How Do I Fix "nf_conntrack:table full, dropping packet"?
Symptom
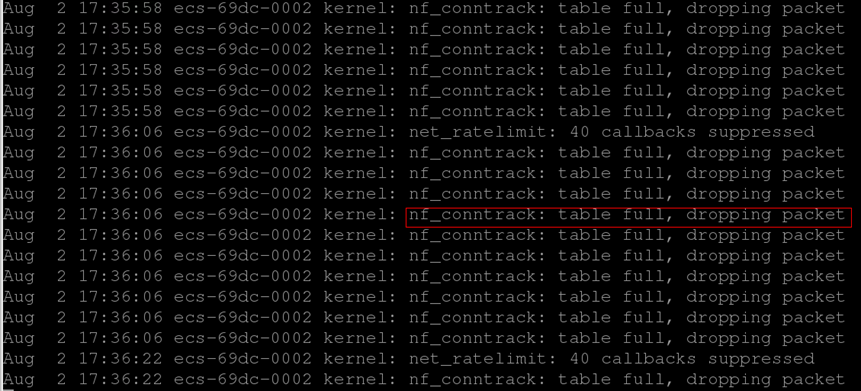
Packet loss occasionally occurs when you connect to applications in an ECS. The kernel: nf_conntrack:table full, dropping packet is printed in /var/log/messages system logs.
Constraints
Operations in this section involve modifying kernel parameters at runtime, which may cause kernel instability. Evaluate risks before modification and restart the system at a proper time after modification.
Possible Causes
The connection-tracking module of iptables uses some system memory to track connections in the table. The message "table full, dropping packet" indicates that the connection tracking table is full and no new entry can be created for new connections. As a result, the "dropping packet" problem occurs.
To resolve the problem, increase the number of connection tracking entries or filter out connections that do not need to be tracked.
Solutions
Solution 1: Adjust parameter values in the nf_conntrack module.
- Increase the value of net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max, which indicates the maximum number of connections supported by the nf_conntrack module.
For example:
If the memory is 64 GB and you want to change the net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max value to 2097152, run the following command to apply the setting immediately:sysctl -w net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=2097152
Run the following command to ensure that the setting is still valid after the ECS is restarted:echo "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 2097152" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
- A larger net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max value is not necessarily better. Set net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max based on the memory size.
- Calculate an appropriate value for nf_conntrack_max using the following formula (64-bit):
CONNTRACK_MAX = RAMSIZE (inbytes)/16384/2
For example, if your ECS is running a 64-bit OS with 64 GB of memory, calculate an appropriate nf_conntrack_max value as follows:
CONNTRACK_MAX = 64 × 1024 × 1024 × 1024/16384/2 = 2097152
- Adjust the value of nf_conntrack_buckets, which indicates the size of the hash table in the nf_conntrack module.
If the number of entries in the conntrack table increases significantly (for example, by 4-fold), you should increase the size of the hash table for storing conntrack entries.
For CentOS 6 and later versions, calculate a new hash value using formula hashsize = nf_conntrack_max/4.
Run the following command to set a new hash value:
sysctl -w net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_buckets=524288
Run the following command to ensure that the setting is still valid after the ECS is restarted:
echo "net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_buckets=524288" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
In earlier versions, you may not be able to adjust the nf_conntrack_buckets value. In this case, you can adjust the hashsize value.
Method:
In /etc/modprobe.d/nf_conntrack.conf, run the following command:
echo "options nf_conntrack hashsize=524288" >> /etc/modprobe.d/nf_conntrack.conf
Restart the ECS to apply the setting.
Solution 2: Use iptables to filter out connections that do not need to be tracked.
You can add the -j NOTRACK parameter to the iptables rule to filter out connections that do not need to be tracked. This method removes the records of the connections that do not need to be tracked from the hash table and prevents excessive connections from causing "nf_conntrack:table full, dropping packet" errors.
iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p udp -j NOTRACK iptables -t raw -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 22 -j NOTRACK
The commands indicate that the UDP connections and TCP connections over port 22 are not tracked. They are provided for reference only.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





