What Are the Differences Between IAM and Enterprise Management?
Enterprise Management allows you to hierarchically manage resources with enterprise projects to align with your organizational structure. It includes enterprise project, personnel, accounting, and application management.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is an identity management service that provides identity authentication, permissions management, and access control.
You can use both IAM and Enterprise Management to manage personnel and permissions. Enterprise Management also provides accounting and application management, and supports more fine-grained access control. For medium- and large-sized enterprises, Enterprise Management is a better choice.
For more information about IAM functions, see the Identity and Access Management User Guide.
Differences Between IAM and Enterprise Management
- Enabling method
- IAM is an identity management service. It is free of charge, and you can use it immediately after signing up for Huawei Cloud.
- Enterprise Management is a resource management service. It is free of charge, and you can use it after signing up for Huawei Cloud.
- Resource isolation
- IAM allows you to create multiple projects in a region for resource isolation. An IAM project can contain resources of only one region. If you assign permissions based on IAM projects, users with related permissions can access all resources in a specific project.
- Enterprise Management allows you to create multiple enterprise projects in a region for resource isolation. An enterprise project can contain resources of multiple regions. You can control access to a specific resource. For example, you can add an Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) to an enterprise project, and assign permissions to a user for managing the ECS in the project instead of other ECSs.
Relationship Between Enterprise Management and IAM
- The functions of creating users and user groups are the same for IAM and Enterprise Management.
- If you have enabled Enterprise Management, you need to use the policies managed in IAM to assign permissions to user groups created in Enterprise Management. If the system-defined policies cannot meet your requirements, you can create custom policies in IAM. The custom policies will be synchronized to Enterprise Management and can be associated with user groups in both IAM and Enterprise Management.
- If you grant a user group with permissions in both IAM and Enterprise Management, users in the group will have permissions from the policies attached to the group in both IAM and Enterprise Management. Requests of these users will then be authenticated based on the actions in the attached policies.
- If the attached policies contain the same action, the effect of the action in IAM takes priority. For example, when a user requests for creating a cloud server, the Deny effect defined in IAM is applied. Therefore, the user cannot create cloud servers.
A policy attached in an IAM project contains the following action: { "Action": [ "ecs:cloudServers:create" ], "Effect": "Deny" } A policy attached in an enterprise project contains the following action: { "Action": [ "ecs:cloudServers:create" ], "Effect": "Allow" } - All different actions in the policies attached in IAM and Enterprise Management will take effect. The following are two actions that allow users to create and delete cloud servers.
A policy attached in an IAM project contains the following action: { "Action": [ "ecs:cloudServers:create" ], "Effect": "Allow" } A policy attached in an enterprise project contains the following action: { "Action": [ "ecs:cloudServers:delete" ], "Effect": "Allow" }
- If the attached policies contain the same action, the effect of the action in IAM takes priority. For example, when a user requests for creating a cloud server, the Deny effect defined in IAM is applied. Therefore, the user cannot create cloud servers.
Authentication Process
When a user initiates an access request, the system authenticates the request based on the actions in the policies that have been attached to the group to which the user belongs. The following figure shows the authentication process.
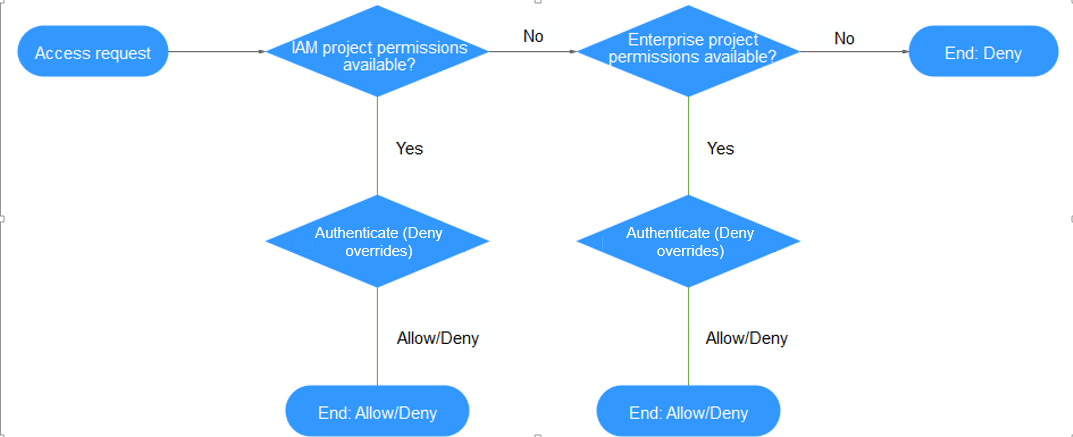
- A user initiates an access request.
- The system checks actions in IAM-project-based policies.
- If a matched Allow or Deny action is found, the system returns an authentication result (Allow or Deny), and the authentication finishes.
- If no matched actions are found in IAM project policies, the system continues to check actions in enterprise-project-based policies.
- If a matched Allow or Deny action is found, the system returns an authentication result (Allow or Deny), and the authentication finishes.
- If no matched actions are found, the system returns a Deny, and the authentication finishes.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





