Modifying the Host Header
A host is specified in HTTP request headers. It is the domain name of the site accessed by CDN during origin pull.
Background
- The origin server decides the address to be accessed during origin pull.
- The host header decides the site that is associated with the requested content.
Assume that your origin server is an Nginx server. Its IP address is x.x.x.x, and its domain name is www.test.com. The following sites are deployed on the origin server.
server { listen 80; server_name www.a.com; location / { root html; } } server { listen 80; server_name www.b.com; location / { root html; } }If you want CDN to pull content from this Nginx server, set the origin server address to x.x.x.x or www.test.com on CDN. Since there are multiple sites on the origin server, you need to specify the specific site to pull content. If you want CDN to obtain content from the www.a.com site, set the host to www.a.com on CDN. If you want CDN to obtain content from the www.b.com site, set the host to www.b.com on CDN.
Precautions
- After a domain name is added, CDN regards it as the host by default. If you do not want CDN to pull content from the acceleration domain name, set a host to specify the location of the requested content.
- If your origin server address is an IP address or a domain name, your host type is the acceleration domain name by default.
- The actual host of a wildcard domain name is the domain name accessed by users, even though the default host is listed as the wildcard domain name itself.
- Do not set the host to a wildcard domain name for an acceleration domain that is not a wildcard domain name, as this will result in an invalid host.
- When a Huawei Cloud OBS bucket is used as an origin server, the bucket's domain name is used as the host by default. To use a custom host, ensure that the host has been added as a user domain name of the bucket. Or, bucket access will fail.
- If you set your origin server address as a domain name, and specify the domain name as that of an object storage bucket of Huawei Cloud or another vendor, set the host to the domain name of your object storage bucket. Otherwise, the origin pull fails.
Procedure
- Log in to the CDN console.
- In the navigation pane, choose .
- In the domain list, click the target domain name or click Configure in the Operation column.
- In the Origin Server Settings area, click Edit in the Operation column of the row containing the target origin server.
Figure 1 Editing the origin server
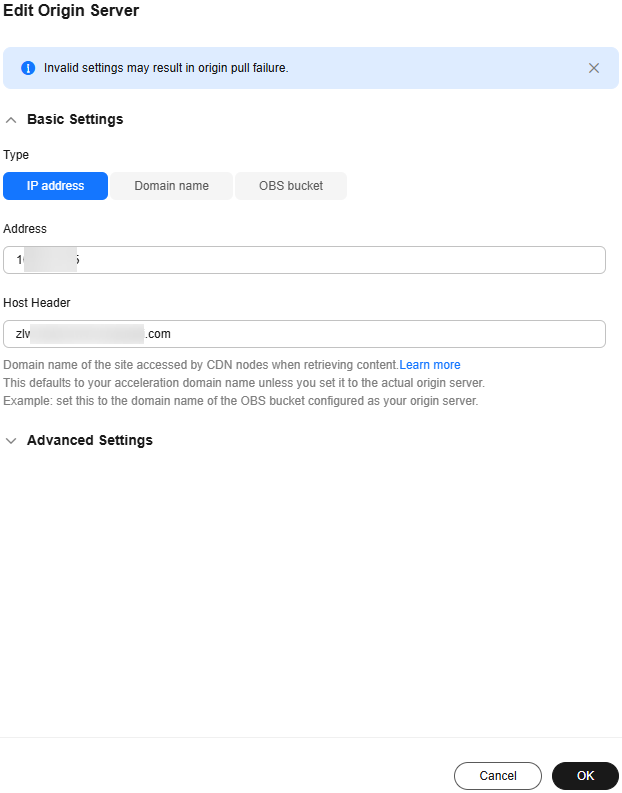
- Enter the domain name of the host and click OK.
Each label of a domain name (for example, *** in ***.***.com) can contain up to 63 characters.
- To edit host headers in a batch, click Edit above the origin server list.
In the Host Header column, modify the information and click Save.
The configuration takes about 5 minutes.
Examples
Assume that you have an acceleration domain name www.example.com. Its origin server domain name is www.origin.com, and the host is www.example01.com.
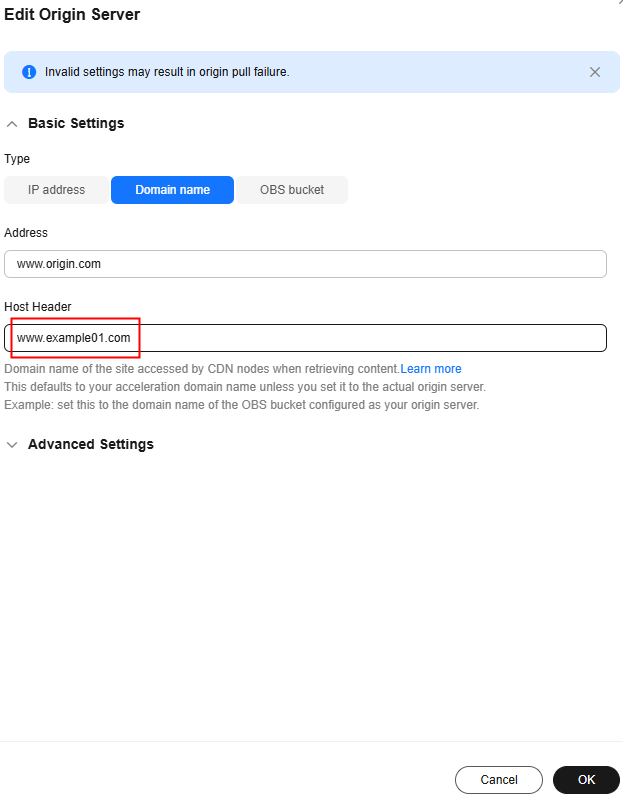
When a user requests the http://www.example.com/test.jpg file, the file is not cached on CDN, and CDN pulls that file from the origin server www.origin.com whose IP address is 192.168.1.1. The file is found in the www.example01.com site of the origin server. CDN then returns the file to the user, and caches the file on PoPs.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





