Creating a Snapshot and Backup
CCE Autopilot clusters allow you to create snapshots for storage volumes of the EVS type. A snapshot is a complete copy or image of the disk data at a specific point in time, which can be used for data disaster recovery. If data is lost, you can roll back the disk data to the state when a snapshot was created.
- Creating a Snapshot: You can create a snapshot to save the disk data at a specific point in time and restore the data if needed.
- Using a Snapshot to Create a PVC: If the data in a PV is lost or damaged due to misoperations, system exceptions, or upgrade and migration, you can create a new PVC using an existing snapshot to quickly restore the PV to the state when the snapshot was created, ensuring service continuity.
Prerequisites
- You have created a cluster.
- If you want to create a cluster by running commands, kubectl has been used to connect to the cluster. For details, see Connecting to a Cluster Using kubectl.
Constraints
- EVS volumes are not supported in all regions. View the regions where EVS volumes are supported on the console.
- The cluster version must be v1.27.8-r0, v1.28.6-r0, or later. If the cluster version does not meet the requirements, you need to upgrade the cluster.
- The subtype (such as common I/O, high I/O, or ultra-high I/O), disk mode (SCSI or VBD), data encryption, sharing status, and capacity of an EVS disk created from a snapshot must be the same as those of the disk associated with the snapshot. These attributes cannot be modified after being checked or configured.
- Snapshots can be created only for EVS disks that are available or in use, and a maximum of seven snapshots can be created for a single EVS disk.
- The snapshots of encrypted disks are stored encrypted, and those of non-encrypted disks are stored non-encrypted.
Scenario
Snapshots can help meet your following needs:
- Routine data backup
You can create snapshots for EVS disks regularly and use snapshots to recover your data in case that data loss or data inconsistency occurred due to misoperations, viruses, or attacks.
- Rapid data restoration
You can create a snapshot or multiple snapshots before an OS change, application software upgrade, or a service data migration. If an exception occurs during the upgrade or migration, service data can be rapidly restored to the time point when the snapshot was created.
For example, a fault occurred on system disk A of ECS A, and therefore ECS A cannot be started. Because system disk A is already faulty, the data on system disk A cannot be restored by rolling back snapshots. In this case, you can use an existing snapshot of system disk A to create EVS disk B and attach it to ECS B that is running properly. Then, ECS B can read data from system disk A using EVS disk B.
The snapshots provided by CCE Autopilot are the same as the CSI snapshots provided by the Kubernetes community. They can only be used to create EVS disks, but cannot be used to roll back to source EVS disks.
- Rapid deployment of multiple services
You can use a snapshot to create multiple EVS disks containing the same initial data, and these disks can be used as data resources for various services, for example, data mining, report query, and development and testing. This method protects the initial data and creates disks rapidly, meeting the diversified service data requirements.
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the cluster name to go to the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Storage. Then click the Snapshots and Backups tab.
- In the upper right corner, click Create Snapshot. In the displayed dialog box, configure the parameters.
Figure 1 Creating a snapshot

Table 1 Parameters for creating a snapshot Parameter
Description
Snapshot Name
Enter the snapshot name, for example, disksnap-test1.
Storage
Select the PVC for which you want to create a snapshot. Only PVCs of the EVS type can be selected. In this example, select pvc.
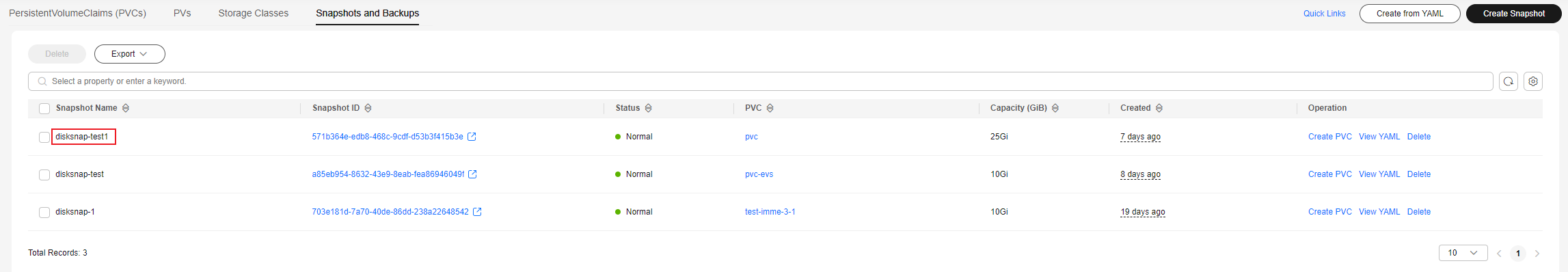
- Click Create. On the Snapshots and Backups tab, view details about the snapshot.
Figure 2 New snapshot
- Use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
- Create snapshot.yaml for a snapshot. You can use any file name.
vim snapshot.yamlExample file content:kind: VolumeSnapshot apiVersion: snapshot.storage.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: disksnap-test1 # Snapshot name namespace: default spec: source: persistentVolumeClaimName: pvc # PVC name. Only an PVC of the EVS type can be selected. volumeSnapshotClassName: csi-disk-snapclass
- Create the snapshot. Parameter -n indicates the namespace. You can replace default with the target namespace.
kubectl apply -f snapshot.yaml -n default
Information similar to the following is displayed:
volumesnapshot.snapshot.storage.k8s.io/disksnap-test1 created
- Check whether the snapshot has been created.
kubectl get volumesnapshot -n defaultIf the value of READYTOUSE is true, the snapshot has been created.
NAME READYTOUSE SOURCEPVC SOURCESNAPSHOTCONTENT RESTORESIZE SNAPSHOTCLASS ... disksnap-test1 true pvc-evs-test <none> 10Gi csi-disk-snapclass ...
Using a Snapshot to Create a PVC
If data in a PV is lost or damaged due to misoperations, system exceptions, or upgrade and migration, you can create a PVC using an existing snapshot to quickly restore the PV to the state when the snapshot was created, ensuring service continuity. The disk type, encryption setting, and disk mode of the created EVS PVC are consistent with those of the snapshot's source EVS disk. You can create a PVC through the console or using kubectl.
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the cluster name to go to the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Storage. Then click the Snapshots and Backups tab.
- Locate the snapshot that you want to use for creating a PVC, click Create PVC, and configure PVC parameters in the displayed dialog box.
Figure 3 Using a snapshot to create a PVC

Table 2 Parameters for creating a PVC using a snapshot Parameter
Description
PVC Name
Enter a PVC name, for example, pvc-disksnap.
(Optional) PV Name Prefix
This parameter specifies the name of the underlying storage that is automatically created. The actual underlying storage name is in the format of "PV name prefix + PVC UID". If this parameter is left blank, the default prefix pvc will be used.
For example, if the storage volume name prefix is set to test, the actual underlying storage name is test-{UID}.
Resource Tag
You can add resource tags to classify resources.
You can create predefined tags on the TMS console. The predefined tags are available to all resources that support tags. You can use predefined tags to improve the tag creation and resource migration efficiency. For details, see Creating Predefined Tags.
CCE automatically creates system tags CCE-Cluster-ID={Cluster ID}, CCE-Cluster-Name={Cluster name}, and CCE-Namespace={Namespace name}. These tags cannot be modified.
- Click Create. Click the PVCs tab to view the created PVC.
- Use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
- Create pvc-test.yaml and use a snapshot to create a PVC. You can use any file name.
vim pvc-test.yamlBelow is the file content. For details about PVCs, see Using kubectl.apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: pvc-disksnap # PVC name namespace: default annotations: everest.io/disk-volume-type: SSD # EVS disk type, which must be the same as that of the snapshot's source EVS disk. everest.io/disk-iops: '3000' # (Optional) IOPS of only a GPSSD2 EVS disk everest.io/disk-throughput: '125' # (Optional) Throughput of only a GPSSD2 EVS disk labels: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/region: <your_region> # Replace the region with the one where the cluster is located. failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone: <your_zone> # Replace the AZ with the one where the EVS disk is located. spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 10Gi storageClassName: csi-disk dataSource: name: disksnap-test1 # Snapshot name kind: VolumeSnapshot apiGroup: snapshot.storage.k8s.io
- Run the following command to create a PVC: Parameter -n indicates the namespace. You can replace default with the target namespace.
kubectl apply -f pvc-test.yaml -n default
Information similar to the following is displayed:
persistentvolumeclaim/pvc-disksnap created
- Check whether the PVC has been created.
kubectl get pvc pvc-disksnap
If STATUS is Bound, the PVC has been created.
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE pvc-disksnap Bound pvc-7b9f4c8d-1a2b-3c4d-5e6f-7g8h9i0jkl 10Gi RWO csi-disk 1m
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





