Overview
Scenario
VPN can be used to enable communication between an on-premises data center and ECSs in a VPC.
Networking
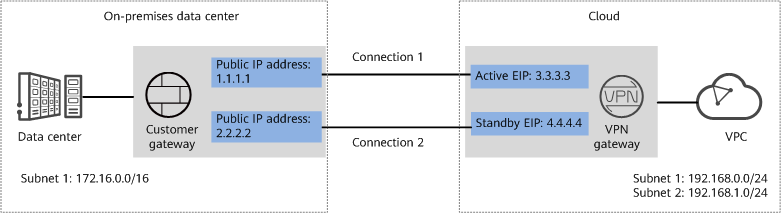
In this example, two VPN connections working in active/standby mode are set up between an on-premises data center and a VPC to ensure network reliability. If one VPN connection fails, traffic is automatically switched to the other VPN connection, ensuring service continuity.
Solution Advantages
- A VPN gateway provides two IP addresses to establish dual independent VPN connections with a customer gateway. If one VPN connection fails, traffic can be quickly switched to the other VPN connection.
- Active/Standby mode: A VPN gateway communicates with a customer gateway through the active connection. If the active connection fails, traffic is automatically switched to the standby VPN connection. After the fault is rectified, traffic is switched back to the original active VPN connection. Traffic leaving the cloud is preferentially transmitted through the active EIP, allowing you to determine the VPN connection through which traffic is transmitted.
Limitations and Constraints
- The local and customer subnets of the VPN gateway cannot be the same. That is, the VPC subnet and the data center subnet to be interconnected cannot be the same.
- The IKE policy, IPsec policy, and PSK of the VPN gateway must be the same as those of the customer gateway.
- The local and remote interface address configurations on the VPN gateway and customer gateway are reversed.
- The security groups associated with ECSs in the VPC permit access from and to the on-premises data center.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





