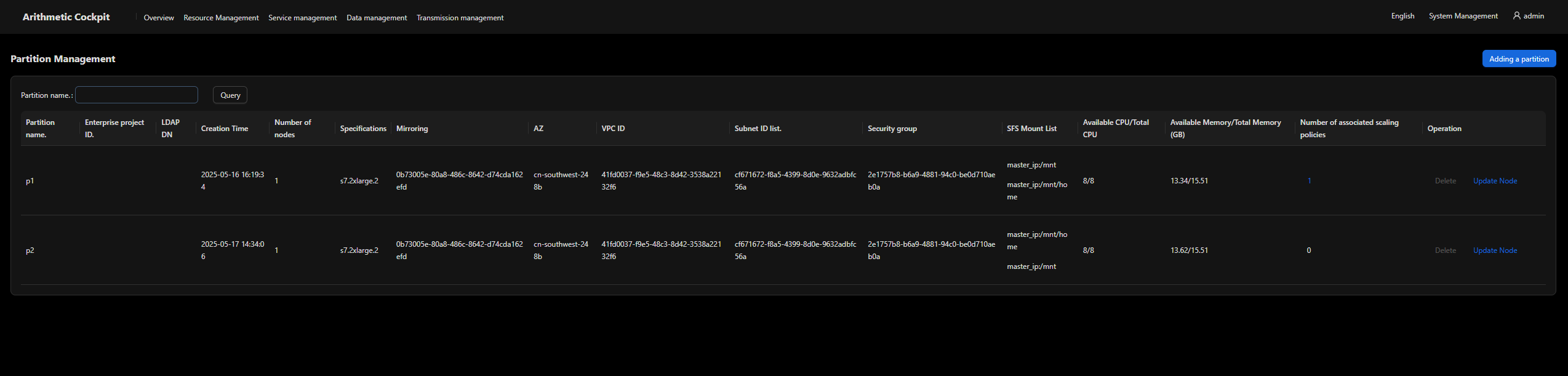
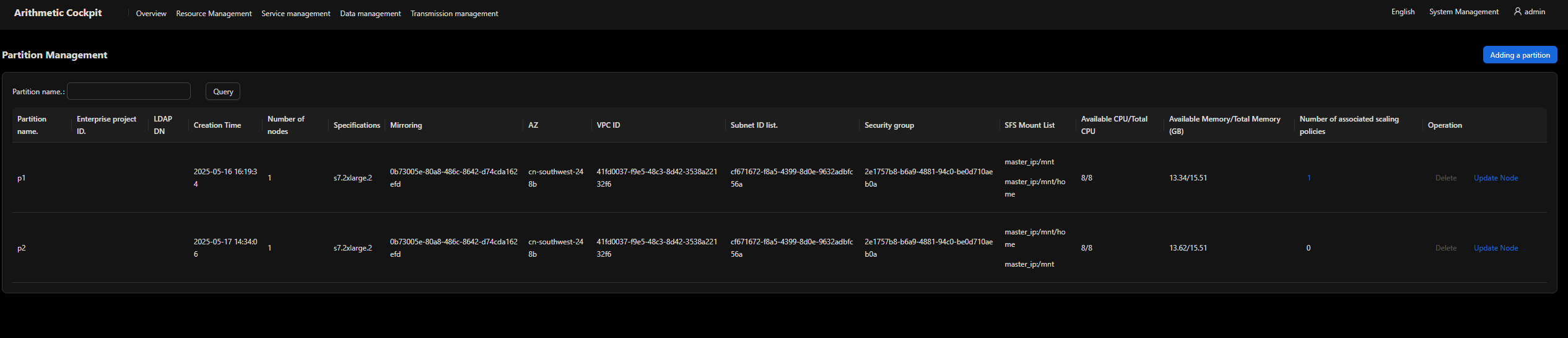
Partition Management
Partitions are used to divide cluster nodes into logical resource pools to meet job scheduling requirements (such as by priority, hardware type, and resource limit). There are no limitations on the number of nodes in each partition. Nodes in different partitions are independent of each other.
Partition
- Partition
- Partitioning is the most basic method for creating resource pools from nodes in a cockpit. Physical nodes are divided into multiple logical resource groups.
- You can configure resource limits, scheduling policies, and access permissions for each partition.
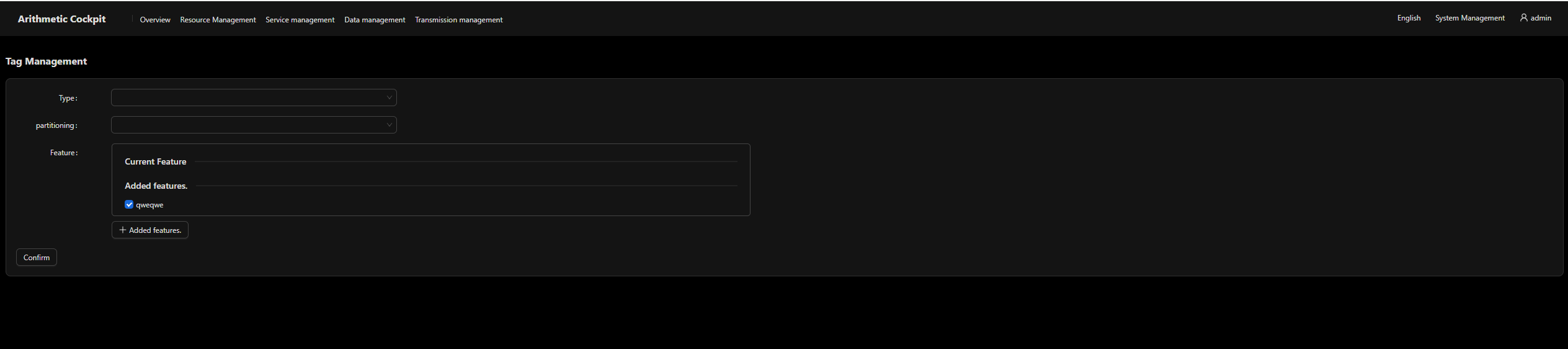
- Node features
Nodes are tagged by features such as hardware type and network architecture. Logical partitions are further divided based on these features.
- Dynamic node pools
Cloud auto scaling or node status management can be used together to dynamically scale a node pool, for example, creating nodes on demand and adding them to a partition.
Configuring a Partition
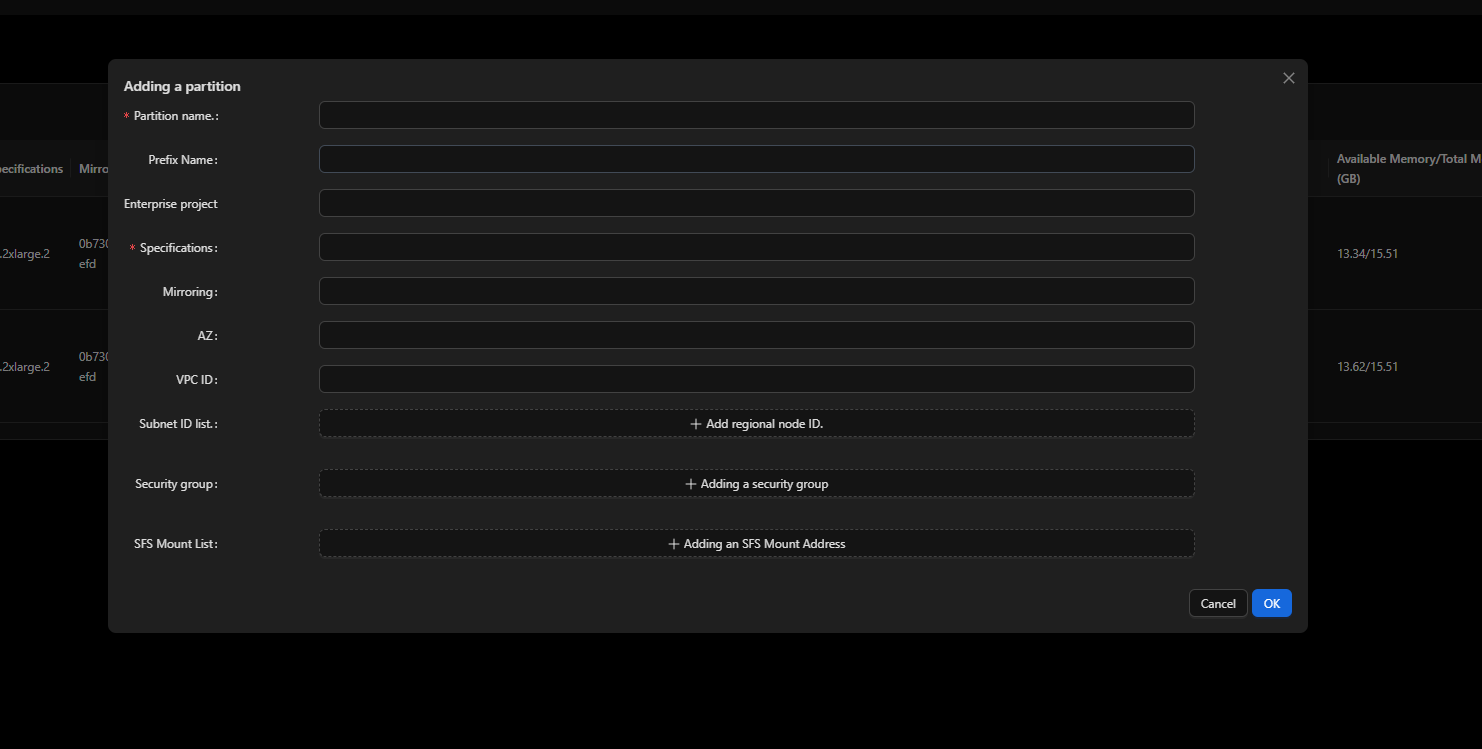
- Create a partition.
Specify parameters such as the image, network, and security group for the partition. Nodes can be dynamically added to or deleted from the partition when the partition is running.
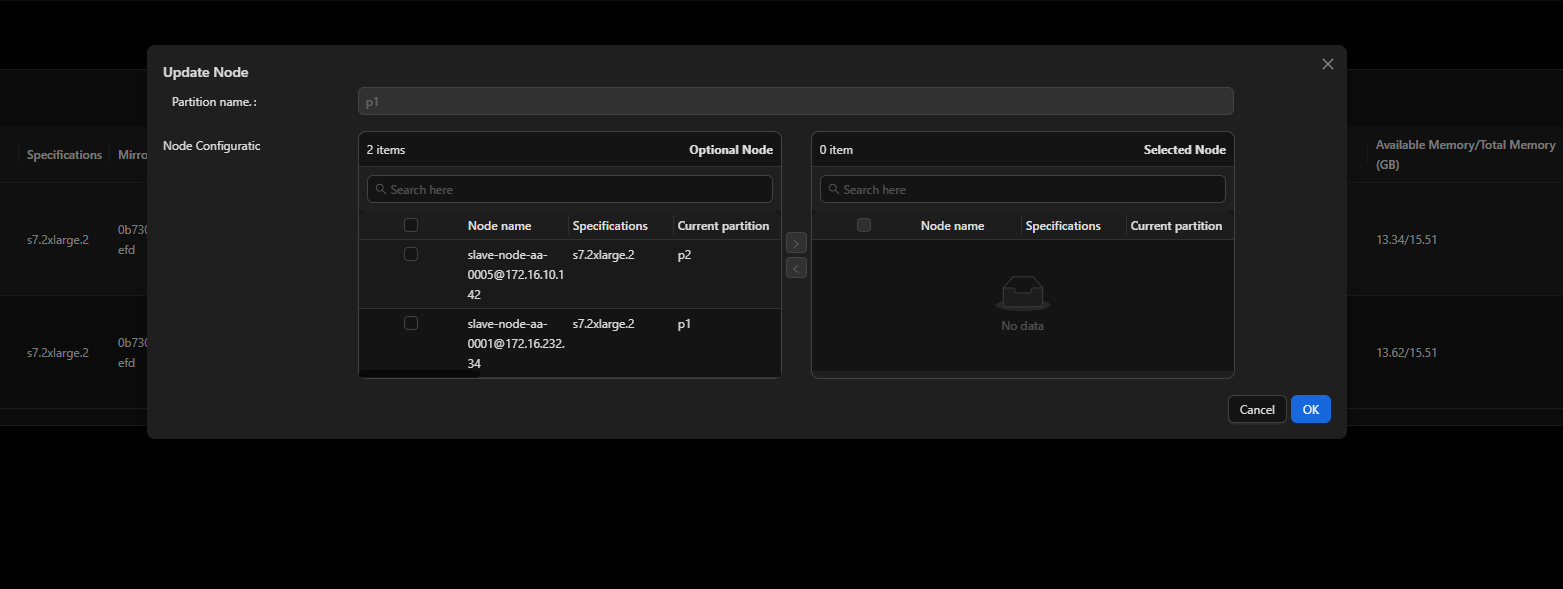
- Edit the partition.
Modify the partition of a node.
- Submit a job to a partition. For details, see Job Queues.
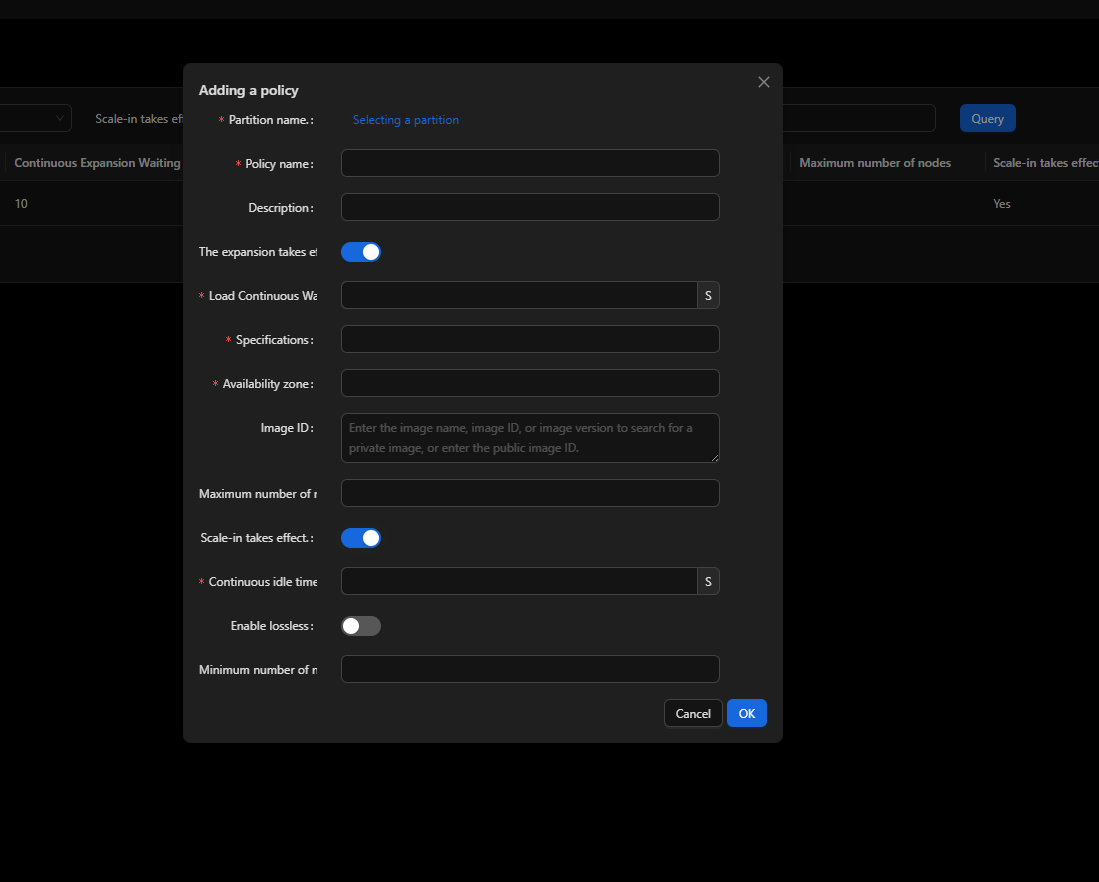
Applying a Scaling Policy to a Partition
Specify a scale-out or scale-in policy on the UI.
Viewing Partition Details
- List all partitions.
sinfo -s # Check the partition summary.
sinfo -p gpu # Check the node statuses in a partition.
- View node details.
scontrol show nodes node1 # Check the details such as the partition, features, and resources.
- Monitor the partition usage.
squeue -p gpu -o "%i %P %u %T" # Check the job statuses in the partition named p1.
- View partitions.
- View the job statuses in a partition.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot