Using Global Accelerator to Accelerate Access to an Application
Suppose a multinational enterprise has branches worldwide, with the Singapore branch deploying an application on two servers in the CN South-Guangzhou region and the Hong Kong branch deploying an application on two servers in the CN-Hong Kong region. Each branch's two servers handle traffic.
With Global Accelerator, each branch can access their applications faster from the nearest access point.
You can use Global Accelerator to enable your global users to access your applications faster.

When users in the Singapore branch access the application in the CN South-Guangzhou region, requests are sent to the anycast IP address in Singapore. The listener then distributes the requests evenly between endpoint 1 and endpoint 2.
When users in the Hong Kong branch access the application in the CN-Hong Kong region, requests are sent to the anycast IP address in Hong Kong. The listener then distributes 20% of the requests to endpoint 3 and 80% of the requests to endpoint 4.
Operation Process
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Step 1: Apply for a Cross-Border Permit (Mandatory for Cross-Border Communications) |
In accordance with the laws and administrative regulations of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of the People's Republic of China, only China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom are allowed for cross-border network communications, and a cross-border permit is required if you carry out business activities outside the Chinese mainland. If the acceleration area is inside the Chinese mainland but the endpoint group is outside the Chinese mainland, or if the endpoint group is inside the Chinese mainland but the acceleration area is outside the Chinese mainland, you need to apply for a cross-border permit. |
|
To use Global Accelerator for faster access, you first need to create a global accelerator. |
|
|
Each global accelerator must have at least one listener to receive and distribute requests to endpoints based on client affinity and weights you set. |
|
|
An endpoint group includes one or more endpoints in a given region. You can set a weight for each endpoint group, and Global Accelerator will route requests based on the weight you specified. |
|
|
The listener uses TCP to receive requests from clients, so you can run the curl command to verify whether the access is accelerated. |
Step 1: Apply for a Cross-Border Permit (Mandatory for Cross-Border Communications)
In accordance with the laws and administrative regulations of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) of the People's Republic of China, only China Mobile, China Telecom, and China Unicom are allowed for cross-border network communications, and a cross-border permit is required if you carry out business activities outside the Chinese mainland.
If the acceleration area is inside the Chinese mainland but the endpoint group is outside the Chinese mainland, or if the endpoint group is inside the Chinese mainland but the acceleration area is outside the Chinese mainland, you need to apply for a cross-border permit.
- Log in to the Cross-border Permits page.
- Click Request a Cross-border Permit.
The Cross-Border Service Application System page is displayed.
- On the application page, set related parameters and upload related materials.
Table 1 Online cross-border permit application Parameter
Description
Applicant Name
The applicant name, which must be the same as the company name in the Letter of Commitment to Information Security.
Huawei Cloud UID
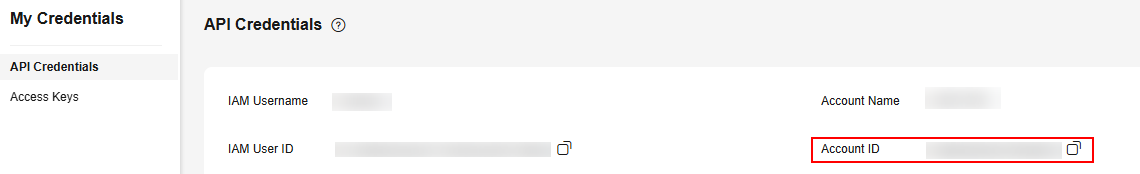
The account ID, rather than the user ID or project ID, used to log in to the management console.
You can perform the following operations to obtain your account ID.- Log in to the management console.
- Move your cursor over the username in the upper right corner and select My Credentials from the drop-down list.
Figure 2 My credentials
- On the displayed API Credentials page, view Account ID and obtain the ID.
Figure 3 Obtaining the account ID
Bandwidth(M)
The bandwidth size, which must be the same as the bandwidth in the Letter of Commitment to Information Security.
The information is for reference only and does not affect the actual service bandwidth.
Start Date
For reference only.
Termination Date
For reference only.
Customer Type
The customer type. Select a type as required.
Country of the Customer
Country where the applicant is located.
Contact Name
-
Contact Number
-
Type of ID
-
ID Number
-
Scope of Business
Briefly describe the main business.
Number of Employees
For reference only.
Branch Location Country
Country where the applicant branch is located. Set this parameter as required.
Table 2 Required materials Material
Signature
Seal
Description
A scanned copy of your company's business license
-
√
See the template Huawei Cloud provides for the position of the seal.
A scanned copy of Huawei Cloud Cross-Border Circuit Service Agreement
√
√
- Sign the material on the signature block.
- Stamp the seal over the signature.
A scanned copy of China Unicom Letter of Commitment to Information Security of the Cross-Border Circuit Service
√
√
- Sign the material on the signature block.
- Stamp the seal over the signature.
- Specify the bandwidth you estimated and your company name.
- Click Submit.
Step 2: Create a Global Accelerator
To use Global Accelerator for faster access, you first need to create a global accelerator.
- Log in to the Global Accelerator console.
- Click Buy Global Accelerator.
- Specify the parameters listed in Table 3.
Figure 4 Creating a global accelerator

Table 3 Parameters required for creating a global accelerator Parameter
Example Value
Description
Name
ga-test
Name of the global accelerator you want to create.
You can enter a maximum of 64 characters. Only letters, digits, and hyphens are allowed.
Enterprise Project
default
An enterprise project you would like to use to centrally manage your Global Accelerator resources.
You can use an existing enterprise project or create one.
Applicability
Outside the Chinese mainland
Where the global accelerator will be used.
You can select Outside Chinese mainland or Chinese mainland.
Default value: Outside the Chinese mainland.
IP Address Type
IPv4
The type of the IP address used by the global accelerator.
If you select Chinese mainland for Applicability, you can select IPv4 or IPv4+IPv6.
Default value: IPv4.
Tags
example_key1
example_value1
Tags that identify global accelerators. They can be modified.
Description
test
Supplementary information about the global accelerator.
A maximum of 255 characters are allowed.
- Click Next.
The Add Listener page is displayed.
Step 3: Add a Listener to the Global Accelerator
Associate an endpoint group with the listener in the AP-Singapore region and add endpoint 1 and endpoint 2 to the endpoint group. The listener will listen to requests and route them to the two endpoints based on the client affinity and weight you set.

|
Parameter |
Example Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Name |
listener-test |
Listener name. You can enter a maximum of 64 characters. Only letters, digits, and hyphens are allowed. |
|
Protocol |
TCP |
The protocol used by the listener to receive requests from clients. The protocol can be TCP or UDP. |
|
Port |
80 |
The ports or port ranges used by the listener to receive requests from clients. The port number ranges from 1 to 65535. You can enter one or more ports or port ranges separated by commas (,). Example: 1-10,11-50,51,52-200 |
|
Client Affinity |
Source IP address |
TCP and UDP listeners support only Source IP address. |
|
Tags |
- |
The identifier of a listener. Each tag consists of a key and a value. You can add up to 20 tags to a listener. |
|
Description |
- |
Supplementary information about the listener. A maximum of 255 characters are allowed. |
Step 4: Associate an Endpoint Group with the Listener
Associate an endpoint group with the listener in the CN-Hong Kong region, and add endpoint 3 and endpoint 4 to this endpoint group.
- Click Add Endpoint Group and specify the parameters listed in Table 5.
Table 5 Parameters required for adding an endpoint group Item
Parameter
Example Value
Description
Endpoint Groups
Name
endpointgroup2
Name of the endpoint group.
Each listener can be associated with only one endpoint group in a given region.
You can enter a maximum of 64 characters. Only letters, digits, and hyphens are allowed.
Region
CN-Hong Kong
Region where the endpoint group is used.
Description
-
Supplementary information about the endpoint group.
A maximum of 255 characters are allowed.
Traffic Dial
1
The percentage of traffic directed to the endpoint group.
If you increase the traffic dial, more requests will be distributed to this endpoint group.
If you set the traffic dial to 0, no requests will be distributed to this endpoint group.
The value ranges from 0 to 100.
NOTE:If a listener has multiple endpoint groups, traffic will be first distributed to the endpoint group with the lowest latency and then to other endpoint groups based on the traffic dial value you set.
Endpoint
97.xx.xx.159
10.xx.xx.240
An endpoint serves as a single point of contact for clients, and Global Accelerator distributes incoming traffic across healthy endpoints.
- Endpoint 3: EIP bound to server 3 (97.xx.xx.159)
- Endpoint 4: EIP bound to server 4 (10.xx.xx.240)
Set the weight of endpoint 3 to 1, and the weight of endpoint 4 to 4.
Health Check
Health Check
Enable
Whether to enable health check.
If you disable health check, requests may be forwarded to unhealthy endpoints.
Protocol
TCP
The health check protocol can be TCP or UDP.
Default value: TCP.
Port
80
The port used for health check.
The port number ranges from 1 to 65535.
Advanced Settings
Interval (s)
5
The maximum time between two consecutive health checks, in seconds.
The interval ranges from 1 to 60.
Timeout (s)
5
The maximum time required for waiting for a response to a health check request, in seconds.
The timeout ranges from 1 to 60.
Maximum Retries
3
The maximum number of health check retries allowed.
The value ranges from 1 to 10.
In this example, users in the Singapore branch have faster access to the application on servers in the CN South-Guangzhou region than to that in the CN-Hong Kong region. Requests are preferentially sent to servers in the CN South-Guangzhou region.
If the percentage of traffic directed to the endpoint group 1 and endpoint group 2 are set to 80%, requests from users in the Singapore and Hong Kong branches are distributed as follows:
- 80% of the requests from users in Singapore will be sent to endpoint group 1, and the remaining 20% to the endpoint group 2.
- 80% of the requests from users in Hong Kong (China) will be sent to the endpoint group 2, and the remaining 20% to the endpoint group 1.
Figure 6 Cross-border traffic dial
- Click Save.
- Click Next and confirm the configuration.
- Click Submit.
- If message "Accelerator xxx created successfully" is displayed, click Finish.
Step 5: Verify Acceleration
The listener uses TCP to receive requests from clients, so you can run the curl command to verify that the global accelerator is working normally. Run the curl command before and after you configure Global Accelerator and compare the values of time_connect.
- Before you configure Global Accelerator, run the following command on a server in the tested region:
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "time_connect: %{time_connect}\ntime_starttransfer: %{time_starttransfer}\ntime_total: %{time_total}\n" "http[s]://<IP>[:<Port>]"
- IP: EIP bound to the application server.
- Port: HTTP port number used by the application server.
- time_connect: time taken to establish a TCP connection, in seconds. It is from the time when a TCP connection request is initiated to the time when the connection is established.
- time_starttransfer: time when transfer starts, in seconds. It is from the time when the client sends a request to the time when the endpoint replies with the first byte.
- time_total: total connection time, in seconds. It is from the time when the client sends a request to the time when the endpoint responds to the request.
- After you configure Global Accelerator, run the following command:
curl -o /dev/null -s -w "time_connect: %{time_connect}\ntime_starttransfer: %{time_starttransfer}\ntime_total: %{time_total}\n" "http[s]://<IP>[:<Port>]"
Set IP in the command to the anycast IP address provided by Global Accelerator.
- Compare the values of time_connect and view the latency before and after acceleration.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





