Instructions for Using CDL
CDL is a simple and efficient real-time data integration service. It captures data change events from various OLTP databases and pushes them to Kafka. The Sink Connector consumes data in topics and imports the data to the software applications of big data ecosystems. In this way, data is imported to the data lake in real time.
The CDL service contains two roles: CDLConnector and CDLService. CDLConnector is the instance for executing a data capture job, and CDLService is the instance for managing and creating a job.
CDL allows you to create data synchronization tasks and data comparison tasks on the CDLService web UI.
Data Synchronization Tasks
- CDL supports the following types of data synchronization tasks:
Table 1 Types of data synchronization tasks supported by CDL Data Source
Destination
Description
MySQL
Hudi
Synchronizes data from MySQL to Hudi.
Kafka
Synchronizes data from MySQL to Kafka.
PostgreSQL
Hudi
Synchronizes data from PostgreSQL to Hudi.
Kafka
Synchronizes data from PostgreSQL to Kafka.
Hudi
GaussDB(DWS)
Synchronizes data from Hudi to GaussDB(DWS).
ClickHouse
Synchronizes data from Hudi to ClickHouse.
ThirdKafka
Hudi
Synchronizes data from ThirdKafka to Hudi.
Kafka
Synchronizes data from ThirdKafka to Kafka.
Opengauss
ThirdKafka (DMS/DRS) -> Hudi
Synchronizes data from openGauss to Hudi through ThirdKafka (DMS/DRS).
Hudi
Synchronizes data from openGauss to Hudi.
Kafka
Synchronizes data from openGauss to Kafka.

ThirdKafka supports only drs-opengauss-json, drs-oracle-json, drs-oracle-avro, ogg-oracle-avro and debezium-json data sources.
- Database versions supported by CDL in a data synchronization task:
Kafka (including ThirdKafka that uses MRS Kafka as the source), Hudi, and ClickHouse use related components in the MRS cluster as data sources. Table 2 lists the database versions.
Table 2 Supported database types and versions Database
Data Source
Destination
Version
MySQL
Supported
Not supported
5.7.x, 8.0.x
PgSQL
Supported
Not supported
9.6, 10, 11, 12, and 13
openGauss (open source version)
Supported
Not supported
2.1.0 and later
GaussDB(DWS)
Not supported
Supported
8.1.1 and later
- Restrictions:
- If CDL is required, the value of log.cleanup.policy of Kafka must be delete.
- The CDL service has been installed in the MRS cluster.
- CDL can capture incremental data only from non-system tables, but not from built-in databases of databases such as MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and openGauss.
- When data is synchronized from Hudi to GaussDB(DWS) or ClickHouse, the data that is deleted from Hudi will not be deleted from the destination. For example, if you run the delete from tableName command in Hudi to physically delete table data, the table data still exists on the destination GaussDB(DWS) or ClickHouse.
- Binary logging (enabled by default) and GTID have been enabled for the MySQL database. CDL cannot fetch tables whose names contain special characters such as the dollar sign ($) characters.
To check whether binary logging is enabled for the MySQL database:
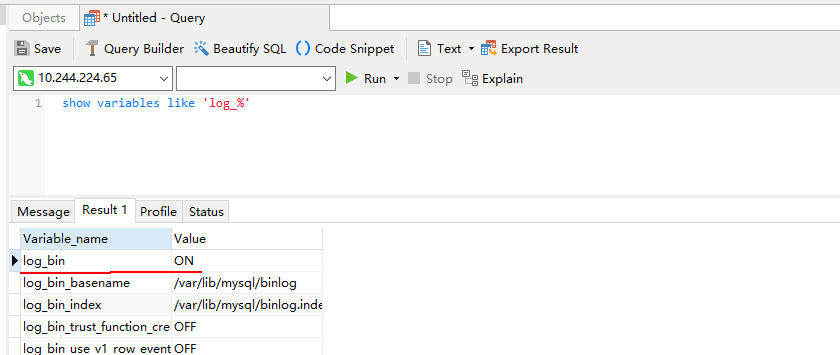
Use a tool (Navicat is used in this example) or CLI to connect to the MySQL database and run the show variables like 'log_%' command to view the configuration.
For example, in Navicat, choose File > New Query to create a query, enter the following SQL statement, and click Run. If log_bin is displayed as ON in the result, the function is enabled successfully.
show variables like 'log_%'
If the bin log function of the MySQL database is not enabled, perform the following operations:
Modify the MySQL configuration file my.cnf (my.ini for Windows) as follows:
server-id = 223344 log_bin = mysql-bin binlog_format = ROW binlog_row_image = FULL expire_logs_days = 10
After the modification, restart MySQL for the configurations to take effect.
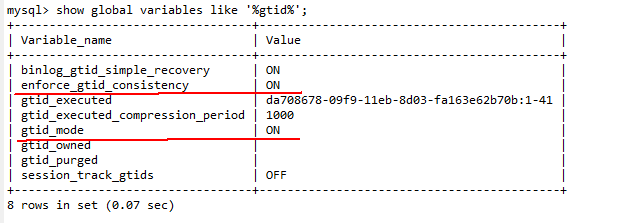
To check whether GTID is enabled for the MySQL database:
Run the show global variables like '%gtid%' command to check whether GTID is enabled. For details, see the official documentation of the corresponding MySQL version. (For details about how to enable the function in MySQL 8.x, see https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/replication-mode-change-online-enable-gtids.html.)
Set user permissions:
To execute MySQL tasks, users must have the SELECT, RELOAD, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE and REPLICATION CLIENT permissions.
Run the following command to grant the permissions:
GRANT SELECT, RELOAD, SHOW DATABASES, REPLICATION SLAVE, REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'Username' IDENTIFIED BY 'Password';
Commands carrying authentication passwords pose security risks. Disable historical command recording before running such commands to prevent information leakage.
Run the following command to update the permissions:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- The write-ahead log policy is modified for the PostgreSQL database.

- The user for connecting to the PostgreSQL database must have the replication permission, the CREATE permission on the database, and is the owner of heartbeat tables.
- CDL cannot fetch tables whose names contain special characters such as the dollar sign ($) characters.
- For PostgreSQL databases, you must have the permission to set the statement_timeout and lock_timeout parameters and the permission to query and delete slots and publications.
- You are advised to set max_wal_senders to 1.5 or 2 times the value of Slot.
- If the replication identifier of a PostgreSQL table is default, enable the full field completion function in the following scenarios:
- Scenario 1:
When the delete operation is performed on the source database, a delete event contains only the primary key information. In this case, for the delete data written to Hudi, only the primary key has values, and the values of other service fields are null.
- Scenario 2:
When the size of a single piece of data in the database exceeds 8 KB (including 8 KB), an update event contains only changed fields. In this case, the values of some fields in the Hudi data are __debezium_unavailable_value.
The related commands are as follows:
- Command for querying the replication identifier of a PostgreSQL table:
SELECT CASE relreplident WHEN 'd' THEN 'default' WHEN 'n' THEN 'nothing' WHEN 'f' THEN 'full' WHEN 'i' THEN 'index' END AS replica_identity FROM pg_class WHERE oid = 'tablename'::regclass;
- Command for enabling the full field completion function for a table:
- Scenario 1:
- Modify wal_level = logical in the database configuration file postgresql.conf (which is stored in the data folder in the PostgreSQL installation directory by default).
#------------------------------------------------ #WRITE-AHEAD LOG #------------------------------------------------ # - Settings - wal_level = logical # minimal, replica, or logical # (change requires restart) #fsync = on #flush data to disk for crash safety ... - Restart the database service.
# Stop pg_ctl stop # Start pg_ctl start
- Write-ahead logging is enabled for the Oracle database.

- The database user configured in the task must have the LogMiner permission on the Oracle database. Use the following command to grant the permission:
GRANT create session, alter session, select any dictionary, select any transaction, select any table, logmining, execute_catalog_role TO <username>;
- CDL cannot fetch tables whose names contain special characters such as the dollar sign ($) characters.
- The CDL does not support names of Oracle database schemas containing the number sign (#).
- Currently, Oracle tasks do not support the PDB mode.
- To synchronize update data to Oracle tasks, run the following command to enable the full field completion function:
ALTER TABLE schema.table_name ADD SUPPLEMENTAL LOG DATA (ALL) COLUMNS;
- Use a tool or CLI to connect to the Oracle database and run the following commands:
SQL> select log_mode from v$database; LOG_MODE ------------ NOARCHIVELOG SQL> shutdown immediate Database closed. Database dismounted. ORACLE instance shut down. SQL> startup mount ORACLE instance started. Total System Global Area 1653518336 bytes Fixed Size 2228904 bytes Variable Size 1291849048 bytes Database Buffers 352321536 bytes Redo Buffers 7118848 bytes Database mounted. SQL> alter database archivelog; Database altered. SQL> alter database open; Database altered. SQL> select log_mode from v$database; LOG_MODE ------------ ARCHIVELOG
- Enable supplemental logging.
SQL> alter database add supplemental log data; Database altered. SQL> alter database add supplemental log data (primary key) columns; Database altered. SQL> select supplemental_log_data_min from v$database; SUPPLEMENTAL_LOG_DATA_MIN -------------------------- YES SQL> alter system switch logfile; System altered.
- The database user configured in the task must have the LogMiner permission on the Oracle database. Use the following command to grant the permission:
- Prerequisites for the GaussDB(DWS) database
Before a synchronization task is started, both the source and target tables exist and have the same table structure. The value of ads_last_update_date in the GaussDB(DWS) table is the current system time.
- Prerequisites for ThirdKafka
The upper-layer source supports openGauss and OGG. Kafka topics at the source end can be consumed by Kafka in the MRS cluster.

ThirdKafka does not support data synchronization from the distributed openGauss database to CDL.
- Prerequisites for ClickHouse
You have the permissions to operate ClickHouse. For details, see ClickHouse User and Permission Management.
- Write-ahead logging required for the openGauss database

- The user connecting to openGauss databases must have logical replication permission.
- openGauss interval partitioned tables cannot be synchronized.
- If a table in the source openGauss database does not have a primary key, data in the table cannot be deleted.
- If the data in the source openGauss database needs to be deleted, enable the field completion function.
- Command for querying the replication identifier of a openGauss table:
SELECT CASE relreplident WHEN 'd' THEN 'default' WHEN 'n' THEN 'nothing' WHEN 'f' THEN 'full' WHEN 'i' THEN 'index' END AS replica_identity FROM pg_class WHERE oid = 'tablename'::regclass;
- Command for enabling the full field completion function for a table:
- Command for querying the replication identifier of a openGauss table:
- Modify wal_level = logical in the database configuration file postgresql.conf (which is stored in the data folder under the openGauss installation directory by default).
- Restart the openGauss database service.
Data Types and Mapping Supported by CDL Synchronization Tasks
This part describes the data types supported by CDL synchronization tasks and the mapping between data types of the source database and Spark data types.
|
PostgreSQL Data Type |
Spark (Hudi) Data Type |
|---|---|
|
int2 |
int |
|
int4 |
int |
|
int8 |
bigint |
|
numeric(p, s) |
decimal[p,s] |
|
bool |
boolean |
|
char |
string |
|
varchar |
string |
|
text |
string |
|
timestamptz |
timestamp |
|
timestamp |
timestamp |
|
date |
date |
|
json, jsonb |
string |
|
float4 |
float |
|
float8 |
double |
|
MySQL Data Type |
Spark (Hudi) Data Type |
|---|---|
|
int |
int |
|
integer |
int |
|
bigint |
bigint |
|
double |
double |
|
decimal[p,s] |
decimal[p,s] |
|
varchar |
string |
|
char |
string |
|
text |
string |
|
timestamp |
timestamp |
|
datetime |
timestamp |
|
date |
date |
|
json |
string |
|
float |
double |
|
Oracle Data Type |
Spark (Hudi) Data Type |
|---|---|
|
NUMBER[P,S] |
Decimal[P,S] |
|
NUMBER[P, 0] P->[1, 9] |
int |
|
NUMBER[P, 0] P->[10, 19] |
long |
|
FLOAT |
double |
|
BINARY DOUBLE |
double |
|
CHAR |
string |
|
VARCHAR |
string |
|
TIMESTAMP |
timestamp |
|
timestamp with time zone |
timestamp |
|
DATE |
timestamp |
|
Oracle Data Type |
Spark (Hudi) Data Type |
|---|---|
|
NUMBER(3), NUMBER(5) |
bigint |
|
INTEGER |
decimal |
|
NUMBER(20) |
decimal |
|
NUMBER |
decimal |
|
BINARY_DOUBLE |
double |
|
CHAR |
string |
|
VARCHAR |
string |
|
TIMESTAMP, DATETIME |
timestamp |
|
timestamp with time zone |
timestamp |
|
DATE |
timestamp |
|
openGauss JSON |
Spark (Hudi) |
|---|---|
|
int2 |
int |
|
int4 |
int |
|
int8 |
bigint |
|
numeric(p,s) |
decimal[p,s] |
|
bool |
boolean |
|
varchar |
string |
|
timestamp |
timestamp |
|
timestampz |
timestamp |
|
date |
date |
|
jsonb |
string |
|
json |
string |
|
float4 |
float |
|
float8 |
double |
|
text |
string |
|
Oracle JSON |
Spark (Hudi) |
|---|---|
|
number(p,s) |
decimal[p,s] |
|
binary double |
double |
|
char |
string |
|
varchar2 |
string |
|
nvarchar2 |
string |
|
timestamp |
timestamp |
|
timestamp with time zone |
timestamp |
|
date |
timestamp |
|
Oracle Avro |
Spark (Hudi) |
|---|---|
|
nuber[p,s] |
decimal[p,s] |
|
float(p) |
float |
|
binary_double |
double |
|
char(p) |
string |
|
varchar2(p) |
string |
|
timestamp(p) |
timestamp |
|
date |
timestamp |
|
openGauss |
Spark (Hudi) |
|---|---|
|
int1 |
int |
|
int2 |
int |
|
int4 |
int |
|
int8 |
bigint |
|
numeric(p,s) |
decimal[p,s] |
|
bool |
boolean |
|
char |
string |
|
bpchar |
string |
|
nvarchar2 |
string |
|
text |
string |
|
date |
date |
|
timestamp |
timestamp |
|
timestampz |
timestamp |
|
json |
string |
|
jsonb |
string |
|
float4 |
float |
|
float8 |
double |
|
real |
float |
|
Spark (Hudi) Data Type |
GaussDB(DWS) Data Type |
|---|---|
|
int |
int |
|
long |
bigint |
|
float |
double |
|
double |
double |
|
decimal[p,s] |
decimal[p,s] |
|
boolean |
boolean |
|
string |
varchar |
|
date |
date |
|
timestamp |
timestamp |
|
Spark (Hudi) Data Type |
ClickHouse Data Type |
|---|---|
|
int |
Int32 |
|
long |
Int64 (bigint) |
|
float |
Float32 (float) |
|
double |
Float64 (double) |
|
decimal[p,s] |
Decimal(P,S) |
|
boolean |
bool |
|
string |
String (LONGTEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, TINYTEXT, TEXT, LONGBLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, TINYBLOB, BLOB, VARCHAR, CHAR) |
|
date |
Date |
|
timestamp |
DateTime |
Data Comparison Tasks
Data comparison checks the consistency between data in the source database and that in the target Hive. If the data is inconsistent, CDL can attempt to repair the inconsistent data. For details, see Creating a CDL Data Comparison Job.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





