Configuring the Container Lifecycle
Container lifecycle hooks are core mechanisms provided by Kubernetes that enable you to insert custom logic at key phases throughout the container lifecycle. These hooks provide refined process controls over containerized applications, enabling applications to better adapt to the dynamic characteristics of the cloud native environment. CCE Autopilot provides the following container lifecycle hooks (for more information, see Container Lifecycle Hooks):
- Startup Command: the command executed when a container starts. It is used to define the main process of a container. The main process is the default entry after the container starts, and its status determines the container lifecycle. This kind of hook is suitable for initialization scenarios where the application entry, environment variables, mount points, or port mapping needs to be specified.
- PostStart Hook: used to execute initialization tasks, such as service registration and dynamic configuration generation, immediately after the main process of a container starts. Such a hook is asynchronously triggered by kubelet and runs in parallel with the main process, preventing the container startup process from being blocked and accelerating the container readiness. This kind of hook is suitable for the scenario where the environment needs to be configured or the initialization logic needs to be executed immediately after the application process starts.
- PreStop Hook: used to execute predefined cleanup logic before a container is terminated. When a pod is deleted or updated, kubelet triggers this hook to perform operations (such as deregistering services and refreshing status), and then sends the SIGTERM signal to the main process of a container for the application to shut down gracefully. This kind of hook is suitable for the scenario where safe shutdown is required to avoid data loss or there are service exceptions.
Startup Command
A startup command is executed when a container starts. It is used to define the main process of a container. The main process status determines the container lifecycle. If the command fails to be executed and no restart policy is configured, the container will be terminated.
By default, the default command is executed during image start. To run a specific command or rewrite the default image setting, you must perform specific operations. By default, the container executes the startup command preset in the image. Docker images contain a set of metadata fields for defining the startup behavior, including ENTRYPOINT and CMD. If the commands and arguments (specified by Command and Args) are not configured in the container specifications, the default values during image build are used.
If the commands and arguments used to run a container are set during workload creation, the default commands ENTRYPOINT and CMD are overwritten during image build.
|
Image ENTRYPOINT |
Image CMD |
Command to Run a Container |
Arguments to Run a Container |
Command Executed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
[touch] |
[/root/test] |
Not set |
Not set |
[touch /root/test] |
|
[touch] |
[/root/test] |
[mkdir] |
Not set |
[mkdir] |
|
[touch] |
[/root/test] |
Not set |
[/opt/test] |
[touch /opt/test] |
|
[touch] |
[/root/test] |
[mkdir] |
[/opt/test] |
[mkdir /opt/test] |
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the cluster name to go to the cluster console, choose Workloads in the navigation pane, and click Create Workload in the upper right corner.
- In Container Settings, choose Container Information > Lifecycle > Startup Command and enter the command and arguments.
Figure 1 Configuring a startup command
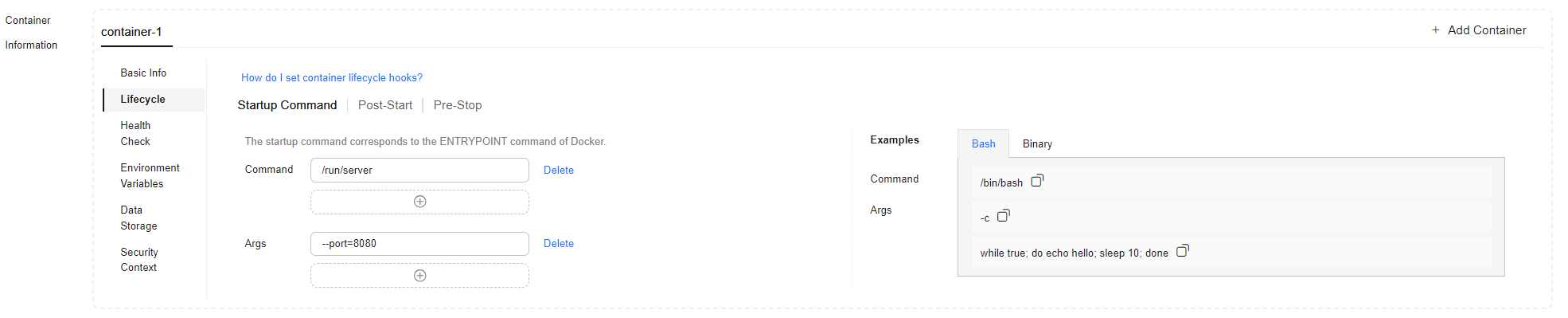
Table 2 Container startup command Parameter
Example Value
Description
Example YAML
Command
/run/server
Enter one or more executable commands. If you need multiple commands, separate them on different lines.
NOTE:In the case of multiple commands, you are advised to run /bin/sh or other shell commands. Other commands are used as parameters.
... spec: containers: - image: nginx:latest command: - /run/server args: - '--port=8080' ...Args
--port=8080
Enter one or more arguments. If you need multiple arguments, separate them on different lines.
- Configure other parameters and click Create Workload in the lower right corner. If the workload is in the Running state, the startup command is successfully executed.
PostStart Hook
A PostStart hook, a container lifecycle hook provided by Kubernetes, is used to execute initialization tasks, such as service registration and dynamic configuration generation, immediately after the main process of a container starts. This hook is asynchronously triggered by kubelet and runs in parallel with the main process. Although the PostStart hook is executed asynchronously with the main process of the container, if the PostStart hook takes too long or is suspended, the container may not change to the Running state. If the PostStart hook fails to be executed, the container may fail to start and be terminated.
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the cluster name to go to the cluster console, choose Workloads in the navigation pane, and click Create Workload in the upper right corner.
- In Container Settings, choose Container Information > Lifecycle > Post-Start and configure the parameters based on service requirements.
- If initialization logic (such as running scripts and configuring the environment) needs to be executed in the container, select CLI.
- If external systems or services needs to be notified (for example, when service registration is needed and a configuration center API is called), select HTTP request.
Figure 2 CLI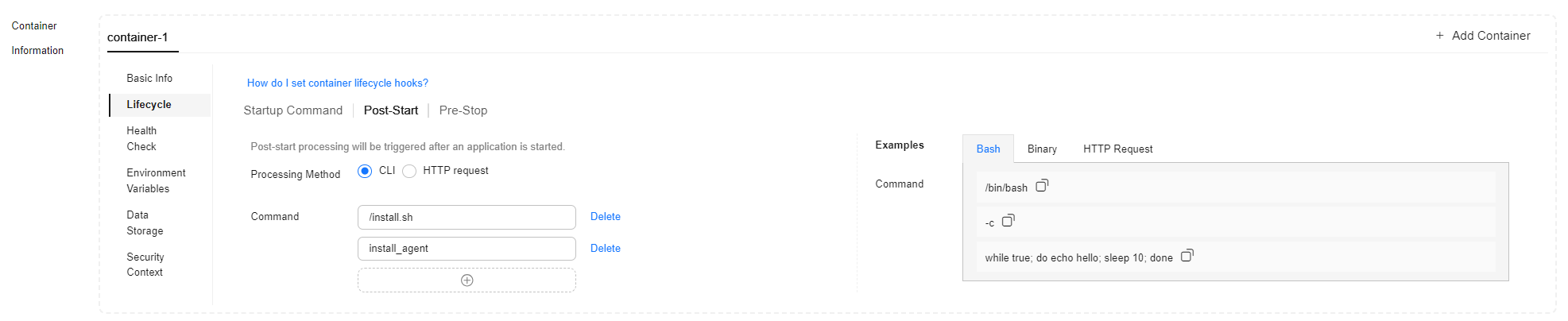
Table 3 Post-start processing Processing Method
Example Value
Description
Example YAML
CLI
/install.sh
install_agent
Used for running the commands in the container. You need to configure Command.
The command format is Command Arg[1] Arg[2]..., where Command indicates a system command or a user-defined executable program. If no path is specified, the system searches for the command in the default path. If multiple commands needed to be executed, write them into a script in the container image in advance and invoke the script using this command. The executable command must be executed synchronously or in the frontend. If it is executed asynchronously or in the backend, the lifecycle hook may fail to be executed.
... lifecycle: postStart: exec: command: - /install.sh - install_agent ...HTTP request
Path: /nginx
Port: 80
Host: 127.0.0.1
Used for initiating an HTTP request. The related parameters are described as follows:
- Path: (optional) request URL.
- Port: (mandatory) requested port.
- Host: (optional) requested host IP address. The default value is the IP address of the pod.
lifecycle: postStart: httpGet: path: /nginx port: 80 host: 127.0.0.1 scheme: HTTP ... - Configure other parameters and click Create Workload in the lower right corner. If the workload is in the Running state, the startup command is successfully executed.
PreStop Hook
If a container crashes or exits abnormally, the PreStop hook will not be triggered. The pod's termination grace period starts to count down before the PreStop hook is executed. Regardless of the outcome of the hook handler, the container will be terminated within the pod's termination grace period unless the finalizer delays the termination process. Other management operations on the container are blocked until the PreStop hook is complete or the termination grace period is reached.
- Log in to the CCE console.
- Click the cluster name to go to the cluster console, choose Workloads in the navigation pane, and click Create Workload in the upper right corner.
- In Container Settings, choose Container Information > Lifecycle > Pre-Stop and configure the parameters based on service requirements.
Figure 3 PreStop
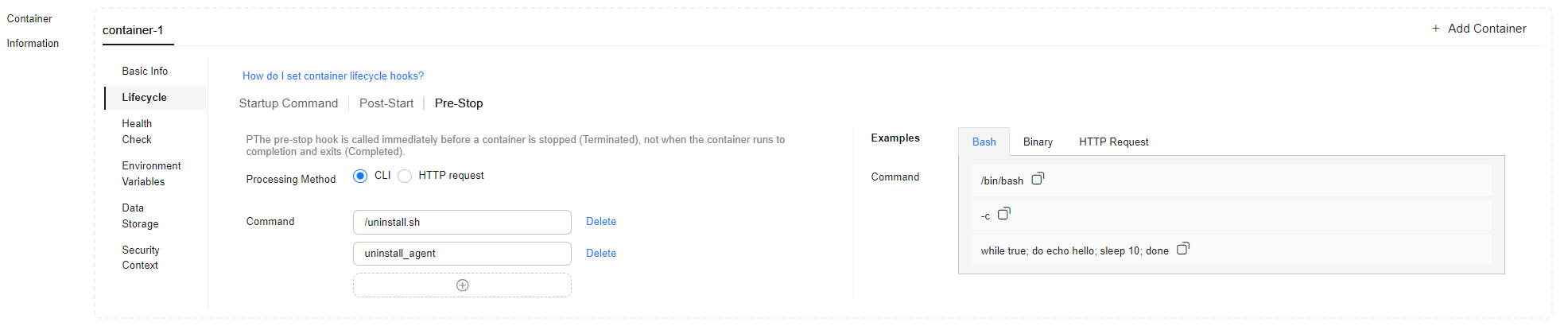
Table 4 Pre-stop processing parameters Parameter
Example Value
Description
Example YAML
CLI
/uninstall.sh
uninstall_agent
Used for running the commands in the container. You need to configure Command.
The command format is Command Arg[1] Arg[2]..., where Command indicates a system command or a user-defined executable program. If no path is specified, the system searches for the command in the default path. If multiple commands needed to be executed, write them into a script in the container image in advance and invoke the script using this command.
... lifecycle: preStop: exec: command: - /uninstall.sh - uninstall_agent ...HTTP request
Path: /nginx
Port: 80
Host: 127.0.0.1
Used for initiating an HTTP request. The related parameters are described as follows:
- Path: (optional) request URL.
- Port: (mandatory) requested port.
- Host: (optional) requested host IP address. The default value is the IP address of the pod.
lifecycle: preStop: httpGet: path: /nginx port: 80 host: 127.0.0.1 scheme: HTTP ... - Configure other parameters and click Create Workload in the lower right corner. If the workload is in the Running state, the startup command is successfully executed.
YAML Example
Nginx is used as an example to describe how to set the container lifecycle.
In the following configuration file, there is a PostStart command (install.sh) in the /bin/bash directory and a PreStop command (uninstall.sh).
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
command:
- sleep 3600 #Startup command
imagePullPolicy: Always
lifecycle:
postStart:
exec:
command:
- /bin/bash
- install.sh #Post-Start command
preStop:
exec:
command:
- /bin/bash
- uninstall.sh #Pre-Stop command
name: nginx
imagePullSecrets:
- name: default-secret
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





