined Scan Paths is not specified, the website paths in your assets are scanned by default. If User-defined Scan Paths is specified, website paths and the specified paths are scanned.
- Click Web Shell Detection.
- On the Web Shell Detection page, modify the settings as required. For more information, see Table 5.
Figure 3 Modifying the web shell detection policy

Table 5 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Scan Time
Time point when detections are performed. It can be accurate to the minute.
Random Deviation Time (Seconds)
Random deviation time. The value ranges from 0 to 7,200s.
Scan Days
Days in a week when web shells are scanned. You can select one or more days.
User-defined Scan Paths
Web paths to be scanned. A file path must:
- Start with a slash (/) and end with no slashes (/).
- Occupy a separate line and cannot contain spaces.
Do not add network directories as protected directories. HSS does not scan them even if they are added. The reasons are as follows:
- Inefficient detection
A network directory usually contains a large number of files and may reach hundreds of terabytes, severely slowing down a scan.
- Network bandwidth consumption
Accessing a network directory consumes network bandwidth. A large-scale scan may fully occupy the network bandwidth and affect your workloads. For example, the access speed may slow down and the network latency may increase.
Action
Action taken on a web shell file. The default action is Automated handling.
- Automatic handling: Web shell files are automatically isolated.
- Manual handling: Only an alarm event is reported when a web shell file is detected. The file is not isolated.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Installation & Configuration > Server Install & Config. In the Security Configuration tab, click Isolation and Killing of Malicious Programs. You can set the parameter to isolate and kill malicious programs globally. To enable automatic handling, ensure that you have enabled isolation and killing of malicious programs. For details, see Isolating and Killing Malicious Programs. You can perform fine-grained management on web shell protection as required.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
File Protection
- Click File Protection.
- On the File Protection page, modify the policy. For more information, see Table 6.
The following figure uses the Linux policy as an example.Figure 4 Modifying the file protection policy

- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Graph Engine Detection
Graph engine detection performs comprehensive source tracing analysis based on the threat information provided by multiple modules (including HIPS detection, AI ransomware detection, and antivirus detection). It can associate and comprehensively analyze multiple suspicious process events to identify intrusion behaviors, enhancing defense against vulnerability exploits.
To use the graph engine, you can enable the graph engine detection policy.
HIPS Detection
- Click HIPS Detection.
- Modify the policy content. For more information, see Table 7.
Figure 5 Modifying the HIPS detection policy
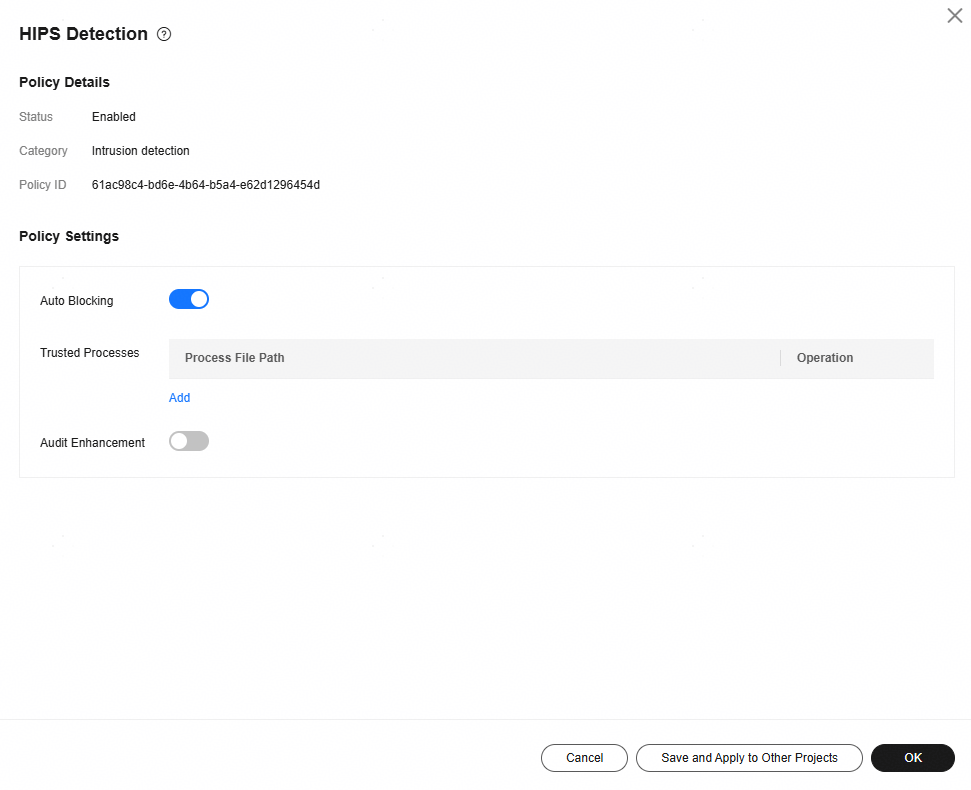
Table 7 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Auto Blocking
If this function is enabled, abnormal changes on registries, files, and processes will be automatically blocked to prevent reverse shells and high-risk commands. : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
Trusted Processes
Paths of trusted processes. You can click Add to add a path and click Delete to delete it.
Audit Enhancement
This function applies to servers with Linux kernel versions earlier than 5.10 and is disabled by default.
Audit, the audit framework of the Linux kernel, is used to monitor and record system security events. You can configure audit rules to control file access, system calling, and user commands, as well as generating detailed audit logs for security analysis, compliance check, and troubleshooting.
 : If audit enhancement is disabled, HSS uses netlink to collect process information by default. Some high-risk instantaneous commands may not be completely captured. As a result, no alarm is generated.
: If audit enhancement is disabled, HSS uses netlink to collect process information by default. Some high-risk instantaneous commands may not be completely captured. As a result, no alarm is generated. : After audit enhancement is enabled, HSS uses the audit mechanism to collect process information, which can effectively identify potential high-risk commands and generate alarms.
: After audit enhancement is enabled, HSS uses the audit mechanism to collect process information, which can effectively identify potential high-risk commands and generate alarms.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Login Security Check
- Click Login Security Check.
- On the displayed page, modify the settings as required. For more information, see Table 8.
Figure 6 Modifying the security check policy

Table 8 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Fast Brute-force Attack
Rule for determining a fast brute-force attack.
- Consecutive Login interval: Enter an integer in the range 10 to 180, in the unit of seconds. The default value is 30.
- Consecutive login failures: Enter an integer in the range 3 to 30. The default value is 5.
Slow Brute-force Attack
Rule for determining a slow brute-force attack.
- Consecutive Login interval: Enter an integer in the range 1,800 to 7,200, in the unit of seconds. The default value is 3600.
- Consecutive login failures: Enter an integer in the range 10 to 60. The default value is 15.
Action
- Report alarm: An alarm is generated for a brute-force attack, but the IP address of the brute-force attack is not blocked.
- Report alarm and block IP: An alarm is generated for a brute-force attack, and the IP address of the brute-force attack is blocked. If the software in a container is attacked, the IP address of the brute-force attack is not automatically blocked. Only an alarm is generated.
IP Address Blocking Time
IP address blocking duration, ranging from 1 to 525,600. A blocked IP address cannot be used for login within the duration. After the duration ends, the IP address is automatically unblocked. The default value is 720 minutes.
IP Address Whitelist
After an IP address is added to the whitelist, HSS does not block brute-force attacks from the IP address in the whitelist. A maximum of 50 IP addresses or network segments can be added to the whitelist. Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses are supported.
Brute-force Attack Alarm on Whitelisted IP
If it is enabled, the system generates alarms for brute-force attacks from whitelisted IP addresses, but does not block the IP addresses.
Detection on Multi-IP Brute-force Attacks
Multi-source IP brute-force attack is an attack that initiates brute force cracking attempts to the target system using multiple IP addresses, thereby obtaining access credentials such as accounts and passwords. It uses multiple IP address to attack the system, avoiding the detection and interception of single IP address attacks and improving the cracking success rate.
This function is disabled by default. Once enabled, HSS detects brute force attacks from multiple public IP addresses and reports alarms. As there are multiple IP addresses, HSS will not intercept such attacks for service continuity purpose. You need to check and change the exposed port in a timely manner after receiving the alarm.
Currently, multi-source IP address attacks against private IP addresses and IPv6 addresses cannot be detected.
Login Audit
After this function is enabled, the system reports successful SSH logins, detects remote logins, and generates alarms for remote logins.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Malicious File Detection
- Click Malicious File Detection.
- On the displayed page, modify the policy. For more information, see Table 9.
Figure 7 Modifying the malicious file detection policy

Table 9 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Whitelist Paths in Reverse Shell Check
Process file path to be ignored in reverse shell detection
Start with a slash (/) and end with no slashes (/). Occupy a separate line and cannot contain spaces.
Ignored Reverse Shell Local Port
Local ports that do not need to be scanned for reverse shells.
Ignored Reverse Shell Remote Address
Remote addresses that do not need to be scanned for reverse shells.
Detect Reverse Shells
- Whether to enable reverse shell detection. It monitors the process behavior of users in real time, and can detect and block the reverse shell behaviors from unauthorized shell connections. You are advised to enable this function.
 : enabled
: enabled
 : disabled
: disabled
Abnormal Shell Detection
- Whether to enable abnormal shell detection. It checks for actions on abnormal shells, including moving, copying, and deleting shell files, and modifying the access permissions and hard links of the files. You are advised to enable this function.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
- Whether to enable reverse shell detection. It monitors the process behavior of users in real time, and can detect and block the reverse shell behaviors from unauthorized shell connections. You are advised to enable this function.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Abnormal Process Behaviors
The abnormal process behavior policy supports two detection modes:
- Sensitive: In-depth full scans are performed on all processes, which may cause false positives. Suitable for network protection drills and key event assurance.
- Balanced: All processes are scanned. The scan result accuracy and the abnormal process detection rate are moderate. Suitable for routine protection.
This policy does not need to be configured separately. It changes with the protection mode of the policy group. To enable the sensitive mode, change the protection mode of the policy group to Sensitive by referring to Configuring the Policy Group Protection Mode.
Root Privilege Escalation Detection
- Click Root privilege escalation.
- In the displayed area, modify the settings as required. For more information, see Table 10.
Figure 8 Modifying the root privilege escalation policy

- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Real-time Process
- Click Real-time Process.
- On the displayed page, modify the settings as required. For more information, see Table 11.
Figure 9 Modifying the real-time process policy

Table 11 Parameters for real-time process policy settings Parameter
Description
High-Risk Commands
High-risk commands that contain keywords. The command can contain only letters, numbers, hyphens (-), spaces, and the following special characters: /*\=>.:'"+-
Currently, built-in shell commands cannot be detected.
Whitelist (Do Not Record Logs)
Paths or programs that are allowed or ignored during detection. You can enter the regular expression of the command to be added to the whitelist. The command regular expression is optional.
Example:
- Full path or program name of a process: /usr/bin/sleep
- Command regular expression: ^[A-Za-z0-9[:space:]\\*\\.\\\":_'\\(>=-]+$
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Rootkit Detection
- Click Rootkit Detection.
- On the rootkit detection page, modify the policy content.
Figure 10 Modifying the rootkit detection policy

Table 12 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Example Value
Kernel Module Whitelist
Add the kernel modules that can be ignored during the detection.
Up to 10 kernel modules can be added. Each module occupies a line.
xt_conntrack
virtio_scsi
tun
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
AV Detection
- Click AV Detection.
- On the AV Detection slide pane that is displayed, modify the settings as required. For details, see Table 13.
Table 13 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Example Value
Real-Time Protection
After this function is enabled, AV detection is performed in real time when the current policy is executed. You are advised to enable this function.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
 : enabled
: enabledProtected File Type
Type of the files to be checked in real time.
- All: Select all file types.
- Executable: Executable file types such as EXE, DLL, and SYS.
- Compressed: Compressed file types such as ZIP, RAR, and JAR.
- Text: Text file types such as PHP, JSP, HTML, and Bash.
- OLE: Composite file types such as Microsoft Office files (PPT and DOC) and saved email files (MSG).
- Other: File types except the preceding types.
All
Action
Protective action for target detection alarms. The default value is Automated handling.
- Automated handling: Isolate high-risk virus files by default. Report other virus files but do not isolate them.
- Manual handling: All the detected virus-infected files are reported but not automatically isolated.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Installation & Configuration > Server Install & Config. In the Security Configuration tab, click Isolation and Killing of Malicious Programs. You can set the parameter to isolate and kill malicious programs globally. To enable automatic handling, ensure that you have enabled isolation and killing of malicious programs. For details, see Isolating and Killing Malicious Programs. You can perform fine-grained management on AV detection as required.
Automated handling
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Container Information Collection
- Click Container Information Collection.
- On the Container Information Collection slide pane that is displayed, modify the Policy Settings. For details about the parameters, see Table 14.
Table 14 Container information collection policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Mount Path Whitelist
Enter the directory that can be mounted.
The whitelist has a higher priority than blacklist. If a directory is specified in both the whitelist and blacklist, it is regarded as a whitelisted item.
/test/docker or /root/*
Note: If a directory ends with an asterisk (*), it indicates all the sub-directories under the directory (excluding the main directory).
For example, if /var/test/* is specified in the whitelist, all sub-directories in /var/test/ are whitelisted, excluding the test directory.
Mount Path Blacklist
Enter the directories that cannot be mounted. For example, user and bin, the directories of key host information files, are not advised being mounted. Otherwise, important information may be exposed.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Cluster Intrusion Detection
This policy applies only to third-party clusters.
- Click Cluster Intrusion Detection.
- On the Cluster Intrusion Detection slide pane that is displayed, modify the Policy Settings. For details about the parameters, see Table 15.
Table 15 Cluster intrusion detection policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Basic Detection Cases
You can select check items as needed. The options are as follows:
- High-privilege RoleBinding: Check for high-privilege role binding behaviors. RoleBinding binds an account to a role. Hackers can bind a common account to a high-privilege role to obtain permissions.
- High-privilege ClusterRoleBinding: Check for high-privilege cluster role binding behaviors. ClusterRoleBinding binds an account to a cluster role. Hackers can bind a common account to a high-privilege role to obtain permissions.
- ServiceAccount creations: Checks for the creation of service accounts. Service accounts are important Kubernetes credentials. Hackers can create service accounts and bind them to high-privilege roles to control clusters.
- List Secrets operations: Check for List Secrets operations. Kubernetes Secret is an object that allows users to store and manage sensitive information (such as passwords and connection strings) in a cluster. List Secrets can be referenced in the pod configuration. Attackers who have the permission to retrieve secrets from the API server (for example, by using the service account of the pod) can access sensitive information, which may include the credentials of diverse services.
- DaemonSet creations: Check for DaemonSet creations. Attacker may attempt to run their code in a cluster by creating a new container. DaemonSet is the best way to control all nodes in Kubernetes.
- Cronjob creation: Check for Cronjob creations. Kubernetes jobs can be used to run containers that execute batch processing tasks. These tasks are usually limited.
- Interactive shell used for exec in pods: Check for the exec using an interactive shell in a pod. Hackers may use interactive shell programs such as bash and sh to perform operations in containers.
- Privileged pod creations: Check for privileged pod creations. Creating a privileged container and escaping from it is one of the most common escape methods.
- Pods created with sensitive directory: Check for the creation of pods containing sensitive directories. Hackers may mount sensitive directories, such as /, /root, and /etc, to servers to escalate permissions.
- Pods created with host network namespace: Check for the creation of pods with a host network namespace. Hackers may create containers that use the host network to escape or listen to traffic.
- Pods created with host PID space: Check for the creation of pods with a server PID space. Hackers may create containers with a server PID namespace to escape.
- Unauthorized access to API server: Check for unauthorized access to the API server. Hackers may send API requests to probe the cluster and obtain information about containers, secrets, and other resources in the cluster. These probing behaviors usually trigger alarms for unauthorized access to the API server.
- Access to API Server with curl: Check for the use of curl to access the API server. Generally, tools like kubectl are unlikely to exist in containers. Using curl to intrude pods and probe API servers is one of the most common attack methods.
- Exec in system management space: Check for the exec command used for management components such as kube-apiserver.
- Ingress vulnerability: Check for ingress vulnerabilities. Users who can create or update ingress objects can use custom fragments to obtain all the secrets in the cluster.
- Ingress-alias: Check for ingress aliases. Users who have the permissions to create or update ingress objects can use the spec.rules[].http.paths[].path field in an ingress object (in the networking.k8s.io or extensions API group) to obtain the credential of the ingress-nginx controller. By default, the credential has access to all confidential information in the cluster.
- SelfSubjectRulesReview: Check for the behaviors of querying SelfSubjectRulesReview. When a hacker enters a pod, the hacker needs to check the service account (SA) rights of the pod or the token rights stolen through the pod.
- Pods created in management space: Check for the pod creations in the system management space. Generally, after a Kubernetes cluster becomes stable, the resources in the kube-system namespace will not be created or deleted randomly. Attackers usually forge management components to implement persistence operations.
- Static pod creations: Check for static pod creations. Hackers may use static pods to achieve a certain purpose because static pods cannot be deleted through the API server.
- Man-in-the-middle attack: Check for man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks and medium-risk vulnerabilities (such as CVE-2020-8554).
- Worm, mining, or Trojan: Check for the pods created using the images infected with worms, mining software, or Trojans.
- K8s event deletion: Check for Kubernetes event deletions. Kubernetes events help to identify changes that have occurred in a cluster. Attackers may want to delete these events (for example, by using the kubectl delete events --all command) so that their activities in the cluster cannot be detected.
Select all
Whitelist
You can customize the types and values that need to be ignored during the detection. You can add and delete types and values as required.
The following types are supported:
- IP address filter
- Pod name filter
- Image name filter
- User filter
- Pod tag filter
- Namespace filter
Type: IP address filtering
Value: 192.168.x.x
- Click OK.
- If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same edition.
- After this policy is configured, you need to enable log audit and deploy the HSS agent on the management node (node where the APIServer is located) of the cluster to apply the policy.
Container Escape Detection
- Click Container Escape. The container escape policy details page is displayed.
- On the container escape page that is displayed, edit the policy content. For details about the parameters, see Table 16.
If no image, process, or POD needs to be added to the whitelist, leave the whitelist blank.
Table 16 Container escape detection policy parameters Parameter
Description
Image Whitelist
Enter the names of the images that do not need to perform container escape behavior detection. An image name can contain only letters, numbers, underscores (_), and hyphens (-), and each name needs to be on a separate line. Up to 100 image names are allowed.
Process Whitelist
Enter the full paths of processes that do not need to perform container escape behavior detection. A process path can contain only letters, numbers, underscores (_), and hyphens (-), and each path needs to be on a separate line. Up to 100 process paths are allowed.
Pod Name Whitelist
Enter the names of pods that do not need to perform container escape behavior detection. A pod name can contain only letters, numbers, underscores (_), and hyphens (-), and each name needs to be on a separate line. Up to 100 pod names are allowed.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Container Escape Prevention
- Click Container Escape Prevention. The policy details page is displayed.
- Edit the policy. For details about the parameters, see Table 17.
Figure 11 Container escape prevention policy

Table 17 Container escape prevention policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Action
- Alarm: If an abnormal runtime behavior is detected, only an alarm is reported.
- Block: If an abnormal runtime behavior is detected, an alarm is reported and the container instance is blocked.
- Allow: If an abnormal runtime behavior is detected, the container instance is still allowed to run.
Block
Protection Scope
Select the protection scope of abnormal runtime behavior detection. Specify server and image names to detect abnormal behaviors of the containers that use the specified images on specified servers.
The configuration methods are as follows:
- Server Name: Select a server from the drop-down list and click Add. Alternatively, enter a server name in the text box and press Enter. Each name can contain up to 128 characters. Up to 100 server names can be configured.
- Image Name: Select an image name from the drop-down list and click Add. Alternatively, enter an image name in the text box and press Enter. Each name can contain up to 128 characters. Up to 100 image names can be configured.
- Server name: test01
- Image name: moby/buildkitbuildx-stable-1
Policy Settings
The container anti-escape policy contains preset rules detecting abnormal behaviors in processes, files, and system calls. A detection rule specifically a scenario where abnormal behaviors are checked for. It does not define runtime abnormal behaviors. You can enable or disable the detection rule as required. (The rules are disabled by default.) The rule names and IDs are as follows:
- Escape by Writing in High-risk Directory on Host (ae246a6fb5290701): Check whether a sensitive host directory is mounted to a container, and a process in the container is used to write data to the directory.
- Container Escape Tool Execution (ce246a6fb5290702): Check for the execution of container escape tools such as CDK.
- User Configuration File Change on Host (de246a6fb5290703): Check for modifications on the system and application configuration files on a host.
- High-risk System Call (ee246a6fb5290704): Check for high-risk system calls, such as chown, used by processes.
In addition to the preceding detection rules, the HSS can detect abnormal network activities and process capabilities.
If an abnormal behavior event triggers a detection rule whose Action is Alarm or Block, the ID of the triggered rule is displayed in the alarm summary reported by HSS.
The Action of a detection rule is Alarm by default, but this setting has a lower priority than the Action of the policy. If the policy action is Block, the actual rule action will also be Block.
Enable all (
 )
) - Confirm the information and click OK.
Abnormal Container Behavior Detection
- Click Abnormal Container Behavior Detection.
- Modify the policy. For details about the parameters related to the policy content, see Table 18.
Figure 12 Abnormal container behavior detection policy
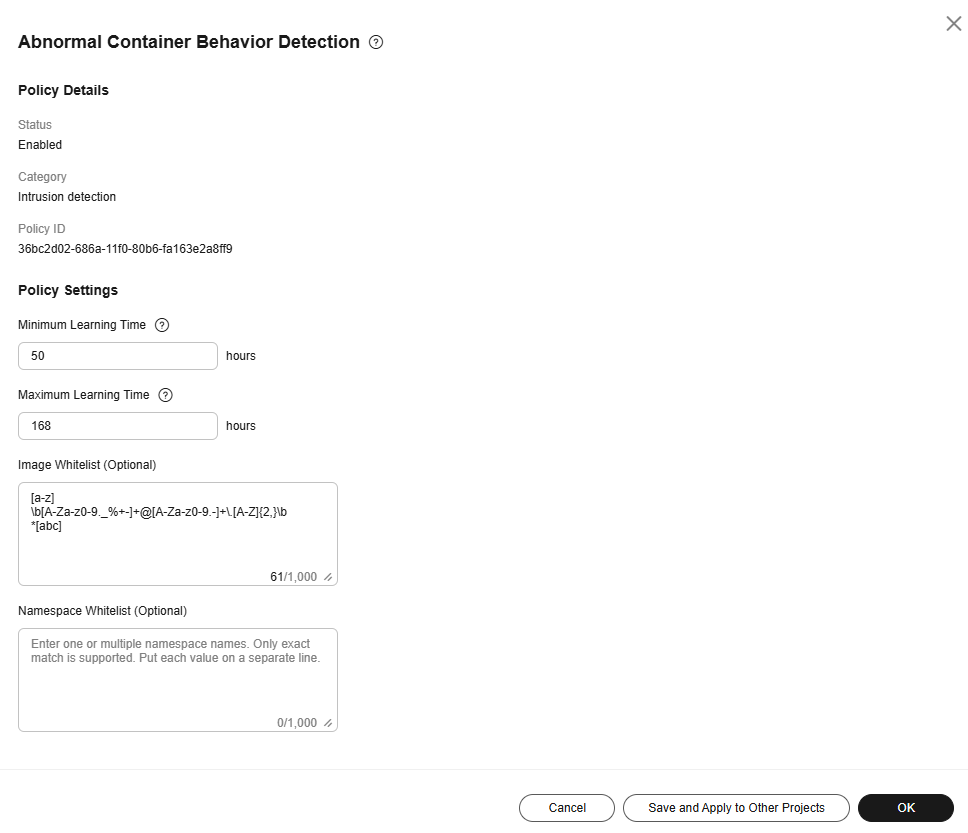
Table 18 Abnormal container behavior detection policy parameters Parameter
Description
Minimum Learning Time
After the learning has continued for this length of time, if the process baseline has not changed for a certain period of time, the learning will stop and the process behavior check will start. The value is an integer ranging from 24 to 72, in hours. The default value is 72 hours.
Maximum Learning Time
After the learning has continued for this length of time, the learning will stop and the process behavior check will start. The value is an integer ranging from 72 to 168, in hours. The default value is 168 hours.
Image Whitelist
Images that do not need to be checked. You can enter an image name or use a regular expression to match a group of image names. Put each name or regular expression on a separate line.
Namespace Whitelist
Namespaces that do not need to be checked. Enter one or multiple namespace names. Put each name on a separate line.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Container Information Module
- Click Container Information Collection.
- Modify the policy content as prompted. For details about the parameters related to the policy, see Table 19.
Table 19 Container information module policy parameters Parameter
Description
Custom Container Whitelist
Enter the container name that can be ignored during the detection.
- Simple names of containers can be configured based on Docker. HSS automatically performs fuzzy match. Other containers perform exact match based on their names.
- Each container name needs to be on a separate line. Up to 100 whitelist items are allowed.
Custom Image Organization Whitelist
Enter the organization name that can be ignored during the detection.
Each organization name needs to be on a separate line. Up to 100 whitelist items are allowed.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Container File Monitoring
If a monitored file path is under the mount path rather than the writable layer of the container on the server, changes on the file cannot trigger container file modification alarms. To protect such files, configure a file protection policy.
- Click Container File Monitoring.
- On the Container File Monitoring slide pane that is displayed, modify the Policy Settings. For details about the parameters, see Table 20.
Table 20 Container file monitoring policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Fuzzy Match
Indicates whether to enable fuzzy match for the target file. You are advised to select this option.
Selected
Image Name
Name of the target image to be checked
test_bj4
Image ID
ID of the target image to be checked
-
File
Name of the file in the target image to be checked
/tmp/testw.txt
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Container Process Whitelist
- Click Container Process Whitelist.
- On the Container Process Whitelist slide pane that is displayed, modify the Policy Settings. For details about the parameters, see Table 21.
Table 21 Container process whitelist policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Dynamic Whitelist
If it is enabled, HSS assumes that a container only runs the process commands configured in its startup parameters. When a container is started, HSS identifies its entrypoint configuration to determine its main process. If other processes are detected running in the container, an alarm will be triggered.

Fuzzy Match
Indicates whether to enable fuzzy match for the target file. You are advised to select this option.
Selected
Image Name
Name of the target image to be checked
test_bj4
Image ID
ID of the target image to be checked
sha256:732aab547cfe56841c02fb83921db4b91f04a1e636cc2cad76e224897056f140
Process
Full path of the file in the target image to be checked
/tmp/testw
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Suspicious Image Behaviors
- Click Suspicious Image Behaviors.
- On the Suspicious Image Behaviors slide pane that is displayed, modify the Policy Settings. For details about the parameters, see Table 22.
Table 22 Suspicious image behaviors policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Rule Name
Name of a rule
-
Description
Brief description of a rule
-
Template
- Configure templates based on different rules. The supported rules are as follows:
- Image whitelist
- Image blacklist
- Image tag whitelist
- Image tag blacklist
- Create container whitelist
- Create container blacklist
- Container mount proc whitelist
- Container seccomp unconfined
- Container privilege whitelist
- Container capability whitelist
- The parameters are described as follows:
- Exact match: Enter the names of the images you want to check. Use semicolons (;) to separate multiple names. A maximum of 20 names can be entered.
- RegEx match: Use regular expressions to match images. Use semicolons (;) to separate multiple expressions. A maximum of 20 expressions can be entered.
- Prefix match: Enter the prefixes of the images you want to check. Multiple prefixes are separated by semicolons (;). A maximum of 20 prefixes can be entered.
- Tag Name: Enter the tag and value of the images you want to check. A maximum of 20 tags can be added.
- Permission Type: Specify permissions to be checked or ignored. For details about permissions, see Table 23.
-
Table 23 Abnormal image permissions Permissions Name
Description
AUDIT_WRITE
Write records to kernel auditing log.
CHOWN
Make arbitrary changes to file UIDs and GIDs.
DAC_OVERRIDE
Bypass file read, write, and execute permission checks.
FOWNER
Bypass permission checks on operations that normally require the file system UID of the process to match the UID of the file.
FSETID
Do not clear set-user-ID and set-group-ID permission bits when a file is modified.
KILL
Bypass permission checks for sending signals
MKNOD
Create special files using mknod.
NET_BIND_SERVICE
Bind a socket to internet domain privileged ports (port numbers less than 1024).
NET_RAW
Use RAW and PACKET sockets.
SETFCAP
Set file capabilities.
SETGID
Make arbitrary manipulations of process GIDs and supplementary GID list.
SETPCAP
Modify process capabilities.
SETUID
Make arbitrary manipulations of process UIDs.
SYS_CHROOT
Use chroot to change the root directory.
AUDIT_CONTROL
Enable and disable kernel auditing; change auditing filter rules; retrieve auditing status and filtering rules.
AUDIT_READ
Allow reading audit logs via multicast netlink socket.
BLOCK_SUSPEND
Allow suspension prevention.
BPF
Allow creating BPF maps, loading BPF Type Format (BTF) data, retrieve JITed code of BPF programs, and more.
CHECKPOINT_RESTORE
Allow operations related to checkpoints and restoration.
DAC_READ_SEARCH
Bypass file read permission checks and directory read and execute permission checks.
IPC_LOCK
Lock memory (such as mlock, mlockall, mmap, and shmctl).
IPC_OWNER
Bypass permission checks for operations on System V IPC objects.
LEASE
Establish leases on arbitrary files
LINUX_IMMUTABLE
Set the FS_APPEND_FL and FS_IMMUTABLE_FL i-node flags.
MAC_ADMIN
Allow MAC configuration or state changes.
MAC_OVERRIDE
Override Mandatory Access Control (MAC).
NET_ADMIN
Perform various network-related operations.
NET_BROADCAST
Make socket broadcasts, and listen to multicasts.
PERFMON
Allow privileged system performance and observability operations using perf_events, i915_perf and other kernel subsystems.
SYS_ADMIN
Perform a range of system administration operations.
SYS_BOOT
Use reboot and kexec_load. Reboot and load a new kernel for later execution.
SYS_MODULE
Load and unload kernel modules.
SYS_NICE
Raise process nice value (nice, set priority) and change the nice value for arbitrary processes.
SYS_PACCT
Enable or disable process accounting.
SYS_PTRACE
Trace arbitrary processes using ptrace.
SYS_RAWIO
Perform I/O port operations (ipl and ioperm).
SYS_RESOURCE
Override resource limits.
SYS_TIME
Set the system clock (settimeofday, stime, and adjtimex) and real-time (hardware) clock.
SYS_TTY_CONFIG
Use vhangup. Employ various privileged ioctl operations on virtual terminals.
SYSLOG
Perform privileged syslog operations.
WAKE_ALARM
Trigger something that will wake up the system.
- Configure templates based on different rules. The supported rules are as follows:
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Port Scan Detection
- Click Port Scan Detection.
- On the Port Scan Detection slide pane that is displayed, modify the Policy Settings. For details about the parameters, see Table 24.
Table 24 Port scan detection policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Source IP Address Whitelist
Enter one or multiple IP addresses or IP address ranges. Use commas (,) to separate multiple values.
Example: 192.168.0.1,192.168.0.2,192.168.10-192.168.100
192.168.0.1
Ports to Scan
Details about the port number and protocol type to be detected
-
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
External Connection Detection
- Click External Connection Detection. The details page is displayed.
- On the page that is displayed, modify the policy details. Table 25 describes the parameters.
Table 25 Parameters of an external connection detection policy Parameter
Description
Example Value
Process Whitelist
Traffic is filtered based on process names or process file paths, and the traffic directions in the whitelist.
- Process name or file path: /usr/local/test
- Traffic direction: bidirectional
Traffic Whitelist
Traffic is filtered based on source or destination IP addresses, ports, or a combination of them.
-
Collection Protocol
The protocol to be detected. The value can be TCP or UDP.
Select all
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Fileless Attack Detection
- Click Fileless attack detection.
- On the policy details page, view or modify the policy. The following table describes the parameters.
Table 26 Parameters of a fileless attack detection policy Parameter
Description
Example Value
Process injection
- Process Injection: Enable or disable process injection detection.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
- Trustlist Matching Specifications: Configure how to match the user-defined path trustlist. Click
 to select a match mode. The options are as follows:
to select a match mode. The options are as follows:
- Full match, case sensitive
- Full match, case-insensitive
- Fuzzy matching
- Path trustlist: Enter the paths that do not need to be checked for process injection. Enter one path on each line.

- Fuzzy matching
- /usr/sbin/hald
LD hijacking
- LD hijacking: Enable or disable LD hijacking detection.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
- Full process detection: Enable or disable LD hijacking threat detection for all processes.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
- Trustlist Matching Specifications: Configure how to match the user-defined path trustlist. Click
 to select a match mode. The options are as follows:
to select a match mode. The options are as follows:
- Full match, case sensitive
- Full match, case-insensitive
- Fuzzy matching
- Path trustlist: Enter the paths that do not need to be checked for LD highjacking. Enter one path on each line.


- Fuzzy matching
- /usr/sbin/hald
Memory-based process
- Memory-based process: Enable or disable memory process detection.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
- Full process detection: Enable or disable memory-based process threat detection for all processes.
 : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled
- Trustlist Matching Specifications: Configure how to match the user-defined path trustlist. Click
 to select a match mode. The options are as follows:
to select a match mode. The options are as follows:
- Full match, case sensitive
- Full match, case-insensitive
- Fuzzy matching
- Path trustlist: Enter the paths that do not need to be checked for memory-based processes. Enter one path on each line.


- Fuzzy matching
- /usr/sbin/hald
VDSO Hijacking
VDSO Hijacking: Enable or disable VDSO hijacking detection. : enabled
: enabled : disabled
: disabled

- Process Injection: Enable or disable process injection detection.
- Confirm the information and click OK.
If All projects are selected for an enterprise project and the policy of the default policy group is modified, you can click Save and Apply to Other Projects to apply the modification to other policies of the same version.
Self-protection
The self-protection policy protects HSS software, processes, and files from being damaged by malicious programs. You cannot customize the policy content.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot













