Configuring a Certificate for a Batch of Domain Names
Background
This topic describes how to set an HTTPS certificate of domain names and deploy the HTTPS configuration on all CDN PoPs to implement secure acceleration.
- HTTP
HTTP transfers content in plaintext without any data encryption. If an attacker intercepts packets transmitted between browsers and website servers, the transmitted content can be read directly.
- HTTPS
Based on HTTP, HTTPS uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to encrypt data transmission. With SSL, servers are authenticated using certificates, and communications between browsers and servers are encrypted.
Scenarios
- If you have a certificate, you can directly upload it. You can also view and delete existing certificates.
- You can update certificates in batches. The new certificates will overwrite the original ones.
- You can buy certificates on CCM.
Configuring a Certificate
- Log in to the CDN console.
- In the navigation pane, choose .
- Click Configure Certificate in the upper left corner.
Figure 1 Configuring a certificate
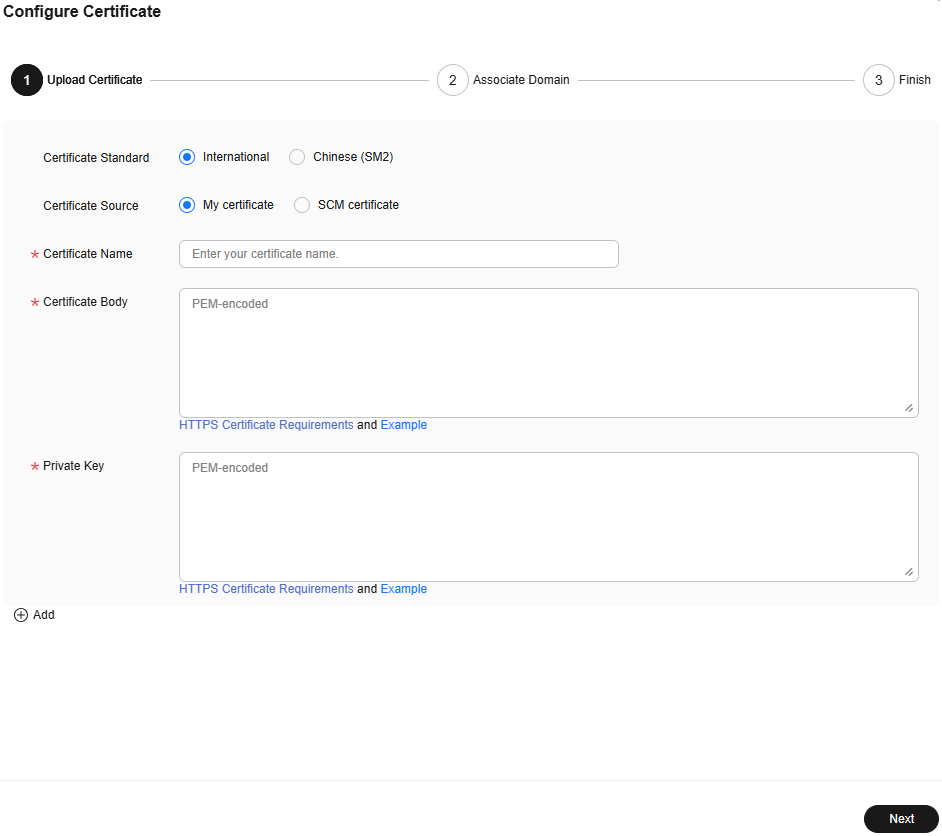
- Set related parameters.
Table 1 Parameters of an international certificate Parameter
Description
Certificate Standard
International
Certificate Source
Either My certificate or SCM certificate
Certificate Name
- My certificate: Enter the certificate name containing up to 32 characters.
- SCM certificate: CDN automatically obtains SSL certificates that have been uploaded to the CCM console and are applicable to your domain name. You only need to select the desired one from the drop-down list.
Certificate Body
- My certificate: Use a local text editor to open the certificate and copy the content to the text box. For details about the certificate format, see HTTPS Certificate Requirements.
- SCM certificate: The certificate body is automatically filled in.
NOTE:- The certificate body cannot contain spaces or blank lines. Otherwise, a message is displayed indicating that certificate parameters are incorrect.
- The size of the certificate body cannot exceed 20 KB.
Private Key
- My certificate: Use a local text editor to open the private key and copy the content to the text box. For details about private key format requirements, see RSA Private Key.
- SCM certificate: The private key is automatically filled in.
- The size of the private key cannot exceed 20 KB.
Table 2 Parameters of a Chinese SM series cryptographic certificate Parameter
Description
Certificate Standard
Chinese (SM2)
Certificate Source
Either My certificate or SCM certificate
Certificate Name
- My certificate: Enter the certificate name containing 3 to 64 characters.
- SCM certificate: CDN automatically obtains SSL certificates that have been uploaded to the CCM console and are applicable to your domain name. You only need to select the desired one from the drop-down list.
Signature Certificate
Open the PEM file in the signature certificate to be uploaded as a text file and copy the certificate content in the file to this text box.
Note that you need to upload a combined certificate file that contains both the server certificate content and certificate chain content into this field. The content of the certificate chain should be pasted right below the content of the server certificate.
Signature Private Key
Open the KEY file in the signature certificate to be uploaded as a text file and copy the private key in the file to this text box.
Encryption Certificate
Open the PEM file in the encryption certificate to be uploaded as a text file and copy the certificate content in the file to this text box.
You do not need to upload the certificate chain here.
Encryption Private Key
Open the KEY file in the encryption certificate to be uploaded as a text file and copy the private key in the file to this text box.
- Click Next to associate the certificate with your domain names.

- Select domain names to be associated and click Next.
- If a selected domain name already uses a certificate, this operation will replace the existing certificate.
- You can search for domain names by HTTPS status.
- You can select up to 50 domain names.
- Click Finish to implement HTTPS secure acceleration for the associated domain names.
The status of delivering the domain certificate configuration is displayed. If the delivery fails, you can rectify the fault based on the cause and submit the certificate configuration task again.
Deleting a Managed Certificate
- Deleting a certificate will remove it from the server but will not delete any data associated with the certificate.
- Disable HTTPS before deleting a certificate associated with your domain name.
- To use the certificate again, re-push it from SCM to CDN.
Procedure
- Click Delete Huawei-managed Certificate.
- On the displayed drawer, select the certificates to be deleted and click OK.
To use the certificate again, re-push it from SCM to CDN.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





